
Quantitative Methods for Business Decisions PDF
Preview Quantitative Methods for Business Decisions
seventh edition Ouantitative MethOds For Business Decisions JON CURWIN ROGER SLATER DAVID EADSON Australia • Brazil • Japan • Korea • Mexico • Singapore • Spain • United Kingdom • United States 60193_FM_pi-xvi.indd 1 09/11/12 4:57 PM Quantitative Methods For Business © 2013, Cengage Learning EMEA Decisions, 7th edition ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this work covered by the copyright herein Jon Curwin, Roger Slater and David Eadson may be reproduced, transmitted, stored or used in any form or by any means Publishing Director: Linden Harris graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including but not limited to photocopy- ing, recording, scanning, digitizing, taping, Web distribution, information Publisher: Andrew Ashwin networks, or information storage and retrieval systems, except as permitted Development Editor: Felix Rowe under Section 107 or 108 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act, or applicable Production Editor: Alison Cooke copyright law of another jurisdiction, without the prior written permission of Production Controller: Eyvett Davis the publisher. Marketing Manager: Anne Renton While the publisher has taken all reasonable care in the preparation of this book, the publisher makes no representation, express or implied, with regard Typesetter: Cenveo Publisher Services to the accuracy of the information contained in this book and cannot accept Cover design: Adam Renvoize any legal responsibility or liability for any errors or omissions from the book Text design: Design Deluxe or the consequences thereof. Products and services that are referred to in this book may be either trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective owners. The publishers and author/s make no claim to these trademarks. The publisher does not endorse, and accepts no responsibility or liability for, incorrect or defamatory content contained in hyperlinked material. For product information and technology assistance, contact emea.info@cengage.com. For permission to use material from this text or product, and for permission queries, email emea.permissions@cengage.com. British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library. ISBN: 978-1-4080-6019-3 Cengage Learning EMEA Cheriton House, North Way, Andover, Hampshire, SP10 5BE, United Kingdom Cengage Learning products are represented in Canada by Nelson Education Ltd. For your lifelong learning solutions, visit www.cengage.co.uk Purchase your next print book, e-book or e-chapter at www.cengagebrain.com Printed in China by RR Donnelley 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 – 15 14 13 60193_FM_pi-xvi.indd 2 05/11/12 5:26 PM CONTENTS Preface ix List of Mini Cases xi About the authours xii About the digital resources xiii Walk through tour xiv 1 Mathematical Background 1 1A Basic Mathematics 2 Objectives 2 1A.1 Basic arithmetic 3 1A.2 Basic algebra 9 1A.3 Logarithms 14 1A.4 Arithmetic and geometric progressions 15 1A.5 Functions 19 1A.6 Conclusions to Part A 32 1B Financial Mathematics 33 Objectives 33 1B.1 Interest: simple and compound 33 1B.2 Depreciation 36 1B.3 Present value 38 1B.4 The internal rate of return 43 1B.5 Incremental payments 45 1B.6 Annual percentage rate (APR) 50 1B.7 Conclusions to Part B 52 1.8 Questions for Parts A and B 53 iii 60193_FM_rev01.indd 3 05/11/12 11:32 AM iv CONTENTS PART ONE UNDERSTANDING QUANTITATIVE INFORMATION 59 2 The Quantitative Approach 65 Objectives 65 2.1 Problem solving 66 2.2 Methodology 70 2.3 Models 73 2.4 Measurement 79 2.5 Scoring models 81 2.6 Conclusions 85 2.7 Questions 86 3 Managing Data 90 Objectives 90 3.1 Issues of data collection 92 3.2 Published sources 94 3.3 Internet sources 96 3.4 A census or a sample? 98 3.5 Market research 100 3.6 Conclusions 101 3.7 Questions 102 4 Survey Methods 105 Objectives 105 4.1 Probability sampling 108 4.2 Non-probability sampling 113 4.3 Survey design 117 4.4 Questionnaire design 123 4.5 Non-response 128 4.6 Conclusions 130 4.7 Questions 131 PART TWO DESCRIBING DATA 135 5 Presentation of Data 139 Objectives 139 5.1 Raw data 140 5.2 Tabulation of data 140 5.3 Presentation of categorical data 147 5.4 Presentation of continuous data 154 5.5 Graphical representation 161 5.6 Conclusions 168 5.7 Questions 169 6 Measures of Location 174 Objectives 174 6.1 Raw data 177 6.2 Tabulated (ungrouped) discrete data 181 60193_FM_rev01.indd 4 05/11/12 11:32 AM CONTENTS v 6.3 Tabulated (grouped) continuous data 184 6.4 Other measures of location 191 6.5 Relationships between averages 193 6.6 Conclusions 194 6.7 Questions 195 7 Measures of Dispersion 199 Objectives 199 7.1 The measures 199 7.2 Raw data 200 7.3 Tabulated data 204 7.4 Grouped data 206 7.5 Relative measures of dispersion 213 7.6 Variability in sample data 216 7.7 Conclusions 218 7.8 Questions 218 8 Index Numbers 223 Objectives 223 8.1 The interpretation of an index number 223 8.2 The construction of index numbers 229 8.3 The weighting of index numbers 235 8.4 The Consumer Prices Index and the Retail Prices Index 236 8.5 Conclusions 242 8.6 Questions 243 PART THREE MEASURING UNCERTAINTy 249 9 Probability 253 Objectives 253 9.1 Basic concepts 254 9.2 Definitions 256 9.3 Basic relationships in probability 261 9.4 Probability trees 266 9.5 Expected values 269 9.6 Decision trees 271 9.7 Bayes’ theorem 274 9.8 Conclusions 276 9.9 Questions 277 10 Discrete Probability Distributions 282 Objectives 282 10.1 Probability distributions 283 10.2 Discrete probability distributions 284 10.3 Poisson approximation to the binomial 301 10.4 Conclusions 302 10.5 Questions 303 60193_FM_rev01.indd 5 05/11/12 11:33 AM vi CONTENTS 11 The Normal Distribution 307 Objectives 307 11.1 Characteristics of the Normal distribution 307 11.2 The standard Normal distribution 308 11.3 Combinations of variables 314 11.4 Normal approximations 317 11.5 Other continuous probability distributions 320 11.6 Conclusions 320 11.7 Questions 321 PART FOUR USING STATISTICAL INFERENCE 325 12 Samples, Estimation and Confidence Intervals 330 Objectives 330 12.1 Statistical inference 331 12.2 Sampling Distributions 332 12.3 Estimation – inference about a population 339 12.4 Confidence interval for the population mean 340 12.5 Confidence interval for a population percentage 347 12.6 The difference between means of independent samples 350 12.7 The finite population correction factor 353 12.8 The t-distribution 355 12.9 Conclusions 361 12.10 Questions 363 13 Significance Testing 367 Objectives 367 13.1 Significance testing using confidence intervals 368 13.2 Hypothesis testing for single large samples 370 13.3 One-sided significance tests 377 13.4 Types of error 383 13.5 Hypothesis testing with two large samples 385 13.6 Hypothesis testing with small samples 388 13.7 Reservations about test conclusions 395 13.8 Conclusions 396 13.9 Questions 397 14 Non-Parametric Tests 401 Objectives 401 14.1 Chi-squared tests 402 14.2 Mann-Whitney U test 416 14.3 Wilcoxon test 419 14.4 Runs test 423 14.5 Conclusions 424 14.6 Questions 426 60193_FM_rev01.indd 6 05/11/12 11:33 AM CONTENTS vii PART FIVE RELATING VARIABLES AND PREDICTING OUTCOMES 431 15 Correlation and Simple Regression Analysis 434 Objectives 434 15.1 Correlation 435 15.2 Measuring linear association 440 15.3 Regression analysis 447 15.4 Simple linear regression 448 15.5 Predictions from the regression line 451 15.6 Regression analysis using ExCEL 456 15.7 Interpretation 457 15.8 Non-linear relationships 458 15.9 Conclusions 462 15.10 Questions 463 16 Multiple Regression Analysis 470 Objectives 470 16.1 The multiple regression model 471 16.2 The effects of adding variables 472 16.3 Investigating the assumptions 475 16.4 Analysis of a multiple regression model 484 16.5 Using multiple regression models 489 16.6 Conclusions 490 16.7 Questions 491 17 Time Series 495 Objectives 495 17.1 Time series models 496 17.2 The trend 499 17.3 The seasonal factors 508 17.4 The cyclical factors 513 17.5 The residual or random factor 514 17.6 Predictions 516 17.7 Developing models for short-term forecasts 519 17.8 Conclusions 525 17.9 Questions 526 ONLINE CONTENTS 531 The following Parts 6-8 can be found by visiting our premium online platform. See the ‘About the digital resources’ page for more details. 