Table Of ContentCounty: Any Hwy: Any Design: BRG Date: 06/2010
CSJ: XXXX-XX-XXX Ck Dsn: BRG Date: 06/2010
Design: Column Design Example
Design example is in accordance with the AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications, 5th Ed. (2010)
as prescribed by TxDOT Bridge Design Manual - LRFD (May 2009).
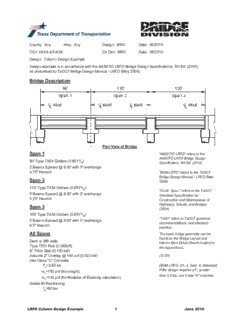
Bridge Description
Plan View of Bridge
Span 1 "AASHTO LRFD" refers to the
AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design
90' Type TX54 Girders (0.851k/ )
ft Specification, 5th Ed. (2010)
5 Beams Spaced @ 8.00' with 3' overhangs
4.75" Haunch "BDM-LRFD" refers to the TxDOT
Bridge Design Manual - LRFD (May
Span 2
2009)
110' Type TX54 Girders (0.851k/ )
ft
"Contr. Spec." refers to the TxDOT
5 Beams Spaced @ 8.00' with 3' overhangs
Standard Specification for
5.25" Haunch
Construction and Maintenance of
Highways, Streets, and Bridges
Span 3
(2004)
100' Type TX54 Girders (0.851k/ )
ft
"TxSP" refers to TxDOT guidance,
5 Beams Spaced @ 8.00' with 3' overhangs
recommendations, and standard
6.5" Haunch
practice.
All Spans The basic bridge geometry can be
found on the Bridge Layout and
Deck is 38ft wide
Interior Bent Detail Sheets located in
Type T551 Rail (0.382k/ft)
the Appendices.
8" Thick Slab (0.100 ksf)
Assume 2" Overlay @ 140 pcf (0.023 ksf) (TxSP)
Use Class "C" Concrete
f' =3.60 ksi (BDM-LRFD, Ch. 4, Sect. 6, Materials)
c
If the design requires a f' greater
w =150 pcf (for weight) c
c
than 3.6 ksi, use Class "H" concrete.
w =145 pcf (for Modulus of Elasticity calculation)
c
Grade 60 Reinforcing
f =60 ksi
y
LRFDColumnDesignExample 1 June2010
Bridge Description (Con't)
Superstructure
NoSp (cid:2) 3 Number of Spans
Span1 (cid:2) 90 ft
Span2 (cid:2) 110 ft Back Span
Span3 (cid:2) 100 ft Forward Span
(Span2 (cid:3) Span3)
AvgSp (cid:2) (cid:2) 105ft Average Span (for Bent 3)
2
BridgeL (cid:2) Span1 (cid:3) Span2 (cid:3) Span3 (cid:2) 300ft Bridge Length
BridgeW (cid:2) 38ft Bridge Width
NoRail (cid:2) 2 Number of T551 Rails
RailW (cid:2) 1 ft Nominal Rail Width (T551)
RailH (cid:2) 2 ft (cid:3) 8 in(cid:2) 2.67ft Rail Height (T551)
RailWgt (cid:2) 0.382 klf Rail Weight (T551)
RoadW (cid:2) BridgeW (cid:5) NoRail(cid:4)RailW (cid:2) 36ft Roadway Width
Lanes (cid:2) 3 Number of Lanes
(AASHTO LRFD 3.6.1.1.1)
SlabTh (cid:2) 8 in Slab Thickness
OlayTh (cid:2) 2 in Overlay Thickness
HaunchTh (cid:2) 6.5in Haunch Thickness
w (cid:2) 0.150 kcf Unit Weight of Concrete
Conc
w (cid:2) 0.140 kcf Unit Weight of Overlay
Olay
NoBm (cid:2) 5 Number of Type IV Beams
BmSpac (cid:2) 8 ft Beam Spacing
BmH (cid:2) 54in Beam Height (IGD)
BmWgt (cid:2) 0.851 klf Beam Weight (IGD)
LRFDColumnDesignExample 2 June2010
Bridge Description (Con't)
Bent Cap
Bent Cap Section View
L (cid:2) 36 ft Cap Length
Cap
b (cid:2) 8 ft (cid:3) 7 in(cid:2) 8.58ft Cap Bottom Flange Width
f_Cap
d (cid:2) 2 ft (cid:3) 4 in(cid:2) 2.33ft Cap Ledge Height
ledge
b (cid:2) 4 ft (cid:3) 3 in(cid:2) 4.25ft Cap Stem Width
stem
d (cid:2) 4 ft (cid:3) 9 in(cid:2) 4.75ft Cap Stem Height
stem
b
stem
e (cid:2) (cid:3) 1 ft (cid:2) 3.13 ft Distance from CL of Bent
Brng
2 to CL of Bearing Pad
(cid:6)b (cid:9)
BkBmL (cid:2) Span2 (cid:5) 2(cid:4)(cid:7) stem (cid:3) 3 in(cid:10) (cid:2) 105.25ft Length of Back Beam
(cid:8) 2 (cid:11)
(cid:6)b (cid:9)
FwdBmL (cid:2) Span3 (cid:5) (cid:7) stem (cid:3) 3 in(cid:10) (cid:5) 3 in(cid:2) 97.38ft Length of Forward Beam
(cid:8) 2 (cid:11)
Typically the beam end is 3" from the
face of the Inverted Tee stem, as
shown in the IGEB standard.
