Table Of ContentBiostatistics(2004),5,2,pp.177–191
PrintedinGreatBritain
Generalized additive models for cancer mapping
with incomplete covariates
JONATHANL.FRENCH†
Biostatistics,GlobalResearchandDevelopment,Pfizer,Inc.,50PequotAvenue,NewLondon,
CT,06320,USA,
Jonathan L [email protected]fizer.com
MATTHEWP.WAND
HarvardSchoolofPublicHealth,Boston,USA
SUMMARY
Maps depicting cancer incidence rates have become useful tools in public health research, giving
valuable information about the spatial variation in rates of disease. Typically, these maps are generated
usingcountdataaggregatedoverareassuchascountiesorcensusblocks.However,withtheproliferation
of geographic information systems and related databases, it is becoming easier to obtain exact spatial
locationsforthecancercasesandsuitablecontrolsubjects.Theuseofsuchpointdataallowsustoadjust
for individual-level covariates, such as age and smoking status, when estimating the spatial variation
in disease risk. Unfortunately, such covariate information is often subject to missingness. We propose
a method for mapping cancer risk when covariates are not completely observed. We model these data
using a logistic generalized additive model. Estimates of the linear and non-linear effects are obtained
using a mixed effects model representation. We develop an EM algorithm to account for missing data
andtherandomeffects.Sincetheexpectationstepinvolvesanintractableintegral,weestimatetheE-step
withaLaplaceapproximation.Thisframeworkprovidesageneralmethodforhandlingmissingcovariate
valueswhenfittinggeneralizedadditivemodels.Weillustrateourmethodthroughananalysisofcancer
incidencedatafromCapeCod,Massachusetts.Theseanalysesdemonstratethatstandardcomplete-case
methodscanyieldbiasedestimatesofthespatialvariationofcancerrisk.
Keywords:Binaryresponse;ExpectationMaximization;Generalizedlinearmodel;Laplaceapproximation;Logistic
regression;Methodofweights;Missingdata.
1. INTRODUCTION
Geographicalinformationsystemsarebecomingwidelyusedinenvironmentalhealthandepidemiol-
ogy.Correspondingly,investigatorswouldliketoproducesummarymapsoftheirdata.Forexample,in
thecontextofenvironmentalepidemiology,wemightbeinterestedinamapofrelativecancerincidence
ratesorcancerrisk.Manystudies,however,areunabletocollectcompletecovariateinformationforeach
subject.Thesevaluesmaybeeithermissingbydesign(e.g.whensomedataarecollectedononlyasubset
ofsubjects)ormissingunintentionally.Inthispaperweproposeamethodtoestimatemapsofcovariate
adjustedrelativecancerriskinthepresenceofincompletecovariatedata.
†Towhomcorrespondenceshouldbeaddressed.
BiostatisticsVol.5No.2(cid:1)c OxfordUniversityPress2004;allrightsreserved.
178 J.L.FRENCHANDM.P.WAND
ThisworkwasmotivatedbyastudyofcancerincidenceonCapeCod,Massachusetts,USA.Fornearly
twenty years the Massachusetts Department of Public Health (MDPH) has maintained a cancer registry
databasewhichrecordsincidentcasesfor22typesofcancers,includinglung,breast,andprostatecancers.
Thereportsummarizingthesedatafortheperiod1982–92showedelevatedstandardizedincidenceratios
for several types of cancer in the towns of Barnstable, Falmouth, Sandwich, Bourne, and Mashpee
(MassachusettsDepartmentofPublicHealth,1997).Collectively,thesetownscomprisearegionknown
as Upper Cape Cod. Prostate cancer in men was of particular concern since it appeared to be the most
elevated.TheMDPHwasinterestedindeterminingiftheelevatedcancerrateswereduetoenvironmental
factors, including contaminants at several sites on the Massachusetts Military Reservation (MMR) that
havebeenlistedontheUSEnvironmentalProtectionAgency’sNationalPriorityList.Thesesitesareof
significantinterestbecausetheMMRissituatedabovethesole-sourceaquiferfortheUpperCape.
Inadditiontothetypeofcancer,theregistrymaintainsdataonthepatient’sresidenceandageatthe
timeofdiagnosis,aswellasgenderandsmokingstatus.Thedataareroutinelysummarizedbygenderat
thetownlevel,butraw,geo-codedresidencelocationshavebeencollectedforthisstudy.Assumingthat
adverseenvironmentaleffectsarelikelytocauseonlycertaintypesofcancer,thisenablesustoovercome
the problem of adjusting for population density which is inherent in calculating standardized incidence
ratios.Suchdataareavailableonlyatthecensustractlevelwhichismuchcoarserthanthecancerdata.
