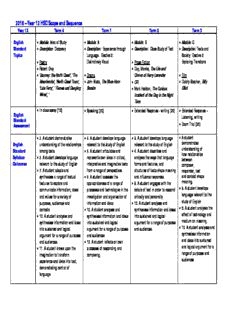
Table Of Content2016 –Year 12 HSC Scope and Sequence
Year 12 Term 4 Term 1 Term 2 Term 3
English • Module: Area of Study • Module: A • Module: B • Module: C
Standard • Description: Discovery • Description: Experience through • Description: Close Study of Text • Description: Texts and
Topics Language: Elective 2: Society: Elective 2:
• Poetry Distinctively Visual • Prose Fiction Exploring Transtions
• Robert Gray • Day, Marele, The Life and
• ‘Journey: the North Coast’, ‘The • Drama Crimes of Harry Lavender • Film
Meantworks’, ‘North Coast Town’, • John Misto, The Shoe-Horn • OR • Daldry Stephen, Billy
‘Late Ferry’, ‘ Flames and Dangling Sonata • Mark Haddon, The Curious Elliot
Wires’, ‘ Incident of the Dog in the Night
Time
• In class essay (15) • Speaking (20) • Extended Response - writing (20) • Extended Response –
English Listening, writing
Standard
Assessment • Exam Trial (25)
• 2. A student demonstrates • 3. A student develops language • 3. A student develops language • A student
English understanding of the relationships relevant to the study of English relevant to the study of English demonstrates
understanding of
Standard among texts. • 8. A student articulates and • 4. A student describes and
how relationships
Syllabus • 3. A student develops language represents own ideas in critical, analyses the ways that language between
Outcomes relevant to the study of English interpretive and imaginative texts forms and features, and composer,
• 7. A student adapts and from a range of perspectives. structures of texts shape meaning responder, text
synthesises a range of textual • 9. A student assesses the and influence responses. and context shape
meaning.
features to explore and appropriateness of a range of • 6. A student engages with the
communicate information, ideas processes and technologies in the details of text in order to respond • 3. A student develops
language relevant to the
and values for a variety of investigation and organisation of critically and personally.
purposes, audiences and information and ideas. • 10. A student analyses and study of English
contexts. • 10. A student analyses and synthesises information and ideas • 5. A student analyses the
• 10. A student analyses and synthesises information and ideas into sustained and logical effect of technology and
medium on meaning.
synthesises information and ideas into sustained and logical argument for a range of purposes
into sustained and logical argument for a range of purposes and audiences. • 10. A student analyses and
synthesises information
argument for a range of purposes and audiences.
and ideas into sustained
and audiences. • 12. A student reflects on own
• 11. A student draws upon the processes of responding and and logical argument for a
range of purposes and
imagination to transform composing.
experience and ideas into text, audiences.
demonstrating control of
language.
2016 –Year 12 HSC Scope and Sequence
English • Module: B: Texts and Society: • Area of Study: Language study • Module: A: Experience through • Module: A: Experience
ESL • Elective 1: Living and Working in within an area of study: language: Elective 2: Australian through language: Elective
Topics the Community ‘discovery’. Visions. 2: Australian Visions
(cont.)
• Description: In this elective • Description: This area of Study • Description: In their
students explore the kinds of requires students to explore the responding and composing • Description: In their
texts that are widely used in the ways in which the concept of students explore the ways in responding and
workplace and the community. discovery is represented in and which language is used to composing students
They respond to and compose through texts. Through close represent visions in texts. They explore the ways in which
texts appropriate to specific language study, and by consider the different types of language is used to
situations designed to meet experimenting with different visions evident in texts and how represent visions in texts.
students’ needs and interests. language choices, students will the creation of a distinctly They consider the
They consider what these texts examine how ideas about Australian vision, or visions, different types of visions
imply about the nature of the discovery vary. affects interpretation and shapes evident in texts and how
workplace or the community in meaning. Students will examine the creation of a distinctly
which they are used. one prescribed text, in addition Australian vision, or
to other texts and examples visions, affects
drawn from their own interpretation and shapes
experience. meaning. Students will
examine one prescribed
text, in addition to other
texts and examples
drawn from their own
experience.
