Organic Chemistry PDF
Preview Organic Chemistry
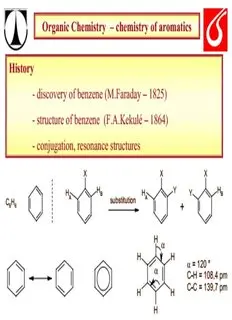
Organic Chemistry – chemistry of aromatics History - discovery of benzene (M.Faraday – 1825) - structure of benzene (F.A.Kekulé – 1864) - conjugation, resonance structures X X X H Y H H H Y B B A substitution A C H + 6 6 H (cid:68) H H α = 120 ° (cid:68) C-H = 108,4 pm C-C = 139,7 pm H H H Organic Chemistry – chemistry of aromatics Aromaticity H H = 6 x H H H H H Delocalisation of π – electrons - is it favourfable process ??? Organic Chemistry – chemistry of aromatics energy ΔH = h estimated delocalisation energy of benzene ΔH = h 410 kJ mol-1 ΔH = h 208 kJ mol-1 ΔH = ΔH = h h 96 kJ mol-1 120 kJ mol-1 Organic Chemistry – chemistry of aromatics Aromaticity „Hückel rule“ Aromatic compounds have to have - cyclic structure - conjugated systém of double bonds - 4n + 2 (n = 1,2,3,4….. Π – electrons - planar structure (shape) of aromatic part Organic Chemistry – chemistry of aromatics Aromaticity – π - orbital picture energy antibonding MO LUMO HOMO bonding MO benzene 1,3-cyclobutadiene Organic Chemistry – chemistry of aromatics Aromatic compounds [10]-annulene [18]-annulene naphthalene anthracene fenanthrene H H + Fe H H H H Organic Chemistry – chemistry of aromatics Heteroaromatic compounds N N N pyridine quinoline isoquinoline N N H N O S H H N N pyrrole furane thiophene porfyrine Organic Chemistry – chemistry of aromatics Aromatic compounds - reactivity OH OsO OsO 4 4 no reaction OH H RCO H RCO H 3 3 no reaction vs. O H Br Br /CCl Br /CCl 2 4 2 4 no reaction Br Organic Chemistry – chemistry of aromatics Aromatic compounds – reactivity – S aromatic E CH =O/HCl Br /FeBr 2 2 3 ClCH Br 2 halogenation chloromethylation SO /H SO HNO /H SO 3 2 4 3 2 4 HO S NO 3 nitration 2 sulfonation CH 3 (CH ) CCl/AlCl CH COCl /AlCl 3 3 3 3 3 3 H C C CO-CH 3 3 F-C alkylation F-C acylation CH 3 Organic Chemistry – chemistry of aromatics Aromatic compounds – retention of aromatic character Br addition H Br Br + Br-Br + Br substitution Br
