in Occupational Therapy Year I PDF
Preview in Occupational Therapy Year I
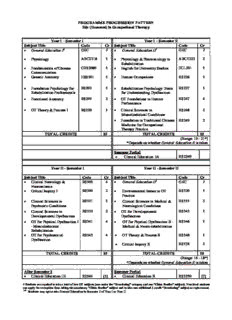
PROGRAMME PROGRESSION PATTERN BSc (Honours) in Occupational Therapy Year I – Semester I Year I – Semester II Subject Title Code Cr Subject Title Code Cr (cid:2) General Education I# GEC 2 (cid:2) General Education II1 GEC 2 (cid:2) Physiology ABCT218 3 (cid:2) Physiology & Pharmacology in ABCT222 2 Rehabilitation (cid:2) Fundamentals of Chinese CBS2080 3 (cid:2) English for University Studies ECL291 3 Communication (cid:2) Generic Anatomy HSS201 3 (cid:2) Human Occupations RS226 3 (cid:2) Foundation Psychology for RS202 3 (cid:2) Rehabilitation Psychology: Basis RS227 3 Rehabilitation Professionals for Understanding Dysfunction (cid:2) Functional Anatomy RS203 2 (cid:2) OT Foundations in Human RS247 4 Performance (cid:2) OT Theory & Process I RS220 3 (cid:2) Clinical Sciences in RS248 2 Musculoskeletal Conditions (cid:2) Foundation in Traditional Chinese RS249 2 Medicine for Occupational Therapy Practice TOTAL CREDITS 19 TOTAL CREDITS 19 (Range: 19– 21*) *Depends on whether General Education II is taken Summer Period (cid:2) Clinical Education IA RS2240 Year II - Semester I Year II - Semester II Subject Title Code Cr Subject Title Code Cr (cid:2) Clinical Neurology & RS303 4 (cid:2) General Education II2 GEC 2 Neuroscience (cid:2) Critical Inquiry I RS304 2 (cid:2) Environmental Issues in OT RS320 3 Practice (cid:2) Clinical Sciences in RS331 3 (cid:2) Clinical Sciences in Medical & RS333 2 Psychiatric Conditions Neurological Conditions (cid:2) Clinical Sciences in RS332 2 (cid:2) OT for Developmental RS343 3 Developmental Dysfunction Dysfunction (cid:2) OT for Physical Dysfunction I RS341 4 (cid:2) OT for Physical Dysfunction II - RS346 3 - Musculoskeletal Medical & Neuro-rehabilitation Rehabilitation (cid:2) OT for Psychosocial RS345 4 (cid:2) OT Theory & Process II RS348 3 Dysfunction (cid:2) Critical Inquiry II RS376 2 TOTAL CREDITS 19 TOTAL CREDITS 18 (Range: 16 –18*) *Depends on whether General Education II is taken After Semester 1 Summer Period (cid:2) Clinical Education 1B R2240 [3] (cid:2) Clinical Education II RS3250 [7] # Students are required to take a total of two GE subjects (one under the “Broadening” category and one “China Studies” subject). Non-local students can apply for exemption from taking the mandatory “China Studies” subject and to take one additional 2-credit “Broadening” subject as replacement. 1&2 Students may opt to take General Education in Semester 2 of Year I or Year II Table 1 (cont’d) Year III - Semester I / Block I Year III - Semester II / Block II (8 weeks) (8 weeks) Subject Title Code Cr Subject Title Code Cr (cid:2) Critical Inquiry III RS405 (cont.) (cid:2) Critical Inquiry III RS405 3 (Final Project) (Final Project) (cid:2) OT Management in Geriatric RS427 3 (cid:2) Health Care Management RS401 3 Practice (cid:2) Occupational Therapy in RS460 3 (cid:2) Professional Elective RS4xx (3*) Vocational Rehabilitation (cid:2) Professional Elective RS4xx (3*) (cid:2) Clinical Education IV RS4260 [7] (cid:2) Clinical Education III RS4250 [7] TOTAL CREDITS 13 TOTAL CREDITS 16 (Range: 13 – 16*) (Range: 13 – 16*) *Depends on the number of electives taken *Depends on the number of electives taken Professional Elective Subjects Note: 1. Students must select a minimum of 3 credits value of elective subjects in Year III. 2. According to the availability of staff and student’s preference, only limited number of occupational therapy specific electives will be run each year. Subject Title Code Cr Remarks (cid:2) Enabling Occupation in Home And Community Practice RS428 3 (cid:2) Occupational Therapy in the Management of Memory RS451 3 Deficits (cid:2) East-Meets-West in Stress Management RS452 3 (cid:2) Biological Psychology for Human Behavior RS455 3 (cid:2) OT in Primary Health Care RS456 3 (cid:2) Theories and Practices of Functional Capacity Evaluation RS457 3 (cid:2) Culturally Competent Practice in Health Care RS458 3 (cid:2) Clinical Practice in Stroke Rehabilitation RS459 3 BSc (Honours) in Occupational Therapy Academic subjects (90 credits) + Clinical Education (24 credits) Total 114 Subject Code ABCT218 Subject Title PHYSIOLOGY Credit Value 3 Level 2, Year 1 – Semester 1 Co-requisites HSS201 Generic Anatomy RS203 Functional Anatomy Objectives To explain and discuss the physiological controlling mechanisms in the human body which are essential to life. After successful completion of this subject, students should be able to appreciate the well-controlled and integrative nature of the operation of the different body systems. Subject Intended Upon completion of the subject, students will be able to: Learning Outcomes a. describe the structures and functions of body systems. b. discuss the interrelations of body systems. c. analyze the integrative nature of the body systems. d. demonstrate physiological measurements of some body systems. e. explain the organization and integration of body systems, organs, cells and organelles. Indicative Syllabus 1. Cell Physiology and Tissues (cid:3) Cell structure & function (cid:3) Organelles (cid:3) Cell membrane, diffusion, active transports (cid:3) Phase of cell cycle (cid:3) Classification of tissues (cid:3) General organization of human body in relation to organs and systems 2. Nervous System (cid:3) Classifications, structure and properties of neurons & synapses (action potentials, resting potentials, inhibition etc.), nerve transmission, reflex activity, muscle spindle basics (cid:3) Organization and functions of CNS/PNS/ANS (cid:3) Localization of brain function (cognition) (cid:3) Segmental circuits, stretch reflex, motor unit, neuromuscular junction, long pathways (cid:3) Nociception, perception of pain (basic) 3. Bone and Muscle (cid:3) Function of system, physiological role of key structures and cell types (cid:3) Normal function and adaptive processes (cid:3) Bone growth, regulation of blood calcium homeostasis & remodeling of bone (cid:3) Mechanism of muscle contraction, adaptation to shortening, lengthening, hypertrophy, atrophy, functions of muscle fiber types 4. Respiratory System (cid:3) Introduction to the respiratory system and exchange of gases (cid:3) Function of the pulmonary circulation (cid:3) Mechanisms of breathing, lung volumes, control of respiration, blood-gas transport 5. Cardiovascular System (cid:3) Introduction to circulatory system, control of cardiac functions, hemodynamics (cid:3) Cardiac action potential/cardiac cycle (cid:3) Basics of vascular structure & function (blood flow, pressure & resistance to flow etc.,) (cid:3) Relation to the control of body fluids 6. Gastrointestinal System (cid:3) Introduction to digestive system, digestion and absorption, regulation of digestive processes (cid:3) GI System and nutritional status (ingestion, absorption, transport, excretion, role in metabolism, dietary requirements and metabolic rate) (cid:3) Basics of nutrition, hunger and thirst mechanisms Teaching & Learning Lectures are conducted to provide students with the knowledge related to the basic Methodology features and operation of different body systems, and to discuss the integration of body systems in different physiological aspects. The lectures are also supplemented with some journal articles and newspaper clippings to provide the up-to-date knowledge related to the subject matters. Laboratory sessions are conducted to help students understand and reinforce the knowledge of selected physiological controlling mechanisms in human body that are essential to life. Laboratory reports are required to be submitted by all students after each experiment to demonstrate their analytical skills and understanding on the subject matters. Assessment Methods in Intended subject learning outcomes to be Specific assessment % Alignment with assessed methods/tasks weighting Intended Learning a b c d e Outcomes Tests 30 (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) Laboratory Reports 30 (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) Examination 40 (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) Total 100 % Students are required to pass the written examination to pass the subject as a whole. Tests It is used to assess students’ knowledge at the mid-term in the recall, comprehension and application aspects Laboratory Reports It is used to assess students’ analytical skills, team work, peer learning and critical thinking during the experiments and explanation of subject matters in a format of written report. Examination It is used as a summative assessment to examine students’ ability to recall, comprehend, analyze and apply the knowledge of physiology to the specific systems. Student Study Effort Class contact: (42 Hrs.) Expected (cid:3) Lecture 38 Hrs. (cid:3) Laboratory 4 Hrs. Other student study effort: (70 Hrs.) (cid:3) Pre-reading 20 Hrs. (cid:3) Preparation for tests and final exam 30 Hrs. (cid:3) Preparation for written assignment 20 Hrs. Total student study effort 112 Hrs. Reading List and Textbooks: References Fox, S.I. (2011). Human Physiology (12th ed). New York:McGraw-Hill Widmaier E.P., Raff H., Strang K.T. (2011) Vander's Human Physiology: The Mechanisms of Body Function with ARIS (12th ed). New York:McGraw-Hill Reading lists: Shier D.N., Butler J.L., Lewis R. (2010) Hole's Human Anatomy and Physiology (12th ed). New York:McGraw-Hill Martini, F. (2001). Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology (5th ed.). New Jersey: Prentice Hall. Rhodes, R., & Pflanzer, R. (2003). Human Physiology (4th ed.). Pacific Grove, Calif.: Thomsen Learning, Brooks/Cole. References: Fox, S.I. (2009). A Laboratory Guide to Human Physiology, Concepts and Clinical Applications (1st ed). New York:McGraw-Hill Fox, S.I. (2009). Laboratory Guide to accompany Human Physiology (13th ed). New York:McGraw-Hill Subject Code CBS2080 Subject Title FUNDAMENTALS OF CHINESE COMMUNICATION Credit Value 3 Level 2, Year 1 – Semester 1 Medium of Instruction Putonghua Pre-requisite / Students whose HKALE result of Chinese Language and Culture is at grade D or Co-requisite/ below are advised to complete / concurrently take non-credit bearing Chinese Exclusion Language Enhancement subject(s) as recommended. Objectives This subject aims to enhance and polish the communication skills of the students in both written Chinese and Putonghua for basic usage in the work-place. Intended Learning Upon completion of the subject, students will be able to: Outcomes (a) develop effective communication skills in both written Chinese and Putonghua required for basic usage in the work-place; (b) master the format, organization, language and style of expression of various genres of Chinese practical writing such as official correspondences, publicity materials, reports and proposals; (c) give formal presentation in Putonghua; (d) engage with formal discussion in Putonghua. Students will be required to read and write intensively for enhancing their proficiency level in written Chinese. They would be required to organize their own ideas, concepts in sensible and logical manner and present them in both written and spoken format for effective transmission of message in given contexts with specific purposes. Such learning activities would engage them in reasoning and analytical processes. The mastering of effective communication skills in both written Chinese and Putonghua will also facilitate their life-long learning in various disciplines. Subject Synopsis/ 1. Written Chinese for practical purposes Indicative Syllabus (cid:2) uses of words and sentences; (cid:2) coherence in Chinese writing (cid:2) format, organization, language and style of