• Revisions:
• Representing / • Listening / Viewing • Speaking • Trial Examination:
English Listening /
• Students view an extract from • Students deliver a speech about • Reading, writing,
ESL Speaking
Assessment their prescribed text and answer a the ways in which Australian listening,
series of questions about ideas of visions are represented in their
• Students compose a
feature article about discovery in the extract and the prescribed text and one other text • Paper 1: Area of Study
the Living and ways in which discovery is shown. of their own choosing.
Working in the • Paper 2: Modules
community elective
• Reading & Responding
and deliver a speech
explaining the • Students compose an extended • Paper 3: Listening
composition response about the ways in which
process. discovery is conveyed in their
prescribed texts and one other
text of their own choosing.
2016 –Year 12 HSC Scope and Sequence
• 5. A student demonstrates • 1 – A student demonstrates • 1 – A student demonstrates • ALL Outcomes
English understanding of how audience understanding of how understanding of how
ESL and purpose affect the language relationships between composer, relationships between composer,
Syllabus and structure of texts. responder, text and context shape responder, text and context shape
Outcomes • 8. A student adapts a variety of meaning. meaning.
textual forms to different • 2 – A student describes and • 4 – A student uses language
purposes, audiences and contexts explains different relationships relevant to the study of English.
in all modes. among texts • 5 - A student demonstrates
• 10. A student assesses the • 3 – A student demonstrates understanding of how audience
appropriateness of a range of understanding of cultural and purpose affect the language
technologies in the investigation reference in a text and structure of texts.
and organization of information • 4 – A student demonstrates • 9 – A student engages with the
and ideas. understanding of cultural details of a text in order to
• 11. A student analyses and reference in a text develop a considered and
synthesizes information and ideas • 6 – A student interprets texts informed personal response
into sustained and logical using key language patterns and • 11 – A student analyses and
argument for a range of purposes structural features. synthesizes information and ideas
and audiences. • 9 – A student engages with the into sustained and logical
details of text in order to develop argument for a range of purposes
a considered and informed and audiences.
personal response.
• 11 – A student analyses and
synthesizes information and ideas
into sustained and logical
argument for a range of purposes
and audiences.
Module B: Texts and Ways of Module B: Texts and Ways of Module B: Texts and Ways of Module B Texts and Ways of
English Thinking Thinking Thinking Thinking
Extension 1 • (Elective: Romanticism) • (Elective: Romanticism) • (Elective: Romanticism) • (Elective: Romanticism)
Topics • Prescribed Texts: • Prescribed Texts: • Prescribed Texts: • Prescribed Texts:
• Coleridge Samuel Taylor, • Shelley Mary, Frankenstein • Campion Jane, Bright Star • Shelley Mary,
Collected Works (This Lime Tree Frankenstein
Bower My Prison, Kubhla Khan, • Campion Jane, Bright
Rime of the Ancient Mariner, Star
Frost at Midnight) • Coleridge Samuel Taylor,
Collected Works (This
Lime Tree Bower My
Prison, Kubhla Khan,
Rime of the Ancient
Mariner, Frost at
Midnight)
2016 –Year 12 HSC Scope and Sequence
English
• Research Paper: 10 /50 Marks • Critical Essay: 20/50 Marks • Trial HSC: 20/50 Marks
Extension 1
Assessment
English • 1 A student distinguishes and • 1 A student distinguishes and • 1 A student distinguishes and • 1 A student distinguishes
Extension 1 evaluates the values expressed evaluates the values expressed evaluates the values expressed and evaluates the values
Syllabus through texts through texts through texts expressed through texts
Outcomes • 2 A students explains different • 2 A students explains different • 2 A students explains different • 2 A students explains
ways of valuing texts ways of valuing texts ways of valuing texts different ways of valuing
• 3 A student composes • 3 A student composes extended • 3 A student composes texts
extended texts extended texts
texts • 3 A student composes
extended texts
English • Module: Major Work • Module: Major Work • Module: Major Work • Module: Major Work
Extension 2
Topics • Description: Students • Description: Students • Description: Students • Description: Students
independently plan and independently plan and complete independently plan and complete independently plan and
complete a Major Work in the a Major Work in the form of an a Major Work in the form of an complete a Major Work in
form of an extended extended composition extended composition the form of an extended
composition composition
• Viva Voce • Report 15 / 50 Marks • Major Work Draft 25/ 50
English (Interview) - 10 /
Marks
Extension 2 50 Marks
Assessment
English • 1 A student develops and • 1 A student develops and • 1 A student develops and
Extension 2 presents an extended presents an extended presents an extended
composition that demonstrates
Syllabus composition that demonstrates composition that
depth insight, originality and
Outcomes depth insight, originality and demonstrates depth
skills in independent
skills in independent investigation. insight, originality and
investigation. skills in independent
• 2 A student reflects on and investigation.
