Pacific slope Cretaceous bivalves of the genus Calva PDF
Preview Pacific slope Cretaceous bivalves of the genus Calva
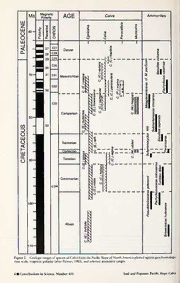
, Pacific Slope Cretaceous Bivalves of the Genus Calva L. R. Saul1 and W. P. Popenoe2 CONTENTS ABSTRACT 1 INTRODUCTION 2 SOURCES OF MATERIAL STUDIED 3 DISTRIBUTION 3 FEATURES MEASURED 9 CHANGES IN CALVA THROUGH TIME 9 SUMMARY 10 ABBREVIATIONS 10 SYSTEMATIC PALEONTOLOGY 10 Genus Calva Popenoe, 1937 10 Subgenus Calva Popenoe, 1937 12 Calva {Calva) heliaca, new species 12 Calva {Calva) regina Popenoe, 1937 13 Calva {Calva) campanae, new species 15 Calva {Calva) peninsularis (Anderson and Hanna, 1935) 17 Calva {Calva) varians (Gabb, 1864) 19 Calva {Calva) baptisia, new species 24 Subgenus Egelicalva, new subgenus 26 Calva {Egelicalva) byblidis new species 27 Calva {Egelicalva) nitida (Gabb, 1864) 27 Calva {Egelicalva) spissa, new species 32 Calva {Egelicalva) taffi (Anderson, 1958) 34 Calva Egelicalva buttensis (Anderson, 1958) 36 ( ) Calva {Egelicalva) bowersiana (Cooper, 1894) 39 Calva {Egelicalva) crassa, new species 44 Subgenus Microcalva, new subgenus 48 Calva {Microcalva) elderi, new species 48 Calva Microcalva haggarti, new species 50 ( ) Subgenus Penecallista, new subgenus 53 ACKNCOaWlvLaE{DPeGneMcEalNliTstSa) marina, new species 5537 LITERATURE CITED 57 LOCALITIES CITED 60 ABSTRACT.Calvaisthecommon,veneridbivalvegenusofshallowwaterNorthAmericanPacificSlope Cretaceous deposits. Sixteen species placed in four subgenera range in age from Albian through latest Maastrichtian.Sixspecies{Calvaheliaca,newspecies,Cenomanian;C. reginaPopenoe, 1937,Turonian; C. campanae, new species, late early to late Campanian; C. peninsularis (Anderson and Hanna, 1935), latest Campanian-early Maastrichtian; C. varians (Gabb, 1864), mid and late Maastrichtian; and C. baptisia, new species, latest Maastrichtian) constitute the typical subgenus and give it an age range of Cenomanian through Maastrichtian. Seven species {Calva byblidis, new species, early Albian; C. nitida (Gabb, 1864), late Albian-Cenomanian; C. spissa, new species, Turonian; C. taffi (Anderson, 1958), Coniacian-Santonian-earliestCampanian;C.buttensis(Anderson,1958),earlyCampanian;C.bowersiana L Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, 900 Exposition Boulevard, Los Angeles, California 90007. 2. Department of Earth and Space Sciences, University of California-Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California 90024. (Deceased 1981.) Contributionsin Science, Number 433, pp. 1-68 Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, 1992 (Cooper, 1894), late early-late Campanian; and C. crassa, new species, early Maastrichtian) constitute the new subgenus Egelicalva,giving it an age range ofAlbian through early Maastrichtian. Calvaelderi, newspecies,Coniacian,andC.haggarti,newspecies,Campanian,constitutethenewsubgenusMicrocalva, andCalva marina,newspecies,lateCampanian-earlyMaastrichtian,istypespeciesofthenewsubgenus Penecallista. Although there is no obvious directional change in the external morphologic featuresstudied,thereis evidenceofatrendinhingemorphologyintheevolutionarylineagesofCalvathatisapparentlytraceable through the Late Cretaceous. The restricted age ranges of species in these lineages makes them useful in dating deposits of Late Cretaceous age. In addition, the typical subgenus has a more southern distribution than the subgenus Egelicalva,suggestingthatchangesin theirdistributionsthroughthe LateCretaceousmayaid inclimatic reconstructions. ; INTRODUCTION scribed from the Upper Greensand of Blackdown, Devon, England, but in 1903 he referred them to Venerid bivalves,especiallyofthegenusCalva,are Meretrix nitida Gabb, 1864, a species oflatest Al- a common constituent of shallow water Late Cre- bian and Cenomanian age. Whiteaves’ material is taceous marine faunas of the Pacific Slope from presently only partially available, but his Cytherea Alaska south to Baja California. Two species of (C.) plana and M. nitida are Calva. Some of his Calva, Meretrix nitida Gabb, 1864,and Venus va- figured specimens have been misplaced, and the rians Gabb, 1864, were among the earliest de- horizonand localityfora numberofhis specimens scribed bivalvesofCretaceousagefromCalifornia. are imprecise. However, these and other species of Calva have The first step toward discriminating between been imprecisely diagnosed and their geologic oc- Gabb’sspeciesandassigningthemtoanappropriate currences incorrectly recognized, in part because genuswas made byStewart(1930)who figuredone severalspeciesarequitesimilarandeasilyconfused. ofGabb’soriginalspecimensofVenus variansand With careful discrimination the species can be use- designatedANSP4383aslectotype.Hefiguredtwo ful in dating beds of Late Cretaceous age. Most of Gabb’s specimens of Meretrix nitida but des- species of Calva from northeast Pacific Slope de- ignated neither as lectotype. He considered that V. posits appear allocatable to two lineages or sub- varians and M. nitida might be conspecific but genera. Geographic occurrences of these two sub- noticedsubtleshapedifferencesbetweenspecimens genera,CalvaandEgelicalva,suggestthatthetypical ofthetwoseparatelots. Hepartiallyexposedhing- lineage was more thermophilic than the other. es of both species, showing that anterior lateral Popenoe (1937) proposed the genus Calva to teeth are present in both, and, therefore, referred include several Pacific Slope Cretaceous venerid both species toAphrodina Conrad, 1869. He con- species of medium to large size. He designated as sidered the type locality of both to be Martinez, type species Calva regina Popenoe, 1937, of Tu- Contra Costa County, California, but commented ronianage,and referredMeretrixnitidavar. major that the striking differences in preservation might Packard, 1922 = Cucullaea bowersiana Cooper, indicate that more than one stratum and perhaps 1894, to Calva. He also tentatively included two morethanonelocalitywasincludedunderthename much-cited speciesdescribed byGabb in 1864, Ve- “Martinez.” He dated the Cretaceous fauna from nus varians and Meretrix nitida, although at that “Martinez” as Cenomanian or earlier, an age ap- time(1937)neitherthemorphologynorstratigraphic propriatetoM. nitida,butnotforV. varians,which occurrence of either species was clearly under- is now known to be of Maastrichtian age. stood. Gabb (1864) cited the two species as occur- Popenoe(1937,p.395)indicatedthatVenusvar- ring together at four California localities: Cow ians,Meretrixnitida,M.nitidavar.majorPackard, Creek, Shasta County; Orestimba Canyon, Stanis- and C. regina Popenoe differ from Aphrodina in laus County; Chico Creek, Butte County; and Di- having posterior lateral teeth. At this time, he also vision A at Martinez, Contra Costa County, and tentativelyassignedMeretrixumzambiensisWoods, the two species have continued to be jointly cited 1906,fromtheLateCretaceousofPondoland,South from numerous Cretaceous localities by many Africa, to Calva, being unaware that M. umzam- workers up to thepresent. Gabb did not designate biensis had been designated type species of Tri- type specimens or type localities and gave no ex- gonocallista Rennie, 1930 (p. 177). Upon discov- planation for placing V. varians and M. nitida in eringRennie’sdesignation,Popenoesentspecimens differentgenera. Heprovided no description ofthe of Calva to Rennie at Rhodes University College, hinge of either species. Grahamstown,SouthAfrica.RennieopinedthatT. Whiteaves (1879) originally identified specimens umzambiensis was congeneric with the California that should probably be referred to Calva from specimens,andPopenoe(1940)placedCalvainthe several localities in the Nanaimo Basin deposits, synonymyofTrigonocallista. Casey(1952,p. 172), British Columbia, as Cytherea Caryatis plana however, recognized both genera because Calva ( ) Sowerby, 1812, a species of late Albian age de- was described as having smooth sided anteriorlat- 2 Contributions in Science, Number 433 Saul and Popenoe: Pacific Slope Calva eral teeth, whereas Trigonocallista has striated an- have been made include the Nanaimo Basin [1-3] teriorlateralteeth. He considered them both to be in southern British Columbia and San Juan Co., dosiniopsids. Washington; the Hudspeth Formation in Wheeler Anderson(1958,p. 138)providedtwonewnames and Grant Cos. [4], Oregon; the Hornbrook For- for species ofCalva collected at Chico Creek and mationinJacksonCo.[6],OregonandSiskiyouCo. figured by Taff et al. (1940): Trigonocallista taffi [7], California; the Jalama Formation in western Anderson for T. nitida (Gabb) (Taff et al., 1940, Santa Barbara Co. [22], California; the Point Loma pi. 2, figs. 3-4) and T. buttensis Anderson for T. Formation ofthe Rosario Group in San Diego Co. varians(Gabb) (Taffetal., 1940,pi. 2, figs. 10-11). [28], California; and the Rosario Formation in Seven of the 15 species referable to Calva s.l. northern Baja California, Mexico [29]. that are present in northeast Pacific Slope Creta- Type specimens of the named taxa were bor- ceousbedswerenamedpriortothisstudy.Tothese rowed. If preservation of the specimen was ade- areadded nine newspecies,givingthegenusatime quate and permission was granted by the loaning range in this region of Albian through Maastrich- institution, matrix was removed so that the hinge tian. In the past generic and specific relations have teeth could be seen. New collections from type been obscured by incomplete knowledge of mor- localities of described species have made possible phology of some species, careless identification of assessments of the range of variation in these spe- many specimens, and resultant confusion of the cies. Although the type localities of species de- stratigraphic occurrences of species. This paper scribed by Gabb and Cooper lack precision, com- summarizesthe species comprisingCalva and their parisonoftypematerialwithlargecollectionsfrom morphologic, geographic, and stratigraphic dis- the vicinity of the “type locality” has made it pos- tinctness. This work was begun by W. P. Popenoe sible to assign these species to descrete horizons. whogaveapaperonCalvaatthe 1963Cordillerian Taxa included in Calva, especially Venus varians Section of the Geological Society of America (Po- andMeretrixnitida,havebeenreportedfrommany penoe, 1964, p. 219) and has been completed by localities; reassessment of reported identifications L. R. Saul. hasbeeneffectedbyexaminingthespecimensupon which the reports were based and/or by studying SOURCES OF MATERIAL STUDIED larger, better located collections from the area. Calvas most commonly occur in sandstone de- During the years that he studied the Late Creta- posits. Where specimens are not obviously dis- ceous molluscan faunas from the Pacific Slope of placed downslope, the conditions appear to have North America, Popenoe amassed collections that been normal marine and sublittoral, nearorbelow were carefully located geographically and strati- wave base. Calva is commonly part of a fairly di- graphically,manyofwhichcontainedspecimensof versemolluscanassemblagethatlivedoff-shorefrom the venerid bivalve Calva. Figure 1 indicates areas communities dominated by Cymbophora and in from which such specimens have been collected, slightlycoarsersubstratethanthoseinwhichCras- andlocalitiesarekeyedtoitbyabracketednumber. satella was most abundant. Although common in Aframeworkforthestudyofthisgroupisprovided manycollections,Calvadoesnotusuallyconstitute by several important sections. The Cretaceous sec- more than a third ofrecoveredspecimens. In com- tionsatthe northern end oftheSacramentoValley parisontosomethinnershelledbivalvesinthesame in the vicinity of Ono [9] and east of Redding [8], deposits, specimens of Calva, which are relatively ShastaCo.,comprisingtheBuddenCanyonandthe robust, probably have a better recovery rate from ReddingFormations,haveprovidedveneridsofAl- hard matrix and are therefore disproportionally bianthroughSantonianage.OutcropsoftheChico abundantinmuseumcollections.AlthoughallCal- Formation,especiallyalongChicoCreek[11],have va have a well-developed pallial sinus and were providedveneridsofSantonianthroughearlyCam- doubtless infaunal filter-feeders, shell morphology panian age. The Santa Ana Mountains [26] section andthetypicallydisarticulatedpreservationofshells in Orange Co., comprising the Ladd and Williams indicate that Calva was probably a shallow bur- Formations, has yielded venerids of Turonian and rower. late Campanian age. In the Simi Hills [24] of Los Angeles and Ventura Cos., the Chatsworth For- DISTRIBUTION mation has yielded venerids of mid-Campanian through early Maastrichtian age. Although mega- In addition to the fourPacific Slope species, Venus fossilsare sparse in much ofthe thick GreatValley varians, Meretrix nitida, Cucullaea bowersiana, Seriescroppingoutalongthewesternborderofthe andCalvaregina,Popenoe(1937,p.395)suggested San Joaquin-Sacramento Valleys, the region has that Meretrix umzambiensis from South Africa, provided venerids of Albian through late Maas- Cytherea subrotunda Sowerbyand Cytherea cape- trichtianage.NorthandsouthofLakeNacimiento rata Sowerby from England, Dosiniopsis nebras- [21] in San Luis Obispo Co., outcrops of the El censis(Meekand Hayden, 1856) fromtheWestern Piojo Formation have yielded late to latest Maas- Interior, and Callista pseudoplana Yabe and Na- trichtian venerids. gao, 1925, from Hokkaido, Japan, might be re- Other areas from which important collections ferred to Calva. The generic placement of M. Contributionsin Science,Number433 Saul and Popenoe: Pacific Slope Calva 3 ———— ————— Figure 1. IndexmaptogeographicoccurrencesofCal- vaspp.Localitiesaregrouped—into33areasthatarenum- bered from north to south: 1 Denman Island, Hornby — 5Is—land, and Texada Island, British Columbia. 2 Depar- tureB—ayandNanaimo,VancouverIsland,BritishC—olum- ! bia.3 SuciaIsland,SanJuanCo.,Washington.4 Day- I ville,GrantCo.,and RockCreek,WheelerCo.,Oregon. AndyBernardRanchandSuplee,CrookCo.,Oregon. 6 Ash—land Creek and Jacksonville, Jackson Co., Ore- gon. 7 Rancheri—a Gulch and Young Ranch, Siskiyou Co.,California.8 CloverCreek,CowCreek,DryCreek, Oak Run, Price Hollow,—Redding, and Stinking Creek, Shasta Co., California. 9 North Fork of Cottonwood Cre—ek, Ono, and Texas Springs, Shasta Co., California. 10 Elder Creek, Tehama Co., California. 11—Butte Creek, Chico Creek, and Pentz, Butte Co.,—California. 12 Stony Creek, Glenn Co., California. 13 Antelope Creek, Peterson Ranch, and Sites, Colusa Co., and — ThompsonCreek,YoloCo.,California. 14 Beniciaand — Glenn Cove,SolanoCo., California. 15 CurryCanyon, DeerValley,and Martinez,ContraCostaC—o.,andPleas- anton area, Alameda Co., California. 16 Bolsa Point, SanMateoCo.,California.17-—GarzasCreek,Orestimba Creek,andSaladoCreek,StanislausCo.,California.18 Laguna Seca, Los Banos Creek, Pachec—o Pass, and Orti- galitaCreek,MercedCo.,California.19 Coalinga,Coo- per Canyon, Los Gatos Creek, Fresno Co., California. 20 GarzaPeak,McClureRidge,northofSunflowerVal- ley,KingsCo.,California.21—CantinasCreek,DipCreek, LakeNacimiento,San LuisObispoCo.,California.22— ; Jalama Creek, Sisquoc River, Hurricane—Deck Quadran- gle, Santa Barbara Co., California. 23 Warm Springs Mountain,LosAngelesCo.,California.24-—BellCanyon, | SimiHills,VenturaCo.,andDaytonCanyon,LosAngeles — Co.,California—.25 SantaMonicaMts.,LosAngelesCo., California.26 Bakerand BlackStarCanyons,BeeCan- yon, Holz Ranch, Pankratz Ranch, Wildcat and White Canyons,andWilliamsCanyon,SantaAna Mts.,Orange Co., California. 27—Carlsbad area, San Diego Co., Cal- ifornia. 28—La Jolla and Point Loma, San Diego Co., Cal—ifornia. 29—Punta Banda, Baja California, Mexico—. 30 SanAntoniodelMar,BajaCalifornia,Mexico.31 Vicinity of El Rosario and Arroyo Santa Catarina, Baja California, Mexico. 32—Cedros Island, Baja California, Mexico. 33—Northwest Vizcaino Peninsula, Baja Cali- forniaSur, Mexico. 34—VizcainoPeninsulainlandfrom PuntaAbreojos,BajaCaliforniaSur,Mexico.Placenames mentioned in text listed alphabeticallyand assigned toa numbered—area: 5—AndyBernar—d Ranch; 13—Antelope Creek;15 ArroyodelValle;31 ArroyoSantaCatarina; 613——Ashland Creek; 26—Baker Canyon; 26—Bee Can- yon;24—BellCanyon;14—Benicia;26—BlackStarCan- yon; 16—Bolsa Point; 11—Butte Creek; 21—Cantinas Creek; 27—Carlsbad; 32—Cedros Island; 11—Chico — — — Creek; 8 Clover Creek; 19 Goalinga; 19 Gooper — — Canyon; 8 Cow Creek; 15—Curry Canyon; 24 Day- ton Canyon;4—Dayville; 15—DeerValley; 1—Denman 2Is1landD;i2p—CrDeeepka;rt8ur—eDBrayy;Cr17e,ek1;8,1109—,2E0ld—erDiCarbeleok;Ra3n1ge—; El Rosario; 20—Garza Peak; 17—Garzas Creek; 14 GlennCove;26—Holz Ranch; 1—HornbyIsland;22 Jalama Creek; 6—Jacksonville; 18—Laguna Seca; 28 km L1a—9—JoLlloas;G2a1to—sLCar—keeek;Na1c5i—miMeanrttoi;ne1z8;——20T—osMcBCalnuorseCRriedegke;; 0 100 250 500 750 _ 1000 2 Nanaimo;15 —NilesCanyon;—9 North—ForkofCot- tonwoodCreek; 8 Oak Run;9 Ono; 17 Orestimba Creek; 18—Ortigalita Creek; 18—Pacheco Pass; 26 Pankratz Ranch; 21—Pebblestone Shut-In; 11——Pentz; Peterson Ranch; 15—Pleasanton area; 28 Point 4 Contributions in Science,Number 433 Saul and Popenoe: Pacific Slope Ca/va — — —— , umzambiensis has already been mentioned. Casey deposits of Coniacian, Santonian, and early Cam- (1952)consideredCythereasubrotundatobeatyp- panian age of Southern California were laid down icalCalvaanddesignatedCythereacaperataasthe in moderately deep or deeper water and have as typespecies ofChimela,anew subgenus ofCalva. yet yielded no specimens of Calva. Speden (1970) consigned Dosiniopsis nebrascensis ThephylogeneticrelationshipbetweenCalvas.s. tothesynonomyofD. deweyi(Meekand Hayden, and Calva (Egelicalva) is not known. Egelicalva 1856) and considered the species appropriately appears in our records before Calva (Calva), and placed in Dosiniopsis therebyextendingthe range the shape of the earliest typical Calva, C. (C.) he- ofDosiniopsis back into the Late Cretaceous. Na- liaca, which is probably of Cenomanian age, re- gao and Otatume (1963) placed Callista pseudo- semblesthat ofC. (E.) tafp ofSantonian age rather planaYabeandNagao, 1925,inAphrodina. Haya- than C. (£.) nitida of latest Albian-Cenomanian mi (1975,p. 145) questionablyrefered Dosiniopsis ageorC.(E.)byblidisofearlyAlbianage.NoCalva (?)cf.D.(?)caperata(Sowerby)ofYabeandNagao, s.s. species can be unequivocally derived from a 1925, from the Cape Khoi beds (Cenomanian-Tu- speciesofEgelicalva, butCalvaandEgelicalva are ronian) in the Aleksandrovsk area, Sakhalin Island, so similar in hinge structures and shape that they Russia, to Calva sp. In contrast, Trigonocallista are probably related. ornataIchikawaand Maeda, 1963, from the Izumi Whiteaves(1879,p. 150;1903,p.377)listedspec- Group(Campanian)inthe Hiketaarea,Tokushima imens that would now be assigned to Calva as Prefecture, Japan, has the striated nymph of a Cytherea Caryatis planaSowerbyorMeretrixni- ( ) Trigonocallista.OnlyspeciesfromthePacificSlope tida Gabb from several Nanaimo Basin [1-3] lo- can with certainty be assigned to Calva. calities. Unfortunately, not all ofhis specimens are ThegenusCalvapersistedalongthePacificSlope available.HislocalitiesincludedDepartureBay,near ofNorthAmericafromAlbianthroughMaastrich- Nanaimo, northwest side of Hornby Island, “214 tian but does not appear to have been common miles up the Nanaimo River,” Texada Island, and elsewhere. Figure2plotschronologicrangesofthe Sucia Island. Work of Muller and Jeletzky (1970), studied species. Calva has been recognized from Ward (1978), and Haggart (1989) suggests that Alaska south to the Vizcaino Peninsula [34], Baja Whiteaves’ localities on Sucia Island, Texada Is- California Sur, Mexico. Only a few Alaskan spec- land, “214 miles up the Nanaimo River,” and pos- imens, mainly from the Campanian Chignik For- sibly near Nanaimo are from the Cedar District mation west of Chignik Bay, have been studied. Formation; localities at Departure Bay and near Reports (Whiteaves, 1879, 1895, 1896, 1903) in- Nanaimo may have been from the Pender or Has- dicated that Calva is common in Late Cretaceous lamFormations,andtheNorthumberlandandSpray deposits of southern Vancouver Island [1-2], Brit- Formations are mapped on the northwest side of ishColumbia,butfewspecimensareavailable,and Hornby Island. The Cedar District Formation is Nanaimo Basin Calva are represented in this study consideredtobeofearlylateCampanianageHopli- mainly by Campanian, Hoplitoplacenticeras van- toplacenticeras vancouverense and Metaplacenti- couverense Zone, specimens from Sucia Island [3], ceras pacificum zones; Calva from this formation Washington.MostofthespecimensfromBajaCal- on Sucia Island are Calva Egelicalva bowersiana ifornia, Mexico, are from the Rosario Formation andCalva(Microcalva)hag(garti.Weh)avenotseen andare ofearly Maastrichtian age, buta fewspec- specimens from Departure Bay or near Nanaimo; imens from formations as old as Cenomanian are theagerangeoftheHaslamandPenderFormations available.Californiahasprovidedthe bulk ofspec- is late Santonian to early Campanian (Ward, 1978; imens and species over the most extensive time Haggart, 1989). In California, beds of late Santon- range and the best geographic distribution. How- ian age have yielded C. (£.) tafp, and beds of early ever, Albian and Cenomanian deposits are un- CampanianagehaveyieldedC. (£.) buttensis. Four knowninSouthernCalifornia,andthemoststudied small specimens from Hornby Island identified by Whiteaves as Meretrix nitida Gabb are similar to Calva Microcalva haggarti, new species (see the ( ) discussionunderthisspecies);Northumberlandand 8— — — lowerSprayFormationsareoflateCampanianage, Loma; PriceHollow;34 PuntaAbreojos;31 Pun- ta Baja; 29—Punta Banda; 17—Quinto Creek; 7—Ran- and the upper Spray is early Maastrichtian in age cheria Gulch; 8—Redding;4—Rock Creek; 17—Salado (Haggart, 1989). !I Cvorier—e;k2;23—0S—anSaRnafAanetlopnriiomidteilv—eMaarrea;;2186——SSaanntaLuAinsaReMstesr.-; eacFhigusrpeeci3esd.epCihcrtsontohleogkincowanndlagteiotgudrianpahlicranrganegeosf 2vi5de;S2a6nt——aSiMlovneiracdaoCMtasn.y;on2;62—4S—anStiimaigHo—i-lAllsi;s7o—CrSeisekkiydoiu- aorfetbhaeseNdatluarraglelyHiosntorsypeMciumseensuminotfheLocsollAencgteiloenss M1t2s.—; 22 Sisquoc R—iver; 13 Sites; 8—Stinking Creek; County,theUniversityofCalifornia,Berkeley,Mu- Tlceahyi;on5moSpPtesoSnonuinypnlseCuCelrr;aee;e1ek2k;—3;—'T32eW—xaaSVduraacminIacsSolpIarusnivldnae;gnrsd9;MIos2uTl0anentxdaa;Sisun3Sn;3pf,r2li6on3wg—4se;—rWh1VV3iaitlze-- sooffeutSmhcieoefUn.cPSea.sl,eGwoeinottloholgaoidgcdyai,ltaiSonundravltehyde,aCtMaaelinfflrooormniPaacroAlkcl,eacRdtoeiyomanyls | Canyon;26—WildcatCanyon;26—WilliamsCanyon;7 ProvincialMuseum,Victoria,BritishColumbia,and Young Ranch. Geological Survey of Canada, Ottawa, Ontario. Contributionsin Science, Number433 Saul and Popenoe: Pacific Slope Calva 5 Ma Magnetic AGE Calva Ammonites Polarity a 2 .JO 1 60- Polarity Reversal CHRON 1O 2 !c TO§g § 0) § PALEOCENE Uj CL mm 27 C27 Danian •a — 28 C28 t 29 C29 . 12 - I C30 nr\ 3 C31 to o Maastrichtian i o' I C32 cc ) oK S £ N .5 o C33 M Campanian .JO ° : i3fcoj I i* Santonian CRETACEOUS \ UJ, 9 S Coniacian m 90- Turonian ft £ N 6 uj i. Cenomanian \ :$ c C34 ^ LNUJ 100- Albian ! i OQ 110- Figure2. GeologicrangesofspeciesofCalvafromthePacificSlopeofNorthAmericaplottedagainstgeochronologic time scale, magnetic polarity (after Palmer, 1983), and selected ammonite ranges. 6 Contributions in Science,Number 433 Saul and Popenoe: Pacific Slope Calva E Figure 3. Latitudinal distribution of species of Calva and Egelicalva, based on range end points of Table 1. All occurrencesofC. (C.)regina,C. (C.)campanae,andC. (C.)baptisiaarewestoftheSanAndreasfault.Alloccurrences ofC. (£.)byblidis,C. ( .)spissa,C. (£.)taffi,andC. (£.)buttensisareeastoftheSanAndreasfault.Thenorthernmost occurrenceofC. (C.)heliaca,C. (C.)peninsularis, C. (£.) nitida,C. (£.)bowersiana,andC. (£.) crassais eastandthe southernmostoccurrencewestofthefault.Northernrangeendsarerounded-offnorthandplottedonthenextnorthern quarter degree; southern range ends are rounded-off south and plotted on the next southern quarter degree. Species known only from essentiallya single localityaregiven a latitudinal range ofone degree. Contributionsin Science,Number433 Saul and Popenoe: Pacific Slope Calva 7 Table 1. Range end points for Calva species. Northern end point Southern end point Calva (Calva) NW heliaca 36°N, McClure Ridge [20] 27°45'N, Vizcaino Peninsula[33]* regina 37°15'N, Quinto Creek [17] 28°N, Cedros Is. [31]* campanae 34°15'N, Simi Hills [24]* 26°45'N, Vizcaino Peninsula [34]* peninsularis 36°N, Coalinga [19] 29°30'N, Santa Catarina[31]* varians 38°N, Martinez [15] 35°45'N, Lake Nacimiento [21]* baptisia 35°45'N, Lake Nacimiento [21]* 34°30'N, Warm Springs Mtn. [23]* Calva (Egelicalva) byblidis 40°30'N, Texas Springs [9] 39°30'N, Sites, Colusa Co. [13] nitida 44°N, Suplee, Oregon [5] 38°N, Martinez [15] spissa 42°15'N,Jackson Co., Oregon [6] 36°N, Garza Peak [20] taffi 40°30'N, Redding [8] 37°15'N, Orestimba [17] buttensis 56°30'N, Chignik Bay, Alaska 39°50'N, Pentz [11] bowersiana 49°30'N, VancouverIs. [2] 33°30'N, Santa Ana Mts. [26]* crassa 37°N, Ortigalita Creek [18] 31°45'N, Punta Banda [29]* Calva (Microcalva) elderi 37°N, San Luis Reservoir[18] haggarti 49°30'N, Vancouver Is. [2] 48°45'N, Suicia Is. [3] Calva (Penecallista) marina 35°45'N, Pebblestone Shut-In [21]* 31°N, San Antonio del Mar[30]* *West ofthe San Andreas Fault. These compiled latitudinal ranges (Table 1) are fil- specimens were collected. The best documented teredthrough the usual deficienciesofthegeologic displacements are those of the San Andreas Fault — record incomplete sections, wrong ecotope pre- system,whicharerelativelynorthwardonthewest. served,andimperfectpreservationofspecimens,as Some species have their entire geographic occur- wellastectonictransport. Howeverwarped bythis rence eithereast orwest ofthis system, but others filter, the occurrences ofCalva (Calva) and Calva straddle it. Calva (C.) peninsularis, C. (Egelicalva) (Egelicalva) form a north-south pattern with spe- bowersiana,andC. (£.) crassaallhavetheirsouth- cies of Calva (Calva) displaying a more southerly ernmost occurrence to the west of this system, on distribution vis a vis contemporaneous species of the north moving block, and their northernmost thesubgenusEgelicalva.AvailableAlaskanandCa- occurrence east of the system. Their present ap- nadian collections surveyed suggest that many parent latitudinal range is less than their original northern occurrences are unreported. Both the distribution by the total displacement on the San northerly distribution of several species of Egeli- Andreassystem(approx.500-600km). Despitedis- calva and the southerly distribution of species of tributional offset due to terrane displacement, lat- Calva s.s. are likely to be extended by additional itudinal ranges of time equivalent species of the collecting. In general, specimens of Calva (Egeli- Calva s.s. group are to the south of the ranges of calva) sp. show more accentuated growth checks theCalva(Egelicalva)group.Anyterranedisplace- thandospecimensofCalva(Calva)sp.Asstrength mentsacrosstheSanAndreassystemappeartohave of growth checks may be encouraged by a more beenlessthantheoriginallatitudinalrangesofthese seasonal climatewith greatersummer-winterfood species. supply differential affectinggrowth potential, spec- Latitudinal ranges in the Cretaceous may have imens from higher latitudes might be expected to been broad, but the pattern of the Calva ranges exhibit stronger growth checks. argues for latitudinal restrictions not too unlike Actual latitudinal ranges have not only been ob- thoseofthepresentNorthAmericanPacificCoast. scured by deficiencies of the geologic record but Sliter (1968), dealing with foraminiferal faunas of have been additionally confounded by the un- earlyMaastrichtianage,postulatedfourmarinecli- known amount of terrane displacement between maticzonesremarkablysimilartothoseofthepres- various Calva-bearing outcrops of similar age. Pa- ent. The molluscan equivalent of his south-central leomagnetic data suggest a northward translation fauna includes such tropical forms as the rudist ofmanyoftheCretaceousdeposits(Fryetah,1985), bivalve Coralliochama but would be equated to a but the Figure 3 ranges are plotted at the present modernwarm temperateratherthanatropicalfau- geographic positions of the rocks from which the na. Although the subgenus Egelicalva is of more 8 Contributions in Science, Number 433 Saul and Popenoe: Pacific Slope Calva ) northern distribution, its range probably extended southintothenorthernpartofthewarmtemperate zone.Thesouthern distributionsofCalva [E.) taffi and C. (£.) buttensisareprobably truncated bythe lack of beds bearing Calva of early Senonian age south of Stanislaus Co. [17], California, and the northward distribution of C. (£.) crassa may also be more reflective of geologic preservation than original distribution. None of the faunas in which Calva is present appear to be truly tropical. But some, e.g., northern California Albian, Oregon Cenomanian, northern California Turonian, and southern California late Campanian, include a few generaoftropicalaspect,suggestingthatthesewere warmtemperatefaunas. Ifthe distributionsofCal- va [Calva) spp. and Calva [Egelicalva spp. are in parttemperature dependent, the ranges in Figure 3 suggestawarmTuronian followed byacoolerCo- niacianandSantonian.ThelateCampanianappears to have been slightly warmer than the early Cam- panian.Theearly Maastrichtianmayhave beenthe coolest interval, but it was followed by a consid- erable late Maastrichtian warming. FEATURES MEASURED In addition to the usual three measurements taken on bivalves, (1) valve height (H), measured perpen- dicular to the ligament, (2) valve length (L), mea- suredparalleltotheligament,and(3)valveinflation (tlIua),nnucfleoeufrlreoonmtghtehtrh(eLmLeb)ae;sa(uk3r)etlomuentnuhtleseawwnietdrerteihomr(aLdeWen):d;(((1B4)));dti(hs2e-) [[liPCceaanllevvcaaa)llpciersnatiasn)ssaumlwaairrtiihns,ac,aanrlddeifnlteaflvtavtleaveletvheaniltnaetbreeirloierodrvoaifnedCwamolefvaaCs[auElrgveead- angle made by drawing lines through lateral teeth features) indicated. H, height measured perpendicular to (LTA) All and PII or sockets for All and PII. The theligament;L,lengthmeasuredparalleltotheligament; number of specimens measured ranged from only I,inflationofasinglevalve; B, distancefromthe beak to 2 specimens of C. Microcalva elderi to 16 of C. theanteriorend; LL, length ofthe lunule; LW,width of [Egelicalva)taffiand( dependedu)ponavailablespec- the lunule; LTA, lateral tooth angle, the angle made by imens of sufficient completeness and the amount drawingalinethroughthesocketsforthelateralsAlland oftimerequiredtoremoveobscuringmatrix.Figure PPIIII iinn tthheerleifgthtvavlavlev.eMoeratshurroeumgehnttheLlTaAteruasletdeeatshaAnllalatenrd- 4 diagrams the features measured on specimens of native to beak angle, which is more difficult to measure Calva. Figure 5 compares ratios of these measure- consistently. ments and the angle through the lateral teeth. Al- though these measurements show specific differ- ences, they provide no directional trends in these lineages. are species of other subgenera of Calva and are comparable to Microcallista in size. Calva [Calva) CHANGES IN CALVA THROUGH TIME heliacaofCenomanianageandC.[E.)taffiofConi- acian-Santonian age are represented by smaller Most of the changes recognized between species specimens than are other species of their lineages. appear undirected within lineages. Even size does Only in the hinge do some developmental trends not increase regularly. The largest species, Calva appear. The anterior laterals become shorter and [Calva) peninsularis, C. [Egelicalva) crassa, and smoother, losing the striation of the early species. Calva (Penecallista) marina, are all ofearly Maas- Cardinal tooth 1 moves dorsally from its earlypo- trichtian age. Some specimens of Cenomanian age sition at the hinge plate edge with its dorsal end C. (£.) nitidaare largerthan any known specimens ventral to that of 3a, whereas in later species its ofTuronianage C. (£.) spissa, Coniacian-Santoni- dorsalendisinamorebeakwardpositionthanthat an age C. (£.) taffi, or early Campanian age C. (£.) of 3a, and its ventral end is no longer at the hinge buttensis some specimens of late Campanian C. plate edge. In C. (C.) heliaca cardinals 3a and 3b ; (£.)bowersianaapproachthesizeofC. (£.)crassa. are connected dorsally by a low arched ridge; in Late Maastrichtian Calva are of average size. Spe- later species this connection is broken as 1 moves cies of Microcalva are considerably smaller than into its more dorsal position. Contributionsin Science,Number 433 Saul and Popenoe: Pacific Slope Calva 9 SpeciesorCalva UH u\ US LL/LW groupedbysubgenus withinsubgenusin moreelongate moreinflated shorteranterior narrowerlunule stratig'-'phicorder 9 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 2.63.03.4 3, 1.82.02.2 2.42.6 2.8 i l l i I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I Calva(Catva)baptisia 1 varians Li peninsularis campanae 3 tF regina heliaca 3 Calva(Egelicalva)crassa zm m irn bowersiana buttensis m taffi m, spissa nitida byblidis Calva(Microcalva)haggarti elderi S3 Calva(Penecallista)marina Z3. Figure 5. Ratios of measurements made on specimens of 16 species of Calva. Measurements from Tables 2-17. Features measured are described and abbreviations decrypted in Figure 4. SUMMARY CSMB California State Mining Bureau GSC Geological Survey of Canada AlthoughforthepastcenturyVenusvariansGabb, LACMIP Natural History Museum of Los An- 1864, and Meretrix nitida Gabb, 1864, have ap- geles County, Invertebrate Paleontol- peared on faunal lists from the same locality, they ogy Section do not occurtogetherand are not ofthe sameage. SDSNH San Diego Society of Natural History These and 14 other species constitute the genus SDSU San Diego State University Calva, which is subdivided into four subgenera, SU (= LSJU) Stanford University (collec- two of which, Calva s.s. and Egelicalva, range tions now housed at the California through the Late Cretaceous of the Pacific Slope. Academy of Sciences, Golden Gate Species ofCalva are difficult to distinguish but can Park, San Francisco) be discriminated and are diagnostic of discrete UCMP UniversityofCalifornia, Berkeley, Mu- chronologic intervals. seum of Paleontology GeographicdistributionsofCalvas.s.andCalva UCLA University of California, Los Angeles m(Eogreleicnaolvrat)h,erwlyhidcihstrriebsuulttioni,n sEuggegleisctalvthaathatveirnrganea (HciosltloercytiMonussenuomwofhoLousseAdngeatlesNaCtouurna-l displacementwasnotequaltothelatitudinalranges ofCalva s.l. speciesand that climaticallytherewas USGS tUyn)itedStatesGeologicalSurvey,Wash- a Coniacian-Santonian cooling, a warming in the ington, D.C. late Campanian, and an early Maastrichtian cool- USGSM UnitedStatesGeologicalSurvey,Menlo ing, followed byawarmingthrough the lateMaas- Park, California trichtian. USNM United States National Museum Only the hinges of Calva display any evolving morphologic trends. The anterior lateral teeth be- SYSTEMATIC PALEONTOLOGY comeprogressivelysmoothersided,andthecentral cardinal tooth of the left valve moves into a more Phylum Mollusca Linnaeus, 1758 beakward position. Class Bivalvia Linnaeus, 1758 Order Veneroida H. and A. Adams, 1856 ABBREVIATIONS Family Veneridae Rafinesque, 1815 ANSP Academy of Natural Sciences of Phil- Genus Calva Popenoe, 1937 adelphia CAS California Academy ofSciences, Gold- TYPE SPECIES. By original designation Calva en Gate Park, San Francisco regina Popenoe, 1937,Turonian, Ladd Formation, CIT CaliforniaInstituteofTechnology(col- Holz Shale Member, Santa Ana Mountains, Cali- lectionsnowhousedatNaturalHistory fornia. Museum of Los Angeles County) DIAGNOSIS.Veneriformbivalveshavinggrowth 10 Contributions in Science, Number 433 Saul and Popenoe: Pacific Slope Calva
