
Bioisosteres in medicinal chemistry PDF
Preview Bioisosteres in medicinal chemistry
54 MethodsandPrinciplesinMedicinalChemistry B Edited by Nathan Brown r o W rittenwiththepracticingmedicinalchemistinmind,thisisthefirst w modernhandbooktosystematicallyaddressthetopicofbioisosterism. n Assuch,itprovidesareadyreferenceontheprinciplesandmethodsof ( E Bioisosteres bioisostericreplacementasakeytoolinpreclinicaldrugdevelopment. d Thefirstpartprovidesanoverviewofbioisosterism,classical . ) bioisosteresandtypicalmolecularinteractionsthatneedtobeconsid- ered,whilethesecondpartdescribesanumberofmoleculardatabasesas in Medicinal Chemistry sourcesofbioisostericidentificationandrationalization.Thethirdpart coversthefourkeymethodologiesforbioisostereidentificationandre- placement:physicochemicalproperties,topology,shape,andoverlaysof protein-ligandcrystalstructures.Inthefinalpart,severalreal-worldexam- plesofbioisosterismindrugdiscoveryprojectsarediscussed. Withitsdetaileddescriptionsofdatabases,methodsandreal-lifecase studies,thisistailor-madeforbusyindustrialresearcherswithlittletime forreading,whileremainingeasilyaccessibletonovicedrugdevelopers duetoitssystematicstructureandintroductorysection. NathanBrownistheHeadoftheInSilicoMedicinalChemistry groupintheCancerResearchUKCancerTherapeuticsUnitat theInstituteofCancerResearchinLondon(UK).AttheICR, Dr.Brownandhisgroupsupporttheentiredrugdiscoveryport- Volume 54 foliotogetherwithdevelopingnewcomputationalmethodologies i B n toenhancethedrugdesignwork. i o NathanBrownconductedhisdoctoralresearchinSheffield M i SeriesEditors: withProfessorPeterWillettfocusingonevolutionaryalgorithms s e andgraphtheoryappliedtochallengesinchemoinformatics.After o d R.Mannhold, atwo-yearMarieCuriefellowshipinAmsterdamincollaboration s withProfessorJohannGasteigerinErlangen,hejoinedthe ic te H.Kubinyi, i NovartisInstitutesforBioMedicalResearchinBaselforathree- n r e yearPresidentialfellowshipinBaselworkingwithProfessorsPeter a G.Folkers s WillettandKarl-HeinzAltmann. l Hisworkhasledtothepioneeringworkonmulitobjectivede C novodesigninadditiontoavarietyofdiscoveriesandmethod h developmentinbioisostericidentificationandreplacement, e scaffoldhopping,moleculardescriptorsandstatisticalmodeling. m Nathancontinuestopursuehisresearchinallaspectsofinsilico i medicinalchemistry. s t r y www.wiley-vch.de Edited by Nathan Brown Bioisosteres in Medicinal Chemistry Methods and Principles in Medicinal Chemistry EditedbyR.Mannhold,H.Kubinyi,G.Folkers EditorialBoard H.Buschmann,H.Timmerman,H.van deWaterbeemd,T.Wieland Previous Volumes of this Series: Gohlke,Holger(Ed.) Sotriffer,Christoph(Ed.) Protein-LigandInteractions VirtualScreening 2012 Principles,Challenges,andPractical ISBN:978-3-527-32966-3 Guidelines Vol.53 2011 Kappe,C.Oliver/Stadler,Alexander/Dallinger,Doris ISBN:978-3-527-32636-5 MicrowavesinOrganic Vol.48 andMedicinalChemistry Rautio,Jarkko(Ed.) Second, CompletelyRevised ProdrugsandTargetedDelivery andEnlargedEdition TowardsBetterADMEProperties 2012 2011 ISBN:978-3-527-33185-7 ISBN:978-3-527-32603-7 Vol.52 Vol.47 Smith,DennisA./Allerton,Charlotte/ Kalgutkar,AmitS./vandeWaterbeemd, Smit,MartineJ./Lira,SergioA./ Han/Walker,DonK. Leurs,Rob(Eds.) PharmacokineticsandMetabolism ChemokineReceptorsasDrugTargets inDrugDesign 2011 Third,RevisedandUpdatedEdition ISBN:978-3-527-32118-6 Vol.46 2012 ISBN:978-3-527-32954-0 Ghosh,ArunK.(Ed.) Vol.51 AsparticAcidProteasesas DeClercq,Erik(Ed.) TherapeuticTargets AntiviralDrugStrategies 2010 2011 ISBN:978-3-527-31811-7 ISBN:978-3-527-32696-9 Vol.45 Vol.50 Ecker,GerhardF./Chiba,Peter(Eds.) Klebl,Bert/Müller,Gerhard/Hamacher, TransportersasDrugCarriers Michael(Eds.) ProteinKinasesasDrugTargets Structure,Function,Substrates 2011 2009 ISBN:978-3-527-31790-5 ISBN:978-3-527-31661-8 Vol.49 Vol.44 Edited by Nathan Brown Bioisosteres in Medicinal Chemistry SeriesEditors AllbookspublishedbyWiley-VCHarecarefully produced.Nevertheless,authors,editors,andpub- Prof.Dr.RaimundMannhold lisherdonotwarranttheinformationcontainedin MolecularDrugResearchGroup thesebooks,includingthisbook,tobefreeoferrors. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Readersareadvisedtokeepinmindthatstatements, Universitätsstrasse1 data,illustrations,proceduraldetailsorotheritems 40225Düsseldorf mayinadvertentlybeinaccurate. Germany LibraryofCongressCardNo.: appliedfor mannhold@uni-duesseldorf.de BritishLibraryCataloguing-in-PublicationData Prof.Dr.HugoKubinyi Acataloguerecordforthisbookisavailablefromthe Donnersbergstrasse9 BritishLibrary. 67256WeisenheimamSand Germany Bibliographicinformationpublishedby kubinyi@t-online.de theDeutscheNationalbibliothek TheDeutscheNationalbibliothekliststhispublica- Prof.Dr.GerdFolkers tionintheDeutscheNationalbibliografie;detailed CollegiumHelveticum bibliographicdataareavailableontheInternetat STW/ETHZurich htt p://dnb.d-nb .de. 8092Zurich #2012Wiley-VCHVerlag&Co.KGaA, Switzerland folkers@collegium.ethz.ch Boschstr.12,69469Weinheim,Germany Allrightsreserved(includingthoseoftranslation VolumeEditor intootherlanguages).Nopartofthisbookmaybe reproducedinanyform–byphotoprinting,micro- Dr.NathanBrown film,oranyothermeans–nortransmittedortrans- TheInstituteofCancerResearch latedintoamachinelanguagewithoutwritten CancerResearchUKCancer permissionfromthepublishers.Registerednames, TherapeuticsUnit trademarks,etc.usedinthisbook,evenwhennot 15CotswoldRoad specificallymarkedassuch,arenottobeconsidered SuttonSM25NG unprotectedbylaw. UnitedKingdom Composition ThomsonDigital,Noida,India PrintingandBinding MarkonoPrintMediaPteLtd, Singapore CoverDesign SchulzGrafik-Design,Fußgönheim PrintISBN: 978-3-527-33015-7 ePDFISBN: 978-3-527-65433-8 ePubISBN: 978-3-527-65432-1 mobiISBN: 978-3-527-65431-4 oBookISBN: 978-3-527-65430-7 PrintedinSingapore Printedonacid-freepaper V Contents List of Contributors XI Preface XV A Personal Foreword XVII PartOne Principles 1 1 BioisosterisminMedicinalChemistry 3 NathanBrown 1.1 Introduction 3 1.2 Isosterism 3 1.3 Bioisosterism 6 1.4 BioisosterisminLeadOptimization 9 1.4.1 CommonReplacementsinMedicinalChemistry 9 1.4.2 Structure-BasedDrugDesign 9 1.4.3 MultiobjectiveOptimization 12 1.5 Conclusions 13 References 14 2 ClassicalBioisosteres 15 CaterinaBarillariandNathanBrown 2.1 Introduction 15 2.2 HistoricalBackground 15 2.3 ClassicalBioisosteres 17 2.3.1 MonovalentAtomsandGroups 17 2.3.2 BivalentAtomsandGroups 17 2.3.3 TrivalentAtomsandGroups 18 2.3.4 TetravalentAtoms 19 2.3.5 RingEquivalents 19 2.4 NonclassicalBioisosteres 20 2.4.1 CarbonylGroup 20 2.4.2 CarboxylicAcid 21 2.4.3 HydroxylGroup 22 2.4.4 Catechol 22 VI Contents 2.4.5 Halogens 23 2.4.6 AmideandEsters 24 2.4.7 Thiourea 25 2.4.8 Pyridine 26 2.4.9 CyclicVersusNoncyclicSystems 27 2.5 Summary 27 References 27 3 ConsequencesofBioisostericReplacement 31 DennisA.SmithandDavidS.Millan 3.1 Introduction 31 3.2 BioisostericGroupingstoImprovePermeability 32 3.3 BioisostericGroupingstoLowerIntrinsicClearance 40 3.4 BioisostericGroupingstoImproveTargetPotency 43 3.5 ConclusionsandFuturePerspectives 47 References 49 PartTwo Data 53 4 BIOSTER:ADatabaseofBioisosteresandBioanalogues 55 IstvánUjváryandJulianHayward 4.1 Introduction 55 4.2 HistoricalOverviewandtheDevelopmentofBIOSTER 56 4.2.1 RepresentationofChemicalTransformationsforReaction Databases 56 4.2.2 TheConceptof‘‘BiostericTransformation’’ 57 4.2.3 OtherAnalogueand BioisostereDatabases 58 4.3 DescriptionofBIOSTERDatabase 59 4.3.1 CoverageandSelectionCriteria 59 4.3.2 Sources 59 4.3.3 