• 2 A student reflects on and documents own process of
documents own process of composition. • 2 A student reflects on
composition. and documents own
process of composition.
2016 –Year 12 HSC Scope and Sequence
Year 12 Term 4 Term 1 Term 2 Term 3
Mathematics • AM3CEC • MM4CEC • PB2CEC • FSHo2CEC
Further Algebraic Skills Further Applications of Area and Multistage Events and Costs of Running a
General
Topics • AM4CEC Volume Applications of Probability Household, Maintenance
Modelling With Functions • FSDe1CEC • DS4CEC and Repairs
• MM4CEC Scale Drawings and House Plans Distributions • FSPe1CEC
Further Applications of Area and • FSDe2CEC • DS5CEC Water Usage and
Design
Volume Interpreting Sets of Data Collection
• FM4CEC • FSPe2CEC
Credit Cards • DS6CEC Electricity
Working With Statistics
• FSHu1CEC • FSPe3CEC
Blood • FSHo1CEC Sustainability and Energy-
Accommodation Costs: Buying
• FSHu2CEC Efficient Housing
and Renting
Body Measurements
• FSHo2CEC
• FSHu3CEC
Costs of Running a Household,
Lung Capacity
Maintenance and Repairs
Mathematics
General • Research/Investigation/Presentati • Research/Investigation/Presentati • Research/Investigation/Presentati
Assessment on/ Class Test component on/ Class Test component on/ Class Test component • Formal examination
Mathematics • MG1H-1 uses mathematics and statistics to evaluate and construct arguments in a range of familiar contexts
General • MG1H-2 analyses representations of data in order to make predictions
Syllabus • MG1H-3 makes predictions about everyday situations based on simple mathematical models
Outcomes • MG1H-4 analyses simple two-dimensional and three-dimensional models to solve practical problems
• MG1H-5 interprets the results of measurements and calculations and makes judgements about reasonableness, including the conversion to
appropriate units
• MG1H-6 makes informed decisions about financial situations likely to be encountered post-school
• MG1H-7 develops and carries out simple statistical processes to answer questions posed
• MG1H-8 solves problems involving uncertainty using basic counting techniques
• MG1H-9 chooses and uses appropriate technology to organise information from a range of practical and everyday contexts
• MG1H-10 uses mathematical argument and reasoning to evaluate conclusions drawn from other sources, communicating a position clearly to
others.
Mathematics
General • http://www.boardofstudies.nsw.edu.au/syllabus_hsc/mathematics-general.html
Syllabus
Link
2016 –Year 12 HSC Scope and Sequence
• ASSESSMENT TASK 1 WEEK 8 • ASSESSMENT TASK 2 WEEK 5 • ASSESSMENT TASK 3 WEEK 4 • TRIAL HSC TASK 4
Mathematics • Common investigation or • Common investigation or • Formal Examination • WEEKS 2/3
2 Unit assignment or written test assignment or written test • Trial HSC
Topics
• The Quadratic Polynomial and the • Geometrical Applications of • Logarithmic and Exponential • Applications of Calculus to
Mathematics
Locus of the Parabola. Differentiation. Functions the Physical World.
2 Unit
Assessment • Series and Application • Integration. • Applications of Calculus to the • Probability.
• Trigonometric Functions. Physical World.
• H1 Seeks to apply mathematical techniques to problems in a wide range of practical contexts.
Mathematics
• H2 Constructs arguments to prove and justify results.
2 Unit
• H3 Manipulates algebraic expressions involving logarithmic and exponential functions.
Syllabus
• H4 Expresses practical problems in mathematical terms based on simple given models.
Outcomes
• H5 Applies appropriate techniques from the study of calculus, geometry, probability, trigonometry and series to solve problems.
• H6 Uses the derivative to determine the features of the graph of a function.
• H7 Uses the features of a graph to deduce information about the derivative.
• H8 Uses techniques of integration to calculate areas and volumes.
• H9 Communicates using mathematical language, notation, diagrams and graphs.
Mathematics • http://www.boardofstudies.nsw.edu.au/syllabus_hsc/mathematics-advanced.html
2 Unit
Syllabus
Link
• Mathematical Induction • Methods of Integration (Simple • Further Methods of Integration • Inverse Functions
Mathematics • Harder examples of graphing Substitutions) involving Logarithmic and (including Inverse
Extension 1 including vertical and horizontal • Primitive of sin2x and cos2x . Exponential Functions Trigonometric Functions).
Topics asymptotes. • Further Methods of Integration • 2. Harder rates of change • Further Methods of
involving Trigonometric Functions. dN dN du Integration involving
= × and Harder
• Iterative Methods for Numerical Inverse Functions.
dt du dt
Estimation of the Roots of a • Binomial Theorem.
Exponential growth and decay
Polynomial (Newton’s Method and • Further Probability.
dN
Halving the Interval) = k(N −P) • Harder Applications of the
dt 2 Unit Course.
• Velocity and Acceleration as a
Function of Displacement.
• Simple Harmonic Motion.
• Projectile Motion
2016 –Year 12 HSC Scope and Sequence
• Assignment/Class Task/modified • Mid-Course Examination • Assignment/Class Task/modified • Formal Examination
Mathematics
Open Book Task Open Book Task
Extension 1
Assessment
• HE1 Appreciates interrelationships between ideas drawn from different areas of mathematics.
Mathematics
• HE2 Uses inductive reasoning in the construction of proofs.
Extension 1
• HE3 Uses a variety of strategies to investigate mathematical models of situations involving binomial probability,
Outcomes
• projectiles, simple harmonic motion, or exponential growth and decay.
• HE4 Uses the relationship between functions, inverse functions and their derivatives.
• HE5 Applies the chain rule to problems including those involving velocity and acceleration as functions of displacement. HE6 Determines
integrals by reduction to a standard form through a given substitution.
• HE7 Evaluates mathematical solutions to problems and communicates them in an appropriate form.
Mathematics http://www.boardofstudies.nsw.edu.au/syllabus_hsc/mathematics-advanced.html
Extension 1
Link
• COMPLEX NUMBERS • POLYNOMIALS • GRAPHS • MECHANICS
Mathematics • Sums, differences, products and • Relationship between roots and • Sketch the reciprocal, absolute • Acceleration proportional
Extension 2 quotients coefficients value, square, square root, power to velocity
Topics • Modulus-argument form • Partial fractions of a function • Harder problems on
• Conjugates, reciprocals, square • Complex roots and quadratic • Features of a curve given its projectiles, S.H.M. etc.
root, square of z factors derivative • Resisted motion under
• De Moivre’s Theorem • THE CONIC SECTIONS • Use implicit differentiation to gravity
• Solve equations • Ellipse, hyperbola and rectangular determine the information of • Circular motion, forces and
• Representations on the Argand hyperbola graphs their resolution
Diagram • Axes, foci, directrix, eccentricity of • INTEGRATION • Describe motion either
• Theorems on moduli, arguments, ellipse and hyperbola • Standard integral tables mathematically or
conjugates • Parametric and Cartesian • Change of variable, using partial physically
• nth roots of unity and solve equations fractions, completing the square
problems • Rectangular hyperbola • Trigonometric functions
• Expressions using properties of • and locus problems • Integrate by parts • HARDER MATHEMATICS
the cube roots of unity • Reduction formulae EXTENSION 1
• GRAPHS • Change of limits • Solve harder questions on
• POLYNOMIALS • Basic curves of rational, any Mathematics (2 Unit)
• VOLUME
• Reduce to factors over a field logarithmic, exponential, circular or Mathematics Extension
• Sketch a “slice” or “shell” from a
• Fully factorise functions 1 topic
solid, and find volume of the solid
• Fundamental Theorem of Algebra • Curves formed by +, -,x, ÷ of
• Volume of a solid which has
and other related theorems ordinates/reflection.
similar cross-sections
• Sketch functions without using
differentiation
2016 –Year 12 HSC Scope and Sequence
• Assignment/Class Task/modified • Mid-Course Examination • Assignment/Class Task/modified • Formal Examination
Mathematics
Open Book Task Open Book Task
Extension 2
Assessment
• E1 appreciates the creativity, power and usefulness of mathematics to solve a broad range of problems
Mathematics
• E2 chooses appropriate strategies to construct arguments and proofs in both concrete and abstract settings
Extension 2
• E3 uses the relationship between algebraic and geometric representations of complex numbers and of conic sections
Outcomes
• E4 uses efficient techniques for the algebraic manipulation required in dealing with questions such as those involving conic sections and
polynomials
• E5 uses ideas and techniques from calculus to solve problems in mechanics involving resolution of forces, resisted motion and circular motion
• E6 combines the ideas of algebra and calculus to determine the important features of the graphs of a wide variety of functions
• E7 uses the techniques of slicing and cylindrical shells to determine volumes
• E8 applies further techniques of integration, including partial fractions, integration by parts and recurrence formulae, to problems
• E9 communicates abstract ideas and relationships using appropriate notation and logical argument
Mathematics http://www.boardofstudies.nsw.edu.au/syllabus_hsc/mathematics-advanced.html
Extension 2
Link
Blueprint of Life Search for Better Health Option: Genetics - The Code Maintaining a Balance
Biology • The continuity of life is assured • When physiological processes Broken? • Countless metabolic
Topics when the chemical information malfunction, the body tries to • Modern genetics is moving processes are essential to
that defines it is passed on from repair the damage. The process is towards an increased sustain the life of an
one generation to the next on the similar in all living things and it is understanding of the biochemical organism. This topic
chromosomes. This topic only when the process fails to role of individual genes. This is examines the structure of
examines the historical contain the damage that disease being enhanced by the Human enzymes, their role in
development of the understanding can be recognised. This topic Genome Project that has metabolism and how the
of inheritance and its link to the traces the historical development sequenced the entire human body maintains
theory of evolution. It also of our understanding of disease genome to identify all the homeostasis in order to
examining how our knowledge of and how scientific research is now encoded genes ensure enzymes are
inheritance is influencing the focussing on preventing disease operating at their most
course of evolution. rather than treating it. efficient at all times.
• Major Research Project: • Written Examination: • Practical Examination: • Research Task:
Biology
• First-hand investigation • Scientific thinking, problem • First and second-hand • Scientific thinking and
Assessment
• (20%) solving and communication (10%) investigations (20%) communication of
understanding (10%)
• HSC Trial Examination:
Knowledge and Understanding
(40%)
2016 –Year 12 HSC Scope and Sequence
• Evaluates how major advances in • Evaluates how major advances in • Evaluates how major advances in • Analyses the ways in which
Biology
scientific understanding and scientific understanding and scientific understanding and models, theories and laws
Outcomes
technology have changed the technology have changed the technology have changed the in biology have been
direction or nature of scientific direction or nature of scientific direction or nature of scientific tested and validated
thinking thinking thinking • Assesses the impact of
• Analyses the ways in which • Analyses the ways in which • Analyses the ways in which particular advances in
models, theories and laws in models, theories and laws in models, theories and laws in biology on the
biology have been tested and biology have been tested and biology have been tested and development of
validated validated validated technologies
• Assesses the impact of particular • Assesses the impact of particular • Assesses the impact of particular • Assesses the impacts of
advances in biology on the advances in biology on the advances in biology on the applications of biology on
development of technologies development of technologies development of technologies society and the
• Assesses the impacts of • Assesses the impacts of • Assesses the impacts of environment
applications of biology on society applications of biology on society applications of biology on society • Evaluates the impact of
and the environment and the environment and the environment human activity on the
• Identifies possible future • Identifies possible future • Identifies possible future interactions of organisms
directions of biological research directions of biological research directions of biological research and their environment
• Explains why the biochemical • Explains why the biochemical • Explains why the biochemical • Justifies the
processes that occur in cells are processes that occur in cells are processes that occur in cells are appropriateness of a