LRFDColumnDesignExample 3 June2010
Bridge Description (Con't)
Bent Cap (Con't)
The x-axis is along the longitudinal
axis of the bent cap.
The y-axis is perpendicular to the
longitudinal axis of the bent cap.
Footing and Drilled Shafts Footing and Drilled Shafts
in the direction of the x-axis in the direction of the y-axis
(the y-axis is into the page) (the x-axis is into the page)
NoCol (cid:2) 1 Number of Columns
L (cid:2) 8 ft Column Length
Col
W (cid:2) 4 ft Column Width
Col
H (cid:2) 50ft Column Height
Col
For the purposes of this design example, the column dimensions are given. For designs where a
column size is not provided, choose a column size that has worked for similar bents. These
dimensions are preliminary and are subject to change if the required reinforcing can not fit in the
column with adequate clear distance between the reinforcing bars.
L (cid:2) 18 ft Footing Length
Ftg
W (cid:2) 6 ft Footing Width
Ftg
H (cid:2) 4 ft Footing Height
Ftg
The footing dimensions are estimates, and are subject to change. A strut-and-tie analysis of the
footing is required to determine the adequacy of these dimensions. A strut-and-tie analysis of the
footing is not included in this design example.
NoDS (cid:2) 2 Number of Drilled Shafts
D (cid:2) 5 ft Drilled Shaft Diameter
DS
π
2 2
A (cid:2) D (cid:2) 19.63ft Drilled Shaft Area
DS DS
4
S (cid:2) 12ft Drilled Shaft Spacing
DS
LRFDColumnDesignExample 4 June2010
Loading
Load Sketch
The fixity of the column in the x-direction is at the top of the footing. This is because there are two
drilled shafts resisting the moment in this direction by coupling action, which causes a dramatic
increase in the rigidity in this direction.
The fixity of the column in the y-direction is below the top of the footing at a distance determined by
a geotechnical engineer. The location of fixity can typically be taken as ten feet below the footing,
unless the soils are poor. When using large mono-shafts, a larger distance may be appropriate.
Distance to Fixity for loads along the x-axis
DistanceToFixity (cid:2) 0 ft
x
Distance to Fixity for loads along the y-axis
DistanceToFixity (cid:2) H (cid:3) 10ft (cid:2) 14ft
y Ftg
Design Cases
Case A: Design for maximum axial load and minimum moment. Load all lanes.
Case B: Design for maximum moment and minimum axial force. Use one lane loaded.
Notes: Only Strength I, III, & V are applicable for column design (AASHTO LRFD 3.4.1).
Use HL93 Loading with Design Speed = 60 mph.
Lanes (cid:2) Lanes(cid:2) 3 Number of Lanes Loaded for Live
A
Load Case A
Lanes (cid:2) 1 Number of Lanes Loaded for Live
B
Load Case B
LRFDColumnDesignExample 5 June2010
Dead Load
Dead Load Moment about the y-axis
Distance between the Superstructure Load Resultant and the Center of the Column
MomentArm (cid:2) 0ft
DL
Distance between the Bent Cap Load Resultant and the Center of the Column
MomentArm (cid:2) 0ft
Cap
Dead Load from Structural Components and Nonstructural Components (DC)
Rail Loads
Span2
Rail (cid:2) NoRail(cid:4) (cid:4)RailWgt(cid:2) 42.0 kip Load due to Rail on Back Span
Bk
2
Span3
Rail (cid:2) NoRail(cid:4) (cid:4)RailWgt(cid:2) 38.2 kip Load due to Rail on Forward Span
Fwd
2
Rail (cid:2) Rail (cid:3) Rail (cid:2) 80.2 kip Total Load due to Rail
Bk Fwd
Slab Loads
Span2
Slab (cid:2) (cid:4)BridgeW(cid:4)SlabTh(cid:4)w (cid:4)1.10 (cid:2) 229.9 kip Load due to Slab on Back Span
Bk Conc
2
The weight of the slab is multiplied by
1.10 to account for weight of the
haunch concrete. (TxSP)
Span3
Slab (cid:2) (cid:4)BridgeW(cid:4)SlabTh(cid:4)w (cid:4)1.10 (cid:2) 209.0 kip Load due to Slab on Forward Span
Fwd Conc
2
Slab (cid:2) Slab (cid:3) Slab (cid:2) 438.9 kip Total Slab due to Rail
DL Bk Fwd
Beam Loads
BkBmL
Beam (cid:2) NoBm(cid:4)BmWgt(cid:4) (cid:2) 223.9 kip Load due to Beams on Back Span
Bk
2
FwdBmL
Beam (cid:2) NoBm(cid:4)BmWgt(cid:4) (cid:2) 207.2 kip Load due to Beams on Forward
Fwd
2 Span
Beam (cid:2) Beam (cid:3) Beam (cid:2) 431.1 kip Total Load due to Beams
Bk Fwd
LRFDColumnDesignExample 6 June2010
Dead Load (Con't)
Dead Load from Structural Components and Nonstructural Components (DC) (Con't)
Bent Cap Loads
2
A (cid:2) d (cid:4)b (cid:3) d (cid:4)b (cid:2) 40.2 ft Cross sectional area of bent cap
Cap ledge f_Cap stem stem
Cap (cid:2) L (cid:4)A (cid:4)w (cid:2) 217.2 kip Dead Load due to the self weight of
Cap Cap Conc
the bent cap
Column Loads
Column (cid:2) H (cid:4)L (cid:4)W (cid:4)w (cid:2) 240.0 kip Dead Load due to the self weight of
Col Col Col Conc
the Column
Total Loads
Superstructure Dead Load from Back Span
DL (cid:2) Rail (cid:3) Slab (cid:3) Beam (cid:2) 495.8 kip
Bk Bk Bk Bk
Superstructure Dead Load from Forward Span
DL (cid:2) Rail (cid:3) Slab (cid:3) Beam (cid:2) 454.4 kip
Fwd Fwd Fwd Fwd
Axial Load due to Dead Load
P (cid:2) DL (cid:3) DL (cid:3) Cap (cid:3) Column (cid:2) 1407.4 kip
DC Bk Fwd Load at the bottom of the Column
The load at the bottom of the column
is used to design the column
Dead Load Moment about the x-axis
M (cid:2) e (cid:4) DL (cid:5) DL (cid:2) 129.6 kip(cid:4)ft
x_DC Brng Fwd Bk
Dead Load Moment about the y-axis
(cid:12) (cid:13)
M (cid:2) DL (cid:3) DL (cid:4)MomentArm (cid:3) Cap(cid:4)MomentArm (cid:2) 0.0kip(cid:4)ft
y_DC Fwd Bk DL Cap
LRFDColumnDesignExample 7 June2010
Dead Load (Con't)
Dead Load from Wearing Surfaces and Utilities (DW)
Wearing Surface Dead Load from Back Span
Span2
Olay (cid:2) (cid:4)RoadW(cid:4)OlayTh(cid:4)w (cid:2) 46.2 kip Load due to Overlay on Back Span
Bk Olay
2
Wearing Surface Dead Load from Forward Span
Span3
Olay (cid:2) (cid:4)RoadW(cid:4)OlayTh(cid:4)w (cid:2) 42.0 kip Load due to Overlay on Forward
Fwd Olay
2 Span
Axial Load due to Dead Load
P (cid:2) Olay (cid:3) Olay (cid:2) 88.2 kip
DW Bk Fwd
Dead Load Moment about the x-axis
M (cid:2) e (cid:4) Olay (cid:5) Olay (cid:2) 13.1 ft(cid:4)kip
x_DW Brng Fwd Bk
Dead Load Moment about the y-axis
M (cid:2) P (cid:4)MomentArm (cid:2) 0.0kip(cid:4)ft
y_DW DW DL
LRFDColumnDesignExample 8 June2010
Live Load
HL93 Loading
AASHTO LRFD 3.6.1.2.2 & AASHTO LRFD 3.6.1.2.4
Live Load Reactions
Truck Load on Back Span
Span2 (cid:5) 14ft 1 kip
Truck (cid:2) (cid:4)32kip (cid:3) (cid:4)32 kip (cid:2) 43.9
Bk
Span2 2 lane
Truck Load on Forward Span
1 Span3 (cid:5) 14ft kip
Truck (cid:2) (cid:4)32 kip (cid:3) (cid:4)8 kip (cid:2) 22.9
Fwd
2 Span3 lane
Total Truck Load per Lane
kip
Truck (cid:2) Truck (cid:3) Truck (cid:2) 66.8
Rxn Bk Fwd
lane
Lane Load on Back Span
Span2 kip
Lane (cid:2) 0.64klf (cid:4) (cid:2) 35.2
Bk
2 lane
Lane Load on Forward Span
Span3 kip
Lane (cid:2) 0.64klf (cid:4) (cid:2) 32.0
Fwd
2 lane
Total Lane Load per Lane
kip
Lane (cid:2) Lane (cid:3) Lane (cid:2) 67.2
Rxn Bk Fwd
lane
LRFDColumnDesignExample 9 June2010
Live Load (Con't)
Case A
Multiple Presence Factor
m (cid:2) 0.85
A (AASHTO LRFD Table 3.6.1.1.2-1)
Transverse Moment Arm for Case A
MomArm (cid:2) 0 ft
LL_A
Case B
Multiple Presence Factor
m (cid:2) 1.2
B (AASHTO LRFD Table 3.6.1.1.2-1)
Transverse Moment Arm for Case B
12 ft lane(cid:4)Lanes (cid:5) 2ft
RoadW B
MomArm (cid:2) (cid:5) (cid:2) 13ft
LL_B
2 2
LRFDColumnDesignExample 10 June2010
Description:Design: Column Design Example Design example is in accordance with the AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specifications, 5th Ed. (2010) as prescribed by TxDOT Bridge Design