60193_FM_pi-xvi.indd 7 07/11/12 2:38 PM viii CONTENTS PART SIX MODELLING 18 Linear programming 19 Networks 20 Modelling stock control and queues 21 Simulation 22 Game theory 23 Factor analysis PART SEVEN MATHEMATICAL TOPICS 24 Matrices 25 Use of Calculus PART EIGHT STUDENT GUIDES Guide to creative problem solving Guide to ExCEL Guide to SPSS Guide to project management software Guide to writing and reporting statistics Appendices 532 A Cumulative binomial probabilities 533 B Cumulative Poisson probabilities 534 C Areas in the right-hand tail of the Normal distribution 535 D Student’s t critical points 537 E c2 critical values 538 F Present value factors 540 G Mann-Whitney test statistic 542 H Wilcoxon test statistic 545 I Runs test 546 J Durbin-Watson statistic 548 K Random number table 550 Answers section 552 Glossary 587 Statistics formula sheet 595 Index 600 60193_FM_pi-xvi.indd 8 07/11/12 2:38 PM PREFACE WE WOUld lIkE TO WElCOmE you to a very different seventh edition of Quantitative Methods for Business Decisions. David Eadson has joined Jon Curwin and Roger Slater in the author team, and together they have sought to offer a more compact book with all the qualities of the previous six editions and strengthened the links to online support materials. This new edition, like the previous editions, is intended for students from a variety of backgrounds who find that their courses require a good understanding of mathematics and statistics in a business context. Few assumptions are made about what a student can remember from pre vious studies and the focus is on developing the important skills of being effective with numbers. Each chapter offers an introduction and explanation of some aspect of the quantitative approach to problem solving. Together these chapters are designed to build a confidence with business problem analysis but are sufficiently selfcontained to be used as a source of reference or for revision purposes. A review of basic mathematics is now included as the first chapter and allows for an easier revision of key mathematical topics and for easier crossreferencing if only as a reminder of a mathematical technique that is required. The book itself is still divided into five parts: Understanding quantitative information; Describing data; Measuring uncertainty; Using statistical inference; and Relating variables and predicting outcomes, with a further three parts offered online, adressing Modelling, Mathematical topics and student guides, respectively. The online support has been considerably strengthened to include chapters on Game theory and Factor analysis, and student guides on creative problem solving, ExCEl, SPSS, Project management software, and writing and reporting statistics. The rationale for the book remains broadly the same, but the following improvements have been made: l A review and revision of basic mathematics takes place at the beginning of the book. l All chapters have been revised to reflect subject and course developments with additional chapters and student guides being offered online. l The questions at the end of each chapter have been revised. In addition to the multiple choice and numeric based exercise questions, a set of discussion questions have been added. These have been designed to encourage you to explore the application of concepts raised in each chapter. l A complete set of fully annotated answers for all end of chapter questions are offered online, and some can still be found at the end of the book. ix 60193_FM_rev01.indd 9 05/11/12 11:33 AM
The list of books you might like

The Spanish Love Deception

The 48 Laws of Power

The Mountain Is You

The Strength In Our Scars

Cisne blanco

Solanum tergosericeum (Solanaceae: sect. Basarthrum): a new species from Peru

Electrical power cable engineering

UVES - VLT High Resolution Spectroscopy of GRB Afterglows

A new genus and three new species of Lygaeoidea from New Guinea (Heteroptera, Lygaeoidea)

The Baptist Record Jan. 25. 2007

Individual Differences in Computer Assisted Language Learning Research

In der ersten Reihe sieht man Meer

Dune

Greek Government Gazette: Part 7, 2006 no. 798

Greek Government Gazette: Part 7, 2006 no. 738

Department of Environmental Management Board Minutes

büyükşehir belediye sisteminin evrimi
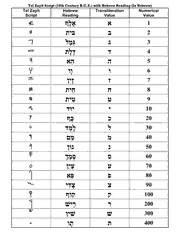
Tel Zayit Script (10th Century B.C.E.) with Hebrew Reading (In Hebrew)