related to macroscopic changes in related to macroscopic changes in related to macroscopic changes in particular investigation
the organism the organism the organism plan
• Analyses the impact of natural • Analyses the impact of natural • Analyses the impact of natural • Evaluates ways in which
and human processes on and human processes on and human processes on accuracy and reliability
biodiversity biodiversity biodiversity could be improved in
• Evaluates the impact of human • Evaluates the impact of human • Describes the mechanisms of investigations
activity on the interactions of activity on the interactions of inheritance in molecular terms • Uses terminology and
organisms and their environment organisms and their environment • Describes the mechanisms of reporting styles
• Describes the mechanisms of • Describes the mechanisms of evolution and assesses the impact appropriately and
inheritance in molecular terms inheritance in molecular terms of human activity on evolution successfully to
• Describes the mechanisms of • Describes the mechanisms of • Uses terminology and reporting communicate information
evolution and assesses the impact evolution and assesses the impact styles appropriately and and understanding
of human activity on evolution of human activity on evolution successfully to communicate • Assesses the validity of
• Justifies the appropriateness of a • Uses terminology and reporting information and understanding conclusions from gathered
particular investigation plan styles appropriately and • Assesses the validity of data and information
• Evaluates ways in which accuracy successfully to communicate conclusions from gathered data • Explains why an
and reliability could be improved information and understanding and information investigation is best
in investigations • Assesses the validity of • Justifies positive values about and undertaken individually or
• Uses terminology and reporting conclusions from gathered data attitudes towards both the living by a team
styles appropriately and and information and non-living components of the • Justifies positive values
successfully to communicate • Justifies positive values about and environment, ethical behaviour about and attitudes
information and understanding attitudes towards both the living and a desire for a critical towards both the living and
• Assesses the validity of and non-living components of the evaluation of the consequences of non-living components of
2016 –Year 12 HSC Scope and Sequence
conclusions from gathered data environment, ethical behaviour the applications of science the environment, ethical
and information and a desire for a critical behaviour and a desire for
• Explains why an investigation is evaluation of the consequences of a critical evaluation of the
best undertaken individually or by the applications of science consequences of the
a team applications of science
• Justifies positive values about and
attitudes towards both the living
and non-living components of the
environment, ethical behaviour
and a desire for a critical
evaluation of the consequences of
the applications of science
The Acidic Environment Chemical Monitoring and Option: Industrial Chemistry Production of Materials
Chemistry • Acidic and basic environments Management • Industry uses chemical reactions • Humans have always
Topics exist everywhere and are used in • An understanding of the chemical to produce chemicals for use by exploited their natural
many industries. This unit processes involved in interactions society. This unit examines the environment for all their
examines the properties of acids in the full range of global ideas that some chemicals have needs and the twentieth
and bases and the importance of environments is indispensable to been produced to replace century saw an explosion
safe handling techniques when an understanding of how naturally occurring chemicals that in both the use of
considering the impact of their environments behave and change. are no longer available or are not traditional materials and in
increased release into the This unit examines how chemists economically viable. It also the research for
environment. can assist in reversing or examines the role of chemists and development of a wider
minimising the environmental chemical engineers in some range of materials. This
problems caused by technology industrial processes and allows unit examines the role
and the human demands for some insight into the qualitative chemists and chemical
products and services. and quantitative aspects of the engineers play in the
chemical industry. search for new sources of
traditional materials and
production of new
materials to replace those
that have been deemed no
longer satisfactory for
society’s needs.
• Research Task: • Practical Task: • HSC Trial Examination: • Written Examination:
Chemistry
• Scientific thinking and • First-hand investigation (20%) Knowledge and Understanding • Scientific thinking, problem
Assessment
communication of understanding (40%) solving and communication
(10%) • Major Research Project: (10%)
• First-hand investigation
• (20%)
Description:meaning. • 3. A student develops language relevant to the study of English. • 5. A student analyses the .. Simple Harmonic Motion. • Projectile Motion .. exploration to become more viable. This unit .. Times: Akhenaten. • All topics.