expression of official correspondences, publicity materials, reports and proposals; (cid:2) context dependent stylistic variation 2. Formal Presentation in Putonghua (cid:2) the articulation in Putonghua (cid:2) the flow of speaking (cid:2) choice of words, manner and gesture 3. Formal Discussion in Putonghua (cid:2) identification of main idea and key messages (cid:2) evaluation of relevancy of information in a message (cid:2) skills of seeking clarity/agree/disagreeing/answering to a question (cid:2) skills of summarizing Teaching/Learning The subject will be conducted in Putonghua, in highly interactive seminars. The Methodology subject will motivate the students’ active participation by assigning group presentation /discussion in class. In a forum-like format, students are guided to : (1) present to the class, their understanding of each genre designed for the syllabus for discussions and improvement; (2) modify passages in a given genre/style into other genres/styles for addressing different audiences and purposes; (3) give a power-point presentation in Putonghua in front of the whole class, then receive on spot feedback for discussion and improvement; then (4) prepare a written report/proposal on the same topic; and (5) engage in formal discussion in Putonghua on topics related to current issues and/or business operation; then (6) produce a written document on the same topic using a chosen genre. Assessment Methods in Alignment with Specific assessment % Intended subject learning outcomes to Intended Learning methods/tasks weighting be assessed Outcomes a b c d 1. Written 30% √ √ Assignment 2. Oral Presentation 30% √ √ 3. Final Examination 40% √ √ √ √ Total 100 % Both written assignments and oral presentation will focus on the functions of communication and the adequacy of language used in authentic social settings. The examination emphasizes the correctness of expression and students’ general competence in Chinese Language. Students obtaining a subject pass must pass both components, i.e. the continuous assessment and examination of the subject. Students will get failure of the subject if he/she fails in either one of the two components. Student Study Effort Class contact: (42 Hrs.) Expected (cid:3) Seminar 42 Hrs. Other student study effort: (84 Hrs.) (cid:3) Outside class practice 3 x 14 = 42 Hrs. (cid:3) Self-study 3 x 14 = 42 Hrs. Total student study effort 126 Hrs. Reading List and (cid:17439)(cid:5607)(cid:6054)(cid:1131)(cid:13336)(1982) (cid:457)(cid:4635)(cid:1420)(cid:7049)(cid:12347)(cid:458)(cid:712)(cid:14879)(cid:7585)(cid:5211)(cid:12788)(cid:3927)(cid:4520)(cid:2090)(cid:10360)(cid:12142)(cid:452) Reference (cid:18149)(cid:4536)(cid:13785)(cid:708)1991(cid:709)(cid:457)(cid:9540)(cid:16715)(cid:1944)(cid:7464)(cid:458)(cid:712)(cid:2617)(cid:7623)(cid:1258)(cid:8769)(cid:2090)(cid:10360)(cid:12142)(cid:452) (cid:19619)(cid:5418)(cid:8769)(cid:708)1994(cid:709)(cid:457)(cid:16602)(cid:16545)(cid:11444)(cid:15373)(cid:16003)(cid:458)(cid:712)(cid:16590)(cid:7095)(cid:2090)(cid:10360)(cid:12142)(cid:452) (cid:7550)(cid:17661)(cid:14879)(cid:708)1996(cid:709)(cid:457)(cid:2579)(cid:6269)(cid:4520)(cid:458)(cid:712)(cid:14879)(cid:1117)(cid:10806)(cid:5141)(cid:3927)(cid:4520)(cid:2090)(cid:10360)(cid:12142)(cid:452) (cid:19619)(cid:10894)(cid:12575)(cid:14983)(cid:708)2000(cid:709)(cid:457)(cid:11087)(cid:9067)(cid:18783)(cid:2133)(cid:4487)(cid:458)(cid:712)(cid:1117)(cid:14879)(cid:7464)(cid:4720)(cid:452) (cid:18130)(cid:12223)(cid:13785)(cid:451)(cid:8858)(cid:3387)(cid:2317)(cid:1131)(cid:13336)(cid:708)2003(cid:709)(cid:457)(cid:10798)(cid:1299)(cid:9554)(cid:16590)(cid:458)(cid:712)(cid:14879)(cid:1117)(cid:5211)(cid:12788)(cid:3927)(cid:4520)(cid:2090)(cid:10360)(cid:12142)(cid:452) (cid:1214)(cid:6208)(cid:21012)(cid:1131)(cid:13336)(cid:708)2003(cid:709)(cid:457)(cid:10798)(cid:1299)(cid:6137)(cid:11096)(cid:7095)(cid:458)(cid:712)(cid:5593)(cid:7190)(cid:3927)(cid:4520)(cid:2090)(cid:10360)(cid:12142)(cid:452) (cid:18862)(cid:7095)(cid:1443)(cid:708)2004(cid:709)(cid:457)(cid:9554)(cid:16590)(cid:2579)(cid:6269)(cid:4520)(cid:458)(cid:712)(cid:16303)(cid:2439)(cid:5211)(cid:12788)(cid:3927)(cid:4520)(cid:2090)(cid:10360)(cid:12142)(cid:452) (cid:7550)(cid:11437)(cid:3637)(cid:451)(cid:1073)(cid:17946)(cid:15049)(cid:708)2004(cid:709)(cid:457)(cid:3927)(cid:4520)(cid:20740)(cid:3515)(cid:4635)(cid:1420)(cid:16451)(cid:13348)(cid:16319)(cid:12347)(cid:458)(cid:712)(cid:1082)(cid:9127)(cid:3927)(cid:4520)(cid:2090)(cid:10360)(cid:12142)(cid:452) (cid:1214)(cid:6208)(cid:21012)(cid:739)(cid:19619)(cid:10894)(cid:12575)(cid:451)(cid:18830)(cid:12830)(cid:7592)(cid:739)(cid:18433)(cid:6495)(cid:18134)(cid:1131)(cid:13336)(cid:708)2011(cid:709)(cid:457)(cid:11174)(cid:1299)(cid:6137)(cid:11096)(cid:7095)(cid:4635)(cid:1420)(cid:16319)(cid:12788)(cid:2578)(cid:7464)(cid:458)(cid:712) (cid:5593)(cid:7190)(cid:3927)(cid:4520)(cid:2090)(cid:10360)(cid:12142)(cid:452) Subject Code HSS201 Subject Title GENERIC ANATOMY Credit Value 3 Level 2, Year 1 – Semester 1 Pre-requisite / Co-requisite/ Nil Exclusion Objectives By completing this subject using a systemic and regional approach in teaching and learning, the students will be able to demonstrate a basic understanding of the structure and function of the human body. Intended Learning Upon completion of the subject, students will be able to: Outcomes a. recognize anatomical terminology of the human body b. identify and locate relevant anatomical structures c. explain functions of anatomical structures d. demonstrate a basic understanding of tissue organization within the human body e. understand the spatial relationship of the systems of the body relative to regional anatomy f. integrate systemic, regional and imaging anatomy Subject Synopsis/ 1. Foundation lecture series in systemic anatomy Indicative Syllabus (cid:2) Introduction to the human (cid:2) Respiratory system body and anatomical (cid:2) Lymphatic system terminology (cid:2) Digestive system (cid:2) Skeletal system (cid:2) Renal (Urinary) system (cid:2) Muscular system (cid:2) Endocrine system (cid:2) Nervous system (cid:2) Reproductive system (cid:2) Special senses (cid:2) Cardiovascular system 2. Foundation lecture series in regional anatomy (cid:2) Upper and lower limbs (cid:2) Thorax (cid:2) Head and neck (cid:2) Abdomen and pelvis 3. Practical and tutorial sessions to integrate systemic and regional anatomy 4. Introduction to normal imaging anatomy Teaching/Learning Lectures will be delivered by introducing the students to systemic anatomy first. Methodology This will then be followed by integration with regional anatomy ensuring the students understand the spatial relationship of the systems of the body relative to regional anatomy. Students will be introduced to an appropriate level of anatomical terminology to provide the basic knowledge for identification of human body structures. Students are encouraged to do some independent study in the form of pre-reading of selected topics prior to attending the lectures. Areas of difficulty will be addressed in the forthcoming lectures. A range of imaging modalities and clinical cases is used to support the lecture contents. Tutorials are used to supplement lectures and may include online activities, face to face tutorials and the use of interactive multimedia. The study of the human body will be reinforced via the use of dissected and museum specimens in the laboratory. Students will be introduced to medical terminology with appropriate emphasis on surface anatomy and diagnostic imaging modalities. Face to face tutorials further check students’ knowledge and understanding. Assessment Methods in Alignment with Intended subject learning outcomes Specific assessment % Intended Learning to be assessed methods/tasks