This type of analysis also allows us to adjust for individual level covariates such as age and smoking
status.
In this paper we analyze data for incidence of prostate cancer on Upper Cape Cod. Data have been
compiled for n = 3191 men diagnosed with one of the 22 types of cancer during the period 1987–
94. While age and location data were collected for all patients, smoking status was not obtained for
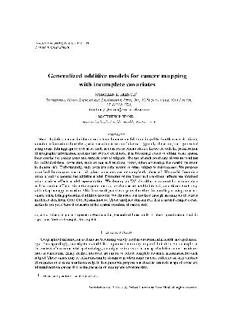
approximately29%ofthemen.Theupper-leftpanelofFigure1displaystheapproximatelocationsofthe
residencesofthepatients.Forconfidentialityreasons,thepointshavebeenjittered.Thesolidandempty
dotscorrespondtoprostatecancerandothercancercases,respectively.Thelinescorrespondtothecensus
tractboundaries.Weseethatthereareseveralareaswithahighdensityofcancercases;thesecorrespond
tothepopulationcentersontheUpperCapeandarenotnecessarilyassociatedwithanysortofexposures.
By using relative cancer mapping, we assume that all cancer cases provide a reasonable surrogate for
populationdensityacrosstheregion.Potentialdifficultieswithrelativecancermappingarediscussedin
Section4.
Table 1 displays summary statistics for age and smoking status classified by cancer type. Age is a
categoricalvariablewithcategoriesdefinedbyagedecade(i.e.age=1foragesbetween1and10years,
age=2for11–20years,etc.).Smokingstatushastwocategories:ever-smokers(smoke=1)andnever-
smokers(smoke=0).Ofthecohortof3191men,998(31.3%)wereprostatecancerpatients.Weseethat
prostatecancerpatientsarelesslikelytobesmokersthanarepatientswithothertypesofcancer.Thisis
partiallyexplainedbytherelativelylargenumberoflungcancerpatients,mostofwhichweresmokers.
Wealsoseethatthepatternofmissingdatadependsoncancertype.Smokingstatusismissingfor41.0%
oftheprostatecancerpatients,while24.2%oftheothercancerpatientsdidnotprovideinformationabout
smokingstatus.Thus,thesedataareclearlynotmissingcompletely-at-randominthesenseofLittleand
Rubin(1987).
Fittingmapsofrelativecancerrisk,andbivariatesurfacesingeneral,canbeaccomplishedinanumber
ofways.Themostcommonlyusedmethodsarekriging(e.g.Cressie,1993)andthinplatesplines(Wahba,
1990).Theextensionofkrigingtodiscreteresponsedataisnotstraightforward.Methodstoaccomplish
this,suchasindicatorkriging,havebeendeveloped,butaresomewhatadhoc.Diggleetal.(1998)have
recentlyproposedanattractivemethodforhandlingsuchdatausingMarkovchainMonteCarlomethods.
Wetakeadifferentapproach,usinggeneralizedadditivemodelswithamixedmodelrepresentation.
Generalizedadditivemodels(e.g.HastieandTibshirani,1990)provideaflexiblemeansofhandling
non-linear covariate effects. These models have gained widespread popularity in a diverse set of
Generalizedadditivemodelsforcancermappingwithincompletecovariates 179
41.80 41.80
41.75 41.75
degrees latitude 41.6541.70 Latitude 41.6541.70
41.60 41.60 Odds Ratio (relative to geometric mean)
41.55 porthoestra ctea nccaenrcer 41.55 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4
-70.6 -70.5 -70.4 -70.3 -70.6 -70.5 -70.4 -70.3
degrees longitude Longitude
41.80
41.75 1.0
41.70 0.8 MCoemthpolde toef CWaesieghts
Latitude 41.65 Odds Ratio 0.6
41.60 Odds Ratio (relative to geometric mean) 0.4
41.55 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 0.2
0.0
-70.6 -70.5 -70.4 -70.3 2 4 6 8 10
Longitude
age decade
Fig.1. UpperCapeCodcancerdata.Upper-leftpanel:Rawdata.Forconfidentialityreasons,thepointshavebeen
jittered. Upper-right: Complete-case estimate of the odds ratio as a function of geography. Lower-left: Method of
weightsestimateoftheoddsratioasafunctionofgeography.Lower-right:Estimatesoftheoddsratioforagerelative
totheaverageageinthecohort.
Table1.Summarystatisticsforageandsmokingstatus,classifiedbycancer
typefortheUpperCapeCoddata
Prostatecancer Othercancers
nobs mean sd nmiss(%) nobs mean sd nmiss(%)
smoke 588 0.56 0.50 410(41.0) 1663 0.75 0.44 530(24.2)
age 998 8.25 0.91 0(0.0) 2193 7.76 1.39 0(0.0)
disciplinesincludingenvironmentalepidemiology,environmentalscience,ecology,publichealth,political
science,andeconomics(e.g.LintonandHa¨rdle,1996;Schwartz,1997;BeckandJackman,1998;Davis
and Speckman, 1999; Engels et al., 1999; Roland et al., 2000). Recently, Kammann and Wand (2003)
showed how kriging could be incorporated into a generalized additive model, with representation as a
generalizedlinearmixedmodel.Becausemixedmodelscanbefitusingmaximumlikelihood,thisallows
ustouselikelihood-basedmethodsforestimationandhandlingofmissingdata.Wedevelopamethodfor
handling missing covariate values in generalized additive models using the EM algorithm (Dempster et
180 J.L.FRENCHANDM.P.WAND
al.,1977).FormodelsotherthantheGaussianresponse,theE-stepinvolvesanintractableintegral.Asin
Steele(1996)weuseLaplace’smethod(Tierneyetal.,1989)toapproximatethisexpectation.
Section 2 introduces the generalized additive model, estimation of penalized regression splines via
a mixed effects model, and methods for estimation in generalized linear mixed effects models with
complete data. Section 3 develops an algorithm for estimation of generalized additive models in which
some covariates exhibit missingness. In Section 4, we analyze the Cape Cod cancer data. We conclude
with a brief discussion in Section 5. Additional computational details are provided in an appendix on
BiostatisticsOnline.
2. MAPPINGCANCERRISKUSINGGENERALIZEDADDITIVEMODELS
Suppose first that the data are (x ,y ), 1 (cid:1) i (cid:1) n, where the y are binary and x ∈ R2 represents
i i i i
geographical location. To assess spatial variation in data of this type, Diggle et al. (1998) propose the
kriging-typemodel
logit{P(y =1|S(x ))}=β +βTx +S(x ), (2.1)
i i 0 1 i i
where{S(x):x∈R2}isastationaryzero-meanstochasticprocess.
The right-hand side of (2.1) is the logarithm of the odds for the event {y = 1}, given x , which we
i i
denotebyLO(x ).ItisoftenusefultomapanestimateofLO(x )overameshofx ∈ R2 values.This
i 0 0
involvesthebivariatefunction
L(cid:1)O(x )=βˆ +βˆTx +Sˆ(x ), (2.2)
0 0 1 0 0
whereβˆ andβˆ aremaximumlikelihoodestimatesand
0 1
Sˆ(x )= E{S(x )|y}
0 0
isan‘optimal’predictorofS(x ).
0
To make (2.2) practical we require a parsimonious model for the inter-point covariances
cov{S(x),S(x(cid:3))},x,x(cid:3) ∈R2.Weproposetousetheisotropicmodel
cov{S(x),S(x(cid:3))}=C ((cid:4)x−x(cid:3)(cid:4)), (2.3)
θ
√
where (cid:4)v(cid:4) = vTv and C is member of the Mate´rn family of covariance functions (see Stein, 1999).
θ
WewillworkinthesubfamilycorrespondingtoasinglevalueoftheMate´rnsmoothnessparameter:
C (r)=σ2(1+|r|/ρ)e−|r|/ρ. (2.4)
θ x
Thefunctiongivenin(2.4)isthesimplestmemberoftheMate´rnfamilythatyieldsdifferentiablesurface
estimate.KammannandWand(2003)providefurtherdiscussionofthechoiceoftheMate´rnsmoothness
parameter.
To ensure scale invariance, increase numerical stability and reduce the computational burden, we
choosetherangeparameterρ viathesimplerule
ρˆ = max (cid:4)x −x (cid:4). (2.5)
i j
1(cid:1)i,j(cid:1)n
Fixing ρ a priori allows the use of the generalized linear model for fitting. In our experience, the
smoothness of the estimate surface depends on the choice of ρ, but the scale of the final map is rather
insensitive.
Generalizedadditivemodelsforcancermappingwithincompletecovariates 181
FittingoftheDiggleetal.(1998)modelrequiresn×nmatrixstorageandinversion.SincetheUpper
Cape Cod cancer data set involves n = 3191 observations, some modification is required for practical
use.Anattractivesolutionistousereducedknotorlow-rankkrigingasproposedbyNychkaetal.(1998).
Let{κ ,... ,κ }bearepresentativesubsetof{x ,... ,x }whichwewillrefertoasknots.Thissubset
1 Kx 1 n
canbeobtainedviaanefficientspacefillingalgorithm(e.g.Johnsonetal.,1990;NychkaandSaltzman,
1998).Let
X=[1xiT]1(cid:1)i(cid:1)n, Z=[C0((cid:4)xi −κk(cid:4)/ρ)]1(cid:1)i(cid:1)n,1(cid:1)k(cid:1)Kx
and
Ω=[C0((cid:4)κk −κk(cid:3)(cid:4)/ρ)]1(cid:1)k,k(cid:3)(cid:1)Kx ,
whereC (r)=(1+|r|)e−|r|.Thenlow-rankkrigingcorrespondstofittingthelogisticmixedmodel
0
logit{P(y =1|b)}=(Xβ+Zb) , (2.6)
i i
where β = (β ,βT)T, E(b) = 0 and cov(b) = σ2Ω−1. Typically, b is taken to have a Gaussian
0 1 x
distribution.Thereparametrization
Z∗ =ZΩ−1/2, b∗ =Ω1/2b
meansthatcov(b∗) = σx2Iandstandardmixedmodelsoftware,suchastheGLIMMIXmacroinSAS,can
beusedforfittingthemodel.Theestimatedlogoddsatx isthen
0
L(cid:1)O(x0)=X(x0)βˆ +Z∗(x0)bˆ∗,
where
X(x )=[1xT]
0 0
and
Z∗(x0)=[C0((cid:4)x0−κk(cid:4)/ρ)]1(cid:1)k(cid:1)Kx Ω−1/2.
In the Upper Cape Cod cancer study there are data on smoking and age for which we would like to
control.Sincetheageeffectispossiblynon-linearweproposetomodelitasanarbitrarysmoothfunction,
f.Assumingadditivityinthelogitscale,wearriveat
logit{P(y =1|b)}=(Xβ+Zb) +β s + f(a ),
i i s i i
wherea istheageofpersoni ands =1ifpersoni waseverasmokerandzerootherwise.
i i
The β s term can be incorporated into the Xβ component. There are a number of mixed model
s i
representations of smoothing that can be used to subsume the f(a ) into the generalized linear mixed
i
model as well (Brumback and Rice, 1998; Wang, 1998; Brumback et al., 1999; Lin and Zhang, 1999,
Verbyla et al., 1999). For example, Kammann and Wand (2003) use linear splines to achieve this. An
alternativethatweconsiderhereistosimplyapplythesameprincipleforthegeographic‘smooth’tothe
agevariable.Letκa,... ,κa beasetofknotsequallyspacedwithrespecttothequantilesofthea and
1 Ka i
set
Ωa =[C0(|κka −κka(cid:3)|/ρa)]1(cid:1)k,k(cid:3)(cid:1)Ka
and
Za =[C0(|ai −κka|/ρa)]1(cid:1)i(cid:1)n,1(cid:1)k(cid:1)Ka ,
forsomeρ >0.Weuseρ =max(a )−min(a ).
a a i i
182 J.L.FRENCHANDM.P.WAND
Ifweredefine
X=[1si ai xiT]1(cid:1)i(cid:1)n (2.7)
and
Z=[ZaΩa−1/2|Z∗], (2.8)
thenthemodelhastherepresentation
logit{P(y =1|b)}=(Xβ+Zb) , (2.9)
i i
Cov(b)=diag(σ21 ,σ21 ), (2.10)
a Ka x Kx
where1 isthe1×nvectorofones.
n
Acommonconventioninadditivemodellingistocentrethecurveestimatesabouttheirmeans.The
components of the additive model can be interpreted as effects about the mean. The same convention
couldbeappliedtothesurfaceestimateinthekrigingcomponentofthegeoadditivemodel.Operationally
wesetC=[X|Z]andletC=[1|C ]beapartitionofCintotheinterceptcolumnandtheremainder.We
r
thenworkwith
C¯ =[1|(I− 111T)C ] (2.11)
n r
ratherthanC.ThisconventionisadoptedinouranalysesinSection4.Aconsequenceofthiscenteringis
thatamapofexp{Sˆ(x )}overameshofx valuesplotstheratiooftheoddsfortheevent{y = 1}atx
0 0 0
relativetothegeometricmeanoddsoverthemappedregion.
2.1 Fittingasageneralizedlinearmixedmodel
In (2.9) and (2.10) we showed that the GAM has a logistic mixed model representation. Assuming that
theelementsofy = (y ,...,y )T areconditionallyindependentgivenb,thejointdensityofyandbis
1 n
givenby p(y,b;ψ)= p(y|b;β) p(b;θ),where
p(y|b;β)=exp{yT(Xβ+Zb)−1TB(Xβ+Zb)+1TC(y)}, (2.12)
B(Xβ + Zb) = [log[1 + exp{(Xβ + Zb)i}]]1(cid:1)i(cid:1)n , C(y) = 0, and, assuming b follows a Gaussian
distributionwithmeanzero,
p(b;θ)=(2π)−M/2 |D |−1/2exp(−1bTD−1b), (2.13)
θ 2 θ
where M = K +K andD isgivenby(2.10).Letψ ≡ (βT,θT)T.Wereferto p(y,b;ψ)asboththe
a x θ
complete-datadensityandcomplete-datalikelihood.
Maximum likelihood inference for generalized linear mixed effects models is based on maximizing
theobserved-datalikelihood
(cid:2)
L(ψ;y)= p(y,b;ψ)db
RM
=(2π)−M/2|D |−1/2exp{1TC(y)}I(β,θ), (2.14)
θ
where
(cid:2)
I(β,θ)= exp{yT(Xβ+Zb)−1TB(Xβ+Zb)− 1bTD−1b}db. (2.15)
2 θ
RM
Generalizedadditivemodelsforcancermappingwithincompletecovariates 183
In most cases, including the logistic mixed model used in (2.9) and (2.10), this integral is intractable.
Thus,wecannotfindmaximumlikelihoodestimatesusingtheexactobserved-datalikelihood.
The GLIMMIX macro in SAS overcomes this with an algorithm commonly referred to as penalized
quasi-likelihood (PQL) that essentially replaces (2.15) by a Laplace approximation. Another approach
to finding maximum likelihood estimate of ψ is to use the EM algorithm (Dempster et al., 1977). The
EM algorithm is a general purpose algorithm for finding the mode of a likelihood or posterior density
function. Viewing the random effects as latent variables, the EM algorithm iterates between calculating
the conditional expectation of the complete-data log likelihood, (cid:6)(ψ;y,b) = logp(y,b;ψ), given the
observed data and maximizing this expected value as a function of ψ. Dempster et al. (1977) have
shown that the EM algorithm will lead to the maximum likelihood estimates based on the observed-
data likelihood given in equation (2.14). In fact, since the observed-data likelihood is log-concave, the
EM algorithm will work quite well because it will not get stuck in local modes. In the context of the
generalizedlinearmixedeffectsmodel,the(m+1)thiterationoftheEMalgorithmis
E-step: Calculate Q(ψ|ψ(m)) = E{(cid:6)(ψ;y,b)|y,ψ(m)}, where the expectation is taken with respect to
p(b|y;ψ(m)).
M-Step: Setψ(m+1) =argmax Q(ψ|ψ(m)).
ψ
Thealgorithmalternatesbetweenthesetwostepsuntilthereisasufficientlysmallchangeintheparameter
valuesbetweeniterations.
Whenworkingwithgeneralizedlinearmixedeffectsmodels,theexpectationstepinvolvesevaluating
thequantity
(cid:2)
Q(ψ|ψ(cid:3))= (cid:6)(ψ;y,b) p(b|y;ψ(cid:3))db
(cid:3)
(cid:6)(ψ;y,b) p(y,b;ψ(cid:3))db
= (cid:3) , (2.16)
p(y,b;ψ(cid:3))db
whichisintractableformostmodels.Toalleviatethisproblem,severalauthorshaveuseaMonteCarloEM
algorithm(WeiandTanner,1990)inwhich(2.16)isreplacedbyaMonteCarloapproximationbasedona
samplefrom p(b|y;ψ).McCulloch(1997)andIbrahimetal.(2001)proposeobtainingtheMonteCarlo
sampleusingMarkovchainmethods,suchastheMetropolis–HastingsalgorithmorGibbssampling.Since
Markov chain sampling induces dependence, both Walker (1996) and Booth and Hobert (1999) suggest
alternative approaches to obtaining the Monte Carlo sample. The methods of Booth and Hobert (1999)
andIbrahimetal.(2001)alsoprovidealgorithmsforadaptivelychoosingtheMonteCarlosamplesize.
