Human Body Minipedia PDF
Preview Human Body Minipedia
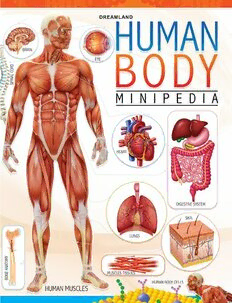
The human body is an amazing living machine and its study is truly a fascinating subject. Inside your body there are millions of parts working together to keep you healthy and active. The present book – Human Body Minipedia is a concise coverage of how our bodies are built and how they work. Equipped with clear-cut images to illustrate the text, this book is a head- to-toe survey of the body that children would enjoy reading. our oTher TiTLeS ISBN 978-93-5089-526-9 DREAMLAND PUBLICATIONS J-128, Kirti Nagar, New Delhi -110 015, India Tel : +91-11-2510 6050, 2543 5657 E-mail : [email protected] Shop online at www.dreamlandpublications.com Like us on www.facebook.com/DreamlandPublications ` 180 DREAMLAND PUBLICATIONS J-128, KIRTI NAGAR, NEW DELHI - 110 015, INDIA Ph. : +91-11-2510 6050, 2543 5657 E-mail : [email protected] Shop online at www.dreamlandpublications.com Like us on www.facebook.com/DreamlandPublications the hUmAN BoDY the human body is a unique machine made up of lots of different parts – all working together to keep us alive and well. We probably know the names of the bits we can see, but there are many more hidden deep inside us. BrA iN Liver heArt StomAch LUNgS SmALL iNte StiNe KiDNe YS LArge iNteStiNe BLADDer BoNe S 2 BrAiN StomAch Liver the control centre An organ in the the largest organ of the body’s upper part of the in the human body. nervous system. abdomen. it is it is a gland which the brain controls an enlarged and lies on the top every activity of muscular pouch- right-hand side the body, such as shaped organ of the of the abdomen, moving the muscles, alimentary canal. the under the ribs. it and breathing. this stomach churns the helps to digest food is where we see, food and mixes it in and keep the blood hear, think and very strong acids clean. dream. that partly digest it. SmALL iNteStiNe LArge iNteStiNe A long wiggly tube where A long tube-liked organ that is connected to the small mushy food enters. it is intestine at one end and the anus at the other. it has the section our digestive four parts: cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. Partly tract where the majority of digested food moves through the cecum into the colon, food digestion and nutrient where water nutrients and electrolytes are removed. absorption takes place. heArt LUNgS BoNeS An organ made of A pair of organs used Bones are the muscle. it is about for respiration. the hard, still substance the size of clenhced lungs lie either side of that make up the fist and lies between the heart in the cavity of body’s framework, the lungs. it pumps the chest, or thorax. the or skeleton. they blood around the lungs take in air when support the body body through blood we breathe, providing and protect the vessels. essential oxygen to our delicate inner body. organs. An adult human has 206 long and short KiDNeY BLADDer bones. two bean-shaped A triangle-shaped, sac- eloxccarteetdo rayt othrgea rnesa r liink eth heo llolowwe ro ragbadno mloecnat. ed Did you Know? of the abdoiminal Liquid waste, called cavity. they filter the urine, is produced by A baby is born with blood and keep it the kidney and stored around 300 bones, clean. the kidneys in the bladder. When some bones fuse filter wastes from the bladder is full, it the blood and pushes the urine out of together as the excrete them and the body through a tube baby grows. water in urine. called the urethra. 3 BUiLDiNg BLocKS the cell is the basic structural and functional unit of human body. every part of our body is made of tiny building blocks called cells, which fit together like bricks in a wall. the human body contains more than 200 types of cells that do different jobs. they provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialised functions. nucleus NUcLeAr eNveLoPe roUgh eNDoPLASmic reticULUm NUcLeoLUS chromAtiN NUcLeAr Pore riBoSomeS riBoSomeS Smooth PeroxiSome eNDoPLASmic reticULUm PLASmA golgi memBrANe apparatus mitochoNDrioN SecretioN from the ceLL SecretorY LYSoSome veSicLe cYtoPLASm ceNtrioLeS microtUBULe Did you Know? More than 2,000 dead skin cells fell off you as you read this sentence. 4 tYPe S of ceLLS cells are classified based upon their structural and functional properties. Depending upon the tissues they form, cells are categorised into the following – ePitheLiAL ceLLS ADiPoSe ceLLS Simple cells that form the cells that store fat the covering surface of and reduce friction to all organs. example: skin the body. example: soles, cells, mucous cells. palms, buttock, etc. SecretorY ceLLS BLooD ceLLS they form gland and these are cells are secretory in nature. that are present example: pancreatic cells in blood, like rBc secrete insulin; salivary and WBc. gland cells secrete salivary amylase, etc. BoNe ceLLS Nerve ceLLS they are the toughest they are very long and body cells and are have branching end. present in bones. mUScLe ceLLS these are long cells with the ability to contract and relax, proving for movements of attached structures (mostly bones). 5 SYStemS of the hUmAN BoDY the human body has various groups of organs, called systems, which individually perform their roles so that the body can function as a whole. Some organs work independently while some work in groups. circULAtorY NervoUS reSPirAtorY DigeStive SKeLetAL mUScULAr SYStem SYStem SYStem SYStem SYStem SYStem SKeLetAL SYStem mUScULAr SYStem it involves the bones, joints, ligaments muscles provide mobility to the different parts of and cartilage, all of which keep the body the body. in shape and enable it to move. reSPirAtorY SYStem NervoUS SYStem it involves the nose, trachea, lungs and bronchi. it consists of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. cArDiovAScULAr or circULAtorY SYStem it consists of the heart, arteries and veins. the DigeStive SYStem heart receives deoxygenated blood from all parts of this system, which processes food, the body and sends it to the lungs. it also receives involves the mouth, esophagus, stomach, oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the liver and intestines. rest of the body. Arteries carry blood from the heart. veins carry blood to the heart. 6 iNtegUme NtArY SYS tem it consists of the skin, hair and nails. LYmPhA tic AND immUNe SYS tem it includes the lymph nodes and vessels, thymus, spleen, bone marrow, lymphoid tissues and many types of protein. eNDocriNe SYS tem the system includes pituitary gland, pineal gland, hypothalamus, ovaries, testes and thyroid gland. reProDUctive SYS tem it consists of the male and female sex organs. UriNArY SYS tem it involves the formation and voidance of urine – the liquid waste. the parts of this system are the kidneys, urinary bladder, urethra and ureters. 7 the mUScULoSKeLetAL SYStem the musculoskeletal system is made up of bones, joints, tendons, ligaments and skeletal muscles that are attached to the bones. muscle tissue is also found inside of heart, digestive organs, and blood vessels. in these organs, muscles serve to move substances throughout the body. the hUmAN SKeLetoN the human skeleton is a framework of over 200 bones with marrow inside them. the skeleton’s bones protect the softer and sensitive body-parts and act as anchors for the muscles and as levers for their movement. 8 riB cAge the rib-cage has 12 pairs of ribs. it is a box around the lungs. it changes its shape to allow the lungs to expand and contract while breathing. SKULL the human skull contains 22 bones. it protects the all-important brain and supports the other soft tissues of the head. the SKeLetoN’S APPeNDeD PArt the skeleton’s appended part includes bones of the arms and legs along with their supports – shoulder girdle and hip girdle. 9