weighting Outcomes a b c d e f Continuous Assessment 50 (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) Examination 50 (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) (cid:4) Total 100% Note: Pass in both continuous assessment and examination is compulsory to pass the subject as a whole. Continuous Assessment Online activities or in-class quizzes will be used to assess students’ ability to: (cid:2) recognize anatomical terms (cid:2) identify and label anatomical structures (cid:2) understand spatial relationships (cid:2) integrate systemic and regional anatomy (cid:2) explain functions of anatomical structures Mid-term test will be checking all of the items listed above using multiple choice questions. Examination This will consist of multiple choice questions and short questions both of which will be assessing all of the intended learning outcomes for the subject and specifically will be checking their understanding of the integration of regional and systemic anatomy. Student Study Effort Class contact: (42 Hrs.) Expected (cid:3) Lecture 28 Hrs. (cid:3) Practical / Tutorial 14 Hrs. Other student study effort: (90 Hrs.) (cid:3) Independent study and online activities 30 Hrs. (cid:3) Preparation for mid-term test and final examination 60 Hrs. Total student study effort 132 Hrs. Reading List and Text book: References Saladin, K.S. (2010) Human Anatomy, 3rd edition. Singapore: McGraw Hill Inc. Reading list: Anatomy & Physiology Revealed (APR) Version 2.0, 2008, An Interactive Cadaver Dissection Experience,CD-ROM, McGraw -Hill. Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR (2010) Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Abrahams, P.H., Hutchings, R.T., Marks, Jr S.C., (2008) McMinn's Colour Alas of Human Anatomy. 5th ed. Mosby Elsevier. Gosling, J.A., Harris, P.F., Humpherson, J.R., Whitmore, I., Willan P.L.T. (2008) Human Anatomy color atlas and text 5th ed. New York: Mosby. Subject Code RS202 Subject Title FOUNDATION PSYCHOLOGY FOR REHABILITATION PROFESSIONALS Credit Value 3 Level 2, Year 1 – Semester 1 Pre-requisite / Nil Co-requisite/ Exclusion Objectives By completing this subject, the students will be able to demonstrate a basic understanding of the psychological theories and functions relevant to professionals in the field of rehabilitation Intended Learning Upon completion of the subject, students will be able to: Outcomes a. understand basic theories and principles in psychology b. apply psychological theories to: (cid:2) understanding of self and individual differences (cid:2) explaining common behaviours of people and patients c. apply basic psychological principles to selected practices in rehabilitation Subject Synopsis/ Key Theories for Understanding Human Behaviour Indicative Syllabus Humanistic, psychoanalytic, behavioral, and cognitive schools of psychology Developmental Psychology Cognitive, psychosocial and personality aspects of development from infancy to ageing Personality Theories, definition and assessment of personality Theories of Learning Acquisition and maintenance of human behaviour Intelligence Definitions, assessments and critical review of IQ tests and their use and misuse in education and in health care practice Psychometric Assessment Different approaches to the assessment of achievement, ability, occupational skills, preference, personality and emotions; validity and reliability of tests Perception Definitions, process and its relevance to rehabilitation Cognition Structure of memory, chunking, coding, elaborate rehearsal, interference, long-term memory, physiological theories of memory, attention and concentration Motivation and Emotion Hunger and eating, sexual motivation and behavior, affiliation, and achievement; theories of emotion Social Psychology Person perception, attribution processes, attitude. close relationships, conformity and obedience; group behavior
Description: