Organised Phonology Data. Umbu-Ungu Language [UMB]. Tambul – Western Highlands & Southern Highlands Provinces PDF
Preview Organised Phonology Data. Umbu-Ungu Language [UMB]. Tambul – Western Highlands & Southern Highlands Provinces
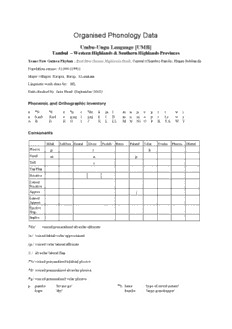
Organised Phonology Data Umbu-Ungu Language [UMB] Tambul – Western Highlands & Southern Highlands Provinces Trans New Guinea Phylum ; East New Guinea Highlands Stock; Central (Chimbu) Family; Hagen Subfamily Population census: 31,000 (1991) Major villages: Kiripia, Birop, LLaiakam Linguistic work done by: SIL Data checked by: June Head (September 2002) Phonemic and Orthographic Inventory b d e i dz k m n o p r t w j a b,mb d,nd e g,ng i j,nj k l ll m n ni o p r t,s w y A B D E G I J K L LL M N Ni O P R T,S W Y Consonants Bilab LabDen Dental Alveo Postalv Retro Palatal Velar Uvular Pharyn Glottal Plosive p t k Nasal m n Trill r Tap/Flap Fricative Lateral Fricative Approx j Lateral Approx Ejective Stop Implos /dz/ voiced prenasalized alveolar affricate /w/ voiced labial-velar approximant // voiced velar lateral affricate / / alveolar lateral flap /b/ voiced prenasalised bilabial plosive /d/ voiced prenasalised alveolar plosive // voiced prenasalised velar plosive p pambo 'let me go' b bana 'type of sweet potato' kapu 'dry' kumbe 'large grasshopper' Umbu-Ungu OPD Printed: September 7, 2004 Page 2 m mama 'uncle' llapo 'lizard sp.' kukume 'butterfly' wallo 'small' w k kapu 'dry' walo 'young animal' kokea 'rafter' owa 'dog' nolka 'he would eat' we 'just' ga 'sweet potato' t tawe 'laugh' kongi 'pig' ata 'father's sister' simu 'he gave' kusa 'salt' niembo 'let me speak' ltembo 'I will throw it' aminie 'your mother' olto 'we two' laporale 'wealth indicator' d dilie 'stick' akilio 'last born' anda 'old man' ltembo 'I will throw away' ulke 'house' lemenu `daughter’ n no 'water' nani 'you may eat' j ye 'man' yuyu 'he himself' r ruki 'type of sweet potato' karo 'car' dz jimi-jimi 'earthquake' unjo 'tree' Vowels i u e o i ingi 'strong' u ulke 'house' pulimo 'he goes' pumbe 'he will go' kondoli 'red' telu 'one' yapie 'red tangket' uwe 'ridgepole' e ele 'bow' o olto 'we two' lekemo 'he put (it)' kongi 'pig' lupe 'another' po 'sugar cane' pea 'that's all' porowe 'hawk' ama 'mother' ie piliendu 'I heard' kango 'boy' ilie 'smoke' pa 'you go!' kaime 'type of tree' io olionga 'yours' kalio 'chips of wood' Umbu-Ungu OPD Printed: September 7, 2004 Page 3 ei tei 'you (sg) do!' oi moime 'cockatoo' (No Penge subdialect) moloi 'you stay' (No Penge subdialect) e oleanga 'yesterday' welea 'quietly' ou ou 'before' koupu 'add' pou 'bird's wing' i kaime 'earwax' pai 'legendary type of dog' o kao 'cow' e kaembo 'type of sugar cane' u aulke 'path' larauwe 'slap' Waape 'a place name' gau 'solid, hard' paa 'very' /ie/ /io/ /ei/ e/ /i/ /e/ // /o/ /u/ /oi/ /ou/ (/ie/ /io/ /e/ occur only following /l/. Others are uncommon except /ou/ ) Suprasegmentals (tone, stress, length) Stress is phonemic. The stress is written only when the choice is not clear from the context, such as: kínie 'when' kinié 'today' ; púngi 'they went' pungí 'they will go' Syllable Patterns V o 'yes' o.li 'mud' wa.e.mbo.no 'dove' pe.a 'you sleep'' VV ou 'before' au.lke 'path' a.mbou.mu 'the old lady' CV ka 'vine' ta.we 'laugh' a.mi.ne 'your mother' pu.ni 'you will go' CVV lou 'axe' kai.me 'earwax' ta.lie.ka 'kind of bird' ka.lio 'chips' CCV lko.ndo 'home' au.lke.mo 'the path' u.lke 'house' CCVV olkou `wallaby’ Conventions: Phonological The consonant /k/ is voiced [] between vowels. The consonants /m/, /n/, and /s/ are palatalized between the vowels /i/ and /e/. /p/ tends to weaken to [ ] or [ ] in all positions /t/ has several allophones. The fricative [s] occurs contiguous to the high vowels [i] and [u], and [s] between the vowels [i] and [e]. The sound [s] also occurs in words songo 'tasty' and sekl 'dual'. The allophone [j] occurs in the environment like: walse [wlje] 'one day', alsu [lju] 'tree kangaroo'. // is a flapped, slightly retroflexed lateral / / has many allophones: [d] occurs before vowels /i/ and /e/, [] before back vowels [a], [o] and [u] and [l] preceding [t] and [k]. Umbu-Ungu OPD Printed: September 7, 2004 Page 4 Consonants /p/, /k/, /b/, //, /m/ and // are labialized between the vowels /u/ and /e/. Conventions: Orthographic /t/ is written both <t> and <s> depending how it sounds, [j] is written as < s >. /b/ is written word initially <b>, <mb> elsewhere /d/ is written word initially <d>, <nd> elsewhere // is written word initially <g>, <ng> elsewhere /nz/ is wirtten <j> word initially, <nj> elsewhere // is written <ll> or < LL >. // is now written <ni > at request of the people. Transcription of a recorded passage /j ou kuru torum jebo kuru torum koorii kume mee nbokrene obie jebo kume timudze nikim nibe wtikim jebo kuru torumu kooriime pe oio puum k nou n knorumuu n knoboie oio jebo koorii jebo kume noko nirii j dop uumuni md edeko nirii jebomo imuni nokomo kuru imuni nokomo k u n knorii pe ku ou ku knum nne i nikirum kidze i nikiru nu piienu nibu jebo p ee knumu ibu mku topo ie..../ <Ya. Ou kuru torumu. Yembo kuru torumu koloringi akume mele nambolkarene ombalie yembo akume lsimunje nikimu nimbe walsikimu. Yembo kuru torumu koloringime pe olio pulumu kanou naa kanorumulu. Naa kanopolie olionga yembo koloringime ou koloringi yembo akume nokou niringi yandopa ungumuni manda lendeko niringi. Yembomo imuni nokomo. Kuru imuni nokomo aku naa kanoringi. Pe aku ou aku kanumu nane i nikirumu. Kinie i nikiru nu pilienu nimbu yembo penge kanumu lipu maku topolie....> 'Now. Concerning sickness. He is asking concerning those people who became ill and died what thing it might have been that came and took those people. We have never understood the root cause of people getting sick and dying. Because we don't know, our people who died told us to look after those dead people so ever since then they followed that example. The person is being eaten (made ill / caused pain) by this. We were not aware that this spirit is eating him. I am telling you that that is what we used to think. Now I am telling and you are listening. We gathered together the (dead) people's skulls and...' Bibliography Head, June. 1990. 'Two verbal constructions in Kaugel' Language and Linguistics in Melanesia 21. Head, Robert, and June Head. 1973-1976. Manuscripts. SIL, Ukarumpa.