The Monte Carlo EM methodology is quite computationally intensive and more suited to smaller
numbersofrandomeffectsandsamplesizes.NeitheristhecaseforthegeoadditivemodelfortheUpper
CapeCoddatawherebmayhavedimensionof100andn = 3191.TheMCEMapproachissimplynot
practicalandanasymptoticapproximationseemsnecessary.Steele(1996)describesanEMalgorithmthat
alternatesbetweencalculating(cid:4)D Q(ψ|ψ(cid:3)),asecond-orderLaplaceapproximationtoD Q(ψ|ψ(cid:3)),and
ψ ψ
solving(cid:4)D Q(ψ|ψ(cid:3))=0.Assumingthattheorderofdifferentiationandintegrationcanbeinterchanged,
ψ
astandardassumptionoftheEMalgorithm,
(cid:2)
D Q(ψ|ψ(cid:3))= D (cid:6)(ψ;y,b) p(b|y;ψ(cid:3))db. (2.17)
ψ ψ
Regularity conditions allow the fully exponential Laplace approximation (Tierney et al., 1989) to the
expected complete-data score vector (2.17), but not the expected complete-data log-likelihood (Steele,
184 J.L.FRENCHANDM.P.WAND
1996).TheLaplaceapproximationapproximationtoD Q(ψ|ψ(cid:3))isgivenby
ψ
(cid:5)
(cid:4)DψQ(ψ|ψ(cid:3))= {Dψ(cid:6)(ψ;y,b)+C(ψ;y,b)}(cid:5)b=bˆ(ψ(cid:3)), (2.18)
where
bˆ(ψ)≡argmax p(y,b;ψ).
b
The term C(ψ;y,b) = {C(ψk;y,b)}1(cid:1)k(cid:1)p+S is an adjustment that allows (cid:4)DψQ(ψ|ψ(cid:3)) to differ from
D Q(ψ|ψ(cid:3))byaO(n−2)term.Theindividualcorrectiontermsaregivenby
ψ
(cid:6) (cid:7) (cid:8) (cid:9) (cid:10) (cid:11)(cid:12) (cid:13) (cid:14)(cid:15)
C(ψ ;y,b)= 1tr A−1 ∂ A−ZTUdiag ZA−1 D ∂ (cid:6)(ψ;y,b) T Z , (2.19)
k 2 ∂ψk b ∂ψk
whereU=diag{B(cid:3)(cid:3)(cid:3)(Xβ+Zb)}andA=−H (cid:6)(ψ;y,b)=ZTdiag{B(cid:3)(cid:3)(Xβ+Zb)}Z+D−1.
Steele(1996)notesthatausefulfirst-orderabpproximationtoD Q(ψ|ψ(cid:3))canbeobtainedθbyignoring
ψ
thelasttermin(2.18).Usingthissimplifiedapproximation,theestimatingequationsforβintheLaplace
EMalgorithm(Steele,1996)andthePQLalgorithm(BreslowandClayton,1993)areidentical.Thatis,
bothalgorithmssolveXT(y−(cid:4)µ)=0,where(cid:4)µ=B(cid:3)(Xβ+Zbˆ).Thetwoalgorithmsdifferinthemanner
inwhichθisestimated.However,whentheestimatesofθaresimilar,theLaplaceEMalgorithmshould
yieldmoreaccurateestimatesofthefixedeffectssincetheyarebasedonasecond-orderapproximation
ratherthanafirst-orderapproximation(Steele,1996).
3. MAPPINGCANCERRISKWITHINCOMPLETECOVARIATES
Missingcovariatevaluesarecommoninenvironmentalandpublichealthdata.Thesevaluesmaybe
missingbydesign(e.g.whensomedataarecollectedonlyonasubsetofsubjects)or,asismorecommonly
thecase,missingunintentionally.Thestandardapproachistoperformacomplete-caseanalysis,inwhich
caseswithmissingvaluesareexcludedfromtheanalysis.Thisapproachcanleadtoasubstantiallossof
informationifmanyvariablesexhibitmissingness.Worsestill,itcanyieldbiasedparameterestimatesif
themissingnessdependsontheresponsevariable(Jones,1996).Likelihood-basedmethods,suchasthe
EM algorithm, use all of the available data, including those observations with missing covariate values.
Theyareparticularlyattractivebecausetheyprovidevalidinferencewhenthemissingvaluesaremissing-
at-randominthesenseofLittleandRubin(1987)andcanbeextendedtoincludesituationswhenthedata
arenotmissing-at-random.Oneinterestingfeatureofthecomplete-caseanalysisisthatestimatesarenot
biased when the missingness depends on the missing covariate values, a property that is not shared by
likelihood-basedmethods.
In the Upper Cape Cod cancer study, the geographic location and age variables are completely
observed for all subjects, but smoking status is missing for 29% of the subjects. Table 1 shows that the
missingness in smoking status depends on the cancer type, with smoking status missing for 41.0% of
prostatecancerpatientsand24.2%ofpatientswithothertypesofcancer.Thisispreciselythesituationin
whichcompletecasemethodswillleadtobiasedinference.So,analternativemethodisneeded.
We begin by considering a model with D discrete and S continuous covariates, whose values for
subject i will be denoted by d and c , respectively. To simplify the notation, we assume that we are
i i
smoothingeachoftheScontinuouscovariates.Supposethattheresponseyandallcontinuouscovariates
arecompletelyobserved,butthatsomeofthevaluesford maybemissing-at-randomforeachsubject.
i
Fortheithsubject,letdobsanddmissdenotethevectorsofobservedandmissingvaluesandn denotethe
i i i
numberofpossiblecombinationsofvaluesfordmiss.FortheappropriateX,Z, andb,wecanexpressthe
i
complete-datadensityas
p(y,d,b|c;φ)= p(y|b,c,d;β) p(d|c;γ) p(b;θ),
Generalizedadditivemodelsforcancermappingwithincompletecovariates 185
whereφ=(βT,γT,θT)Tisa(p+q+S)×1vectorofparameters.Thislikelihooddiffersfromtheone
inSection2becauseweneedtomodel p(d|c;γ),theconditionaldensityofthemissingcovariatesgiven
theobservedcovariates.
Sinceajointmodelfor p(d|c;γ)canbedifficulttospecifyingeneral,wetypicallymodel p(d|c;γ)
as the product of conditional densities in the same manner as Lipsitz and Ibrahim (1996). That is, we
express
p(d|c;γ)= p(d1|c;γ1) p(d2|d1,c;γ2)...p(dD|d1,... ,dD−1,c;γD),
whereγ =(γT,... ,γT)Tistheq×1vectorofparametersfor p(d|c;γ).Whilethisprovidesasimplified
1 D
model for p(d|c;γ), it does have some drawbacks. First, bias can be introduced in estimation of γ.
Second, the order in which conditional densities are taken can influence the estimation of ψ; however,
ithasbeendemonstratedthattheestimatesarequiterobusttotheorderoftheconditioning(Lipsitzand
Ibrahim,1996;Ibrahimetal.,1999a,b,2001).
Sincedmissandbarenotobserved,webaseourinferenceontheobserved-datalikelihood
(cid:2)
(cid:16)
L(φ;y,c,dobs)= p(y,d,b|c;φ)db,
dmiss
wherethesummationisoverallpossiblecombinationsofthemissingdiscretevariables. Theobserved-
data likelihood in the missing covariate case is even more difficult to work with than that in the
complete-covariate case, but the complete-data likelihood remains relatively easy to manipulate. Thus,
data augmentation methods, such as the EM algorithm, are the most natural methods to use to obtain
estimatesofφ.Inthefollowingtwosections,weoutlineourapproachtoestimationofφandVar((cid:4)φ).
3.1 Estimationofφ
Treatingbothdmiss andbasmissingdata,wecanfindthemaximumlikelihoodestimateofφusingthe
EM algorithm (Dempster et al., 1977). However, as in the complete-covariate case, the integral in the
E-stepisintractableformostgeneralizedlinearmixedeffectsmodels.Toremedythis,weproposeusinga
LaplaceEMalgorithm(Steele,1996),handlingthemissingcovariatevalueswiththeMethodofWeights
(Ibrahim,1990).
Let(cid:6)(φ;y,c,d,b)=logp(y,d,b|c;φ),thentheE-stepatthe(m+1)thiterationoftheEMalgorithm
calculates
D Q(φ|φ(m))= E{D (cid:6)(φ;y,c,d,b)|y,c,dobs,φ(m)}
φ (cid:2) φ
(cid:16)
= D (cid:6)(φ;y,c,d,b) p(dmiss,b|y,c,dobs;φ(m))db
φ
(cid:2) dmiss
= Dφ(cid:6)w(φ;y˜,c˜,d˜,b) p(b|y,c,dobs;φ(m))db, (3.1)
where (cid:6)w(φ;y˜,c˜,d˜,b) = E{(cid:6)(φ;y,c,d,b)|b,y,c,dobs,φ(m)} is a weighted complete-data log likeli-
hoodthatiscalculableinclosedformbecausethemissingcovariatevaluesarediscrete.Ibrahim(1990)
derived a similar expression in the context of the generalized linear model. The vectors y˜, c˜,and d˜ are
augmentedversionsofy,c, anddandarediscussedinmoredetailbelow.
FortheUpperCapeCodstudy,thereisonediscretecovariate(d =s )andthreecontinuouscovariates
i i
(c =(a ,xT)T).Wemodel p(y,b|ψ)with(2.12)and(2.13)andmodel p(s |c ;γ)as
i i i i i
logit{P(s |c ;γ)}=(1cT)γ.
i i i
186 J.L.FRENCHANDM.P.WAND
Theweightedcomplete-dataloglikelihoodisgivenby
(cid:6)w(φ;y˜,c˜,d˜,b)=y˜TW(X˜β+Z˜b)−1TWB(X˜β+Z˜b)+s˜TWX˜−sγ
−1TWB(X˜−sγ)− 12bTD−θ1b− 12log|Dθ|, (3.2)
whereX˜−s isthematrixX˜ withthecolumnforsmokingstatusremovedandb=(baT,bTx)T ispartitioned
toconformtothepartitioningofZ. (cid:17)
In general, the n˜ × p matrix X˜ has rows x˜iT(j) = [1, d˜iT(j), siT], where n˜ = ini and d˜i(j) is the
vector d with dmiss = dmiss, the jth possible combination of values for dmiss. Thus, X˜ is constructed
i i i(j) i
byreplacingtheithoriginalrowofXbyn rows,witheachnewrowcontainingoneofthen possible
i i
combinationsforthedmissvalues.Thevaluesdobsremainunchangedoverthen observations.Thematrix
i i i
Wisan˜ ×n˜ diagonalmatrixwithelements
(cid:18)
Pr(dmiss =dmiss|b,y,c,dobs;φ(m)) ifobservationi hasmissingvalues
wi(j) = i i(j) (3.3)
1 otherwise
where
Pr(dmiss =dmiss|b,y,c,dobs;φ(m))= (cid:17) p(yi,d˜i(j),b|ci;φ(m)) (3.4)
i i(j) nk=i 1 p(yi,d˜i(k),b|ci;φ(m))
andthesummationisoverthen possiblevaluesofdmiss.Equation(3.4)followsfromadirectapplication
i i
ofBayes’Theorem.Sincetheycontaincompletelyobserveddata,then˜×M matrixZ˜ andn˜×1vectory˜
arecreatedbyreplacingtheithrowofZandywithn copiesofzTand y ,respectively.
i i i
Since (3.1) cannot be calculated in closed form, we follow Steele (1996) and use an approximation
basedonafullyexponentialLaplaceapproximation(Tierneyetal.,1989).Theapproximationyields
(cid:10) (cid:11)(cid:5)
(cid:4)DφQ(φ|φ(m))= Dφ(cid:6)w(φ;y˜,c˜,d˜,b)+C(φ;y˜,c˜,d˜,b) (cid:5)(cid:5)b=(cid:4)b(φ(m)) , (3.5)
where
(cid:4)b(φ)≡argmax p(y,c,dobs,b;φ).
b
The correction term C(φ;y˜,c˜,d˜,b) is similar to (2.19) with appropriate changes. For example, A is
replacedbyAw =−Hb(cid:6)w(φ;y˜,c˜,d˜,b).Incalculatingthecorrectionterms,wereplacetheEMweights,
wi(j) with a first-order Taylor series expansion about (cid:4)b(φ(m)). A detailed derivation of (3.5) and, in
particular,C(φ;y˜,c˜,d˜,b)isgiveninanappendixfoundonBiostatisticsOnline.
It is well-known that the EM algorithm does not automatically provide a method for estimating
Var((cid:4)φ). Because it relies on the same code used to run the EM algorithm and has been shown to be
atleastasaccurateastheSEMmethod(MengandRubin,1991),weusetheforward-differencemethod
ofJamshidianandJennrich(2000).
3.2 Predictionofb
ToestimatethesurfaceS(x),weneedtopredicttherandomeffectsb.Itiscommontopredictbwithb∗ =
E(b|y,c,dobs,(cid:4)φ), the conditional expectation of b given the observed data evaluated at the maximum
likelihoodestimateforφ.Since,forthegeneralizedlinearmixedeffectsmodel,thisexpectationtypically
cannot be calculated in closed form, we approximate it with a Laplace approximation. The spirit of the
approximationissimilartothatusedtoapproximatetheE-stepoftheEMalgorithmdescribedinSection
3.1.DetailsareprovidedinanappendixfoundonBiostatisticsOnline.