DescriptionoftheLayoutofDatabaseRecords 60 4.3.3.1 IDCode 60 4.3.3.2 BiostericTransformation 60 4.3.3.3 Citation(s) 62 4.3.3.4 Activity 63 4.3.3.5 Fragments 63 4.3.3.6 ComponentMoleculesandFragments 64 4.4 Examples 64 4.4.1 BenzodioxoleBioisosteres 65 4.4.2 PhenolBioisosteres 66 4.4.3 Ketoamides 66 4.5 Applications 69 4.6 Summary 70 4.7 Appendix 70 References 71 Contents VII 5 MiningtheCambridgeStructuralDatabaseforBioisosteres 75 ColinR.Groom,TjelvarS.G.Olsson,JohnW.Liebeschuetz, DavidA.Bardwell,IanJ.Bruno,andFrankH.Allen 5.1 Introduction 75 5.2 TheCambridgeStructuralDatabase 76 5.3 TheCambridgeStructuralDatabaseSystem 78 5.3.1 ConQuest 78 5.3.2 Mercury 78 5.3.3 WebCSD 79 5.3.4 Knowledge-BasedLibrariesDerivedfromtheCSD 80 5.4 TheRelevanceoftheCSDtoDrugDiscovery 83 5.5 AssessingBioisosteres:ConformationalAspects 84 5.6 AssessingBioisosteres:NonbondedInteractions 86 5.7 FindingBioisosteresintheCSD:ScaffoldHoppingand FragmentLinking 91 5.7.1 ScaffoldHopping 91 5.7.2 FragmentLinking 92 5.8 ACaseStudy:Bioisosterismof1H-TetrazoleandCarboxylic AcidGroups 94 5.8.1 ConformationalMimicry 94 5.8.2 IntermolecularInteractions 94 5.9 Conclusions 97 References 98 6 MiningforContext-SensitiveBioisostericReplacements inLargeChemicalDatabases 103 GeorgePapadatos,MichaelJ .Bodkin,ValerieJ.Gillet, andPeterWillett 6.1 Introduction 103 6.2 Definitions 104 6.3 Background 105 6.4 MaterialsandMethods 109 6.4.1 HumanMicrosomalMetabolicStability 109 6.4.2 DataPreprocessing 109 6.4.3 GenerationofMatchedMolecularPairs 110 6.4.4 ContextDescriptors 111 6.4.4.1 WholeMoleculeDescriptors 111 6.4.4.2 LocalEnvironmentDescriptors 112 6.4.5 BinningofDPValues 112 6.4.6 ChartsandStatistics 112 6.5 ResultsandDiscussion 113 6.5.1 GeneralConsiderations 123 6.6 Conclusions 124 References 125 VIII Contents PartThree Methods 129 7 PhysicochemicalProperties 131 PeterErtl 7.1 Introduction 131 7.2 MethodstoIdentifyBioisostericAnalogues 132 7.3 DescriptorstoCharacterizePropertiesofSubstituents andSpacers 132 7.4 ClassicalMethodsforNavigationintheSubstituent Space 135 7.5 ToolstoIdentifyBioisostericGroupsBasedonSimilarity inTheirProperties 136 7.6 Conclusions 138 References 138 8 MolecularTopology 141 NathanBrown 8.1 Introduction 141 8.2 ControlledFuzziness 141 8.3 GraphTheory 142 8.4 DataMining 144 8.4.1 GraphMatching 144 8.4.2 FragmentationMethods 145 8.5 TopologicalPharmacophores 146 8.6 ReducedGraphs 149 8.7 Summary 151 References 152 9 MolecularShape 155 PedroJ.BallesterandNathanBrown 9.1 Methods 156 9.1.1 Superposition-BasedShapeSimilarityMethods 156 9.1.2 Superposition-FreeShapeSimilarityMethods 158 9.1.3 ChoosingaShapeSimilarityTechniqueforaParticular Project 160 9.2 Applications 161 9.3 FutureProspects 164 References 165 10 ProteinStructure 167 JamesE.J.Mills 10.1 Introduction 167 10.2 DatabaseofLigand–ProteinComplexes 168 10.2.1 ExtractionofLigands 168 10.2.2 AssessmentofLigandandProteinCriteria 169
The list of books you might like

The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck

Credence

The Silent Patient

What Happened to You?

Totemismo hoje

Del profumo dei croissants caldi e delle sue conseguenze sulla bontà umana. 19 rompicapi morali

DTIC ADA448671: Religion and the Military: A Growing Ethical Dilemma

DTIC ADA476425: Zero Autocorrelation Waveforms: A Doppler Statistic and Multifunction Problems

By Aaron Grothe NEbraskaCERT

TCPS 1262-2549: Jointed Paper Grass

DTIC ADP023953: Space Power for War Fighters

Materials for the Distribution of Lichens in Japan (15) Toninia sedifolia

The Brooklyn Paper Volume 29 Issue 15
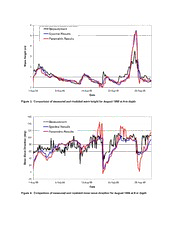
DTIC ADA454270: Incident Boundary Conditions for Wave Transformation

C. Augusta, labourer (1889 Alm).

Greek Government Gazette: Part 7, 2006 no. 780








