Stereoselective reactions of alkenes - Massey University, The PDF
Preview Stereoselective reactions of alkenes - Massey University, The
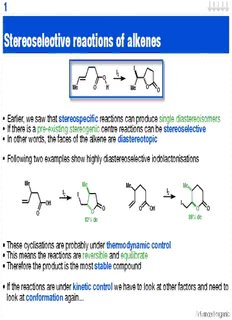
1 Stereoselective reactions of alkenes I I 2 O Me O H Me O O • Earlier, we saw that stereospecific reactions can produce single diastereoisomers • If there is a pre-existing stereogenic centre reactions can be stereoselective • In other words, the faces of the alkene are diastereotopic • Following two examples show highly diastereoselective iodolactonisations Me Me Me Me I I 2 I 2 OH I O O OH O O O O 88% de 82% de • These cyclisations are probably under thermodynamic control • This means the reactions are reversible and equilibrate • Therefore the product is the most stable compound • If the reactions are under kinetic control we have to look at other factors and need to . look at conformation again... .. Advanced organic 2 Stereoselective reactions of alkenes II O O Me Me Me m-CPBA + Me SiMe Ph Me SiMe Ph Me SiMe Ph 2 2 2 >95% <5% • Two diastereoisomers formed as a result of attack from the two diastereotopic faces • Look at possible conformations... • Arguably the lowest energy conformations have greatest separation of substituents HH HH MMee HH HH MMee HH HH Me HH MMee if no cis substituent rotate then only small H bond MMee HH energy difference Me lowest energy: H slightly higher energy: Me eclipses plane of alkene eclipses plane of alkene HH HH MMee HH HH MMee X MMee HH MMee MMee Me cis substituent MMee HH present then only H ONE conformation Me Me high energy: Me–Me lowest energy: H interaction disfavours eclipses plane of alkene conformation • The control of conformation by the interaction of methyl group and stereocentre is . called allylic strain or A(1,3) strain .. Advanced organic 3 Stereoselective reactions of alkenes III • Apply this knowledge to the real system... X O O Me m-CPBA Me Me Me H SiMe2Ph Me H SiMe2Ph Me H SiMe2Ph <5% >95% m-CPBA m-CPBA silyl group blocks X approach Me Ph Me Ph H H H lowest energy H H Si Me H H Si Me Me Me conformation Me H Me H O Si Me Me Me Ph Me formation of minor m-CPBA diastereoisomer results from m-CPBA approaching alkene in above conformation or m-CPBA approaches approaching passed from unhindered face the silyl group Advanced organic 4 Importance of A(1,3) strain O O Me Me m-CPBA Me Me Me Me + H SiMe Ph 2 H SiMe Ph H SiMe Ph 2 2 61% 39% • The importance of a cis-substituent is made clear by the reduced stereoselectivity • This is explained as follows... m-CPBA X PPhh MMee Ph Me O lowest energy MMee HH SSii MMee Me H Si Me Me Me conformation HH H gives major product HH H O H SiMe Ph 2 MMee Me 61% Me Me m-CPBA attacks both conformations low form least hindered energy -- so mixture of H SiMe Ph face products 2 O MMee HH HH Me H H O HH MMee H Me Me Me X SSii MMee Si Me H SiMe Ph 2 PPhh MMee Ph Me 39% m-CPBA Advanced organic 5 Other reactions... • Epoxidation is not the only stereoselective reaction of alkenes • Below is an example of hydroboration, a useful reaction that you should be familiar with... H Me Me H Me H Me H O H Me H Me 2 2 BH NaOH 3 O OBn O H B OBn O OH OBn 2 74% de Attack from the least sterically demanding face of the alkene O O as it resides in the most H CH OBn H CH OBn 2 2 favoured conformation. Me Me H H Followed by stereospecific H B H 2 Me Me oxidation H B H 2 preferred approach Selectivity in addition to cis alkenes H S L S L H S H R 1 1 R R R 3 3 L H S L R1 R1 R1 R1 S = smaller group favoured destabilised by repulsion between C-1 & C-3 L = larger group substituents or A(1,3) strain Advanced organic 6 Directed epoxidation OH OH OH reagent + O O reagent: syn t anti m-CPBA 92 : 8 t-BuO H, VO(acac) 98 : 2 2 2 • A hydroxyl group can reverse normal selectivity and direct epoxidation • Epoxidation with a peracid, such as m-CPBA, is directed by hydrogen bonding and favours attack from the same face as hydroxyl group • The reaction with a vanadyl reagent results in higher stereoselectivity as it bonds / chelates to the oxygen hydrogen Ar bond O O t-BuO Me O O Me O V V O O O O O O H H Me Me O vanadyl acetylacetonate H H Advanced organic 7 Directed epoxidation in acyclic systems O O Me Me m-CPBA Me Me Me Me + Me H OH Me H OH Me H OH 95 5 hydrogen Ar bond Me H H O O Me Me O Me H OH O H H H O O Me H Me H O O H O Me Me H Ar Me favoured disfavoured conformation conformation • Hydroxyl group can direct epoxidation in acyclic compounds as well • Once again, major product formed from the most stable conformation • Thus the cis methyl group is very important • The minor product is formed either via non-directed attack or via the less favoured . conformation .. Advanced organic 8 Directed epoxidation: effect of C-2 substituent Me t-BuO H Me Me 2 VO(acac) Me 2 Me + Me O O H OH OH OH 19 : 1 steric interaction Me t-Bu O L V H O H O L favoured disfavoured conformation as H Me H Me conformation as only Me & H eclipse Me & Me eclipse O L O Me H V L O t-Bu H • The presence of a substituent in the C-2 position (Me) facilitates a highly diastereoselective reaction • The preferred conformation minimises the interaction between the two Me (& Me) groups • With C-2 substituent (H) there is little energy difference between conformations • Therefore, get low selectivity Me t-BuO H 2 H Me Me VO(acac) Me Me Me Me O H 2 H too small to + O O H H differentiate H OH OH OH conformations O L 2.5 : 1 V L O t-Bu Advanced organic 9 Directed reactions SiMe t-BuO H SiMe 3 2 3 Me Me VO(acac) TBAF Me Me 2 Me Me O O OH H OH OH 25:1 • It is possible to form the desired allylic epoxide in a highly selective manner by utilising a temporary blocking group • The silyl group causes one conformation to predominate & can be removed at end • As silyl group bigger than methyl reaction more selective • Other diastereoselective reactions of alkenes can be controlled by a directing group • Below is an example of cyclopropanation by the Simmons-Smith reagent CH I 2 2 Zn Zn I OH OH O CH 2 H H C Zn 2 H C I + I O I Zn H carbenoid >98% de Advanced organic 10 Stereoselective reactions of enolates M O O O E R2 R2 R2 R1 R1 R1 H H H E H • The stereoselectivity of reactions of enolates is dependent on: • Presence of stereogenic centres on R1, R2 or E (obviously!) • Frequently on the geometry of the enolate (but not always) C-α re face C-α si face M M O O MO R2 MO H α R2 α α H α R1 R1 R1 H R1 R2 H R2 (Z)-enolate (E)-enolate (cis) (trans) C-α si face C-α re face • Use terms cis and trans with relation to O–M to avoid confusion Advanced organic
Description: