ERIC ED367841: Minnesota Adult Basic Education. Annual Performance/Narrative Report. Fiscal Year 1992-1993. PDF
Preview ERIC ED367841: Minnesota Adult Basic Education. Annual Performance/Narrative Report. Fiscal Year 1992-1993.
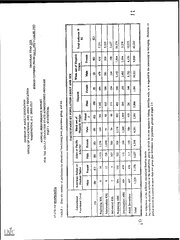
DOCUMENT RESUME CE 065 904 ED 367 841 Minnesota Adult Basic Education. Annual TITLE Performance/Narrative Report. Fiscal Year 1992-1993. Minnesota State Dept. of Education, St. Paul. INSTITUTION PUB DATE [93] NOTE 25p. Descriptive (141) PUB TYPE Reports MF01/PC01 Plus Postage. EDRS PRICE *Adult Basic Education; Adult Programs; Annual DESCRIPTORS Reports; Basic Skills; Coordination; Delivery Systems; Disadvantaged; Educational Cooperation; *Educational Objectives; Individualized Instruction; Literacy Education; Outreach Programs; Program Administration; Program Costs; *Program Effectiveness; *Program Implementation; Shared Resources and Services; Staff Development; *State Programs; Statewide Planning; Systems Approach; Tables (Data) *Minnesota IDENTIFIERS ABSTRACT Adult basic education (ABE) programming efforts in Minnesota for the 1992-93 year were designed to accomplish the (1) continue following state -lan-stipulated goals: developing/implementing a statewide ABE delivery system to enable adults (especially disadvantaged adults) with basic skill deficiencies to identify and achieve their personal and occupational goals; (2) continut) encouraging development of systems to coordinate and cooperate with all available resources and services that could improve and/or expand delivery of individualized ABE and support and (3) continue providing for and expanding the out,--ach services; quality and availability of ABE staff development activities to help adult educators facilitate self-directive, practical, and (4) continue encouraging the development, personalized learning; adoption, and adaptation of innovative, effective, and cost-efficient methods and techniques for providing appropriate and timely adult learning options; and (5) continue developing and implementing a management system that adequately addresses the requirements stipulated in state and federal legislation. Compared to the previous year, enrollment in Minnesota ABE classes was up 3.8% in 1992-93, enrollment in English-as-a-Second-Language classes was up 8.0%, average attendance was up 14.2%, student completion of personal education plans was up 27.6%, and total program costs were up 9.92%. (MN) *********************************************************************** * * Reproductions supplied by EnRS are the best that can be made * * from the w-iginal document. *********************************************************************** C5 MINNESOTA ADULT BASIC EDUCATION REPORT ANNUAL PERFORMANCE/NARRATIVE FISCAL YEAR 1992-1993 U S DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION I Fltyran n and Im,m,..monl .ATIONAL FT( SOUR( L S IN( CIE:MATSON E a CI NH 14 MCI iMs nh, mn.n1 Nas 'en reo,o0,n, ,n( ented nom Ihe tunSOn , oalwal,,,, jwal,ny NI.ges ndr ve n.mn. ,Plnodul t.on . l',,,t,3 ,1,11141." oleni Ile not nfn CII Submitted as the PERMISSION TO REPRODUCE THIS MATEHIAI HAS BEEN GRANTED BY Programs Annual Performance Report of the Adult Education State t Operated Under the Authority of the tn Federal Adult Education Act .0 Public Law 91-230 TO THE EDUCATIONAL RESOURC,P; 2 INFORMATION CENTER (ERIC) kt, BEST COPY MAILABLE Minnesota Adult Basic Education Annual Performance Report Narrative 1992-1993 Program Year Adult education in Minnesota is organized as a statewide delivery system that utilizes different funding sources, different support services and different providers as necessary academic, to help eligible adults learn to address their own concerns as they master problem-solving, evaluation, and other coping skills needed for them to become more self- directed and self-sufficient. The purposes of the adult education activities to be carried out under this statewide delivery system are to: Improve the educational opportunities for adults who lack the level of literacy and other basic skills needed for effective citizenship and productive employment; Expand and improve the current system for delivering adult education, espe- cially the delivery of such services to educationally and economically disadvantaged adults with basic skills proficiency levels below the sixth-grade equivalent; and Encourage the establishment of adult education programs that: Enable adults to acquire basic educational skills needed for literate functioning; Provide adults with sufficient basic education to enable them to benefit from job training and retraining programs and to obtain and retain productive employment so they more fully enjoy the benefits and responsibilities of citizenship; Enable adults who so desire to continue their education to at least the level equivalent to secondary school completion; and Provide adult education and support services that enable adults to identify and plan to achieve their own individual learning goals and objectives in d timeiy and efficient manner. Results of programming efforts for the 1992-1993 year are discussed below in conjunction with each State Plan goal intended to strive toward those purposes. I: Continue developing and implementing a statewide Adult Basic Education deli- GOAL throughout the State, es- very system that will: Enable adults with basic skills deficiencies pecially educationally disadvantaged adults, to identify and achieve their personal educa- tional and occupational goals in an appropriate, effective and efficient manner, and Provide for needed adult learning and support services through collaborative agreements with the agencies and organizations most willing and able to reach appropriately the adults with basic skills deficiencies, especially educationally disadvantaged adults. 1.a. Funding availability was announced in the State REGISTER, the official announcement journal, in CONNECTIONS, our adult education newsletter with a circulation of 4,000, and through direct mailings to all known interested parties, corrections facilities and previously funded agencies. Well-attended two-day workshops were held in Northern Minnesota, the Twin Cities Metropolitan Area and in Southern Minnesota tO discuss all aspects of the application, approval and funding processes, and to provide sessions on development and program design, program evaluation, resource coordination, staff Page 2 Minnesota's 1992-1993 ABE Performance Report Narrative Indicators of ABE other aspects of effective programming, as well as to revisit the Program Quality. districts and more than Applications received represented more than 300 public school American 400 other agencies, including libraries, voluntary literacy tutoring groups, Assistance Associations, correction- Indian reservations and community groups, Mutual organizations and other public and al facilities, job training agencies, community-based school districts and other agencies are private non-profit organizations. All of these organized in 55 ABE projects. has been required to evaluate its prior-year .b. This was the fourth-year that each applicant adult learning opportunities. Individ- performance, and describe its plans for improving well as on-site visits and telephone contacts ual time slots at the regional workshops as narratives and provide technical assistance in imple- were scheduled to go over these menting improvements. changed to allow multi-year program And this was the first year since State law was approval. approval that some projects had to reapply for funding but not program the State ABE law for two- Approximately half of the projects had met the criteria in have to prepare a narrative performance report. year approval, and therefore did not Criteria for multi-year approval are: Adult basic education programs may be approved under this subdivision for up to Two-year program approval shall be granted to an applicant who has two years. demonstrated the capacity to: choices (1) offer comprehensive learning opportunities and support service appropriate for and accessible to adults at all basic skill need levels; (2) provide a participatory and experiential learning approach based on the skill strengths, interests, and needs of each adult, that enables adults with basic needs to: (i) identify, plan for, and evaluate their own progress toward achieving their defined educational and occupational goals; skills, as well ail master the basic academic reading, writing, and computational interpersonal effectiveness, and other life as the problem-solving, decision-making, and learning skills they need to function effectively in a changing society; (iii) locate and be able to use the health, governmental, and social services and families' lives; and resources they need to improve their own and their (iv) continue their education, if they desire, to at least the level of secondary school completion, with the ability to secure and benefit from continuing education that will enable them to become more employable, productive, and responsible citizens; community (3) plan, coordinate, and develop cooperative agreements with services, such as resources to address the needs that the adults have for support transportation, flexible course scheduling, convenient class locations, and child care, (4) collaborate with business, industry, labor unions, and employment-training agencies, as well as with family and occupational education providers, to arrange for resources and services through which adults can attain economic self- sufficiency; it A Page 3 Minnesota's 1992-1993 ABE Performance Report Narrative in (6) provide sensitive and well-trained adult education personnel who participate local, regional, and statewide adult basic education staff development events to master effective adult learning and teaching techniques; and (6) participate in regional adult basic education peer program reviews evaluations; and (7) submit accurate and timely performance and fiscal reports. 1.c. The integrated single application and annual performance report form allowed ap- plication to be made for program approval and funding from Federal Basic Grants, State application ABE Aid, Local ABE Levy, and State Private Non-Profit Contracts. The same form also enables approved projects to access State and Federal welfare reform, job- training, child-care and transportation dollars that become available for our shared clientele. 1.d. After more than five years of public hearings and comment periods and re-writings, we QuaIity. The general were able to finalize Minnesota's Indicators of ABE Program feeling is that what we came up with is not learner-centered enough, and needs to be reworked as we practice using the Indicators for on-site program reviews. Local adult educators and the agency personnel with whom we collaborate report, however, that the current document is a good starting point. 1.e. A State law creating a new, more equitable ABE funding formula went into effect. The formula itself, however, cannot take effect until the State ABE appropriation rises beyond the current "hold-harmless" level. 1.f. End-of-prcigram-year statistics show the following: 1992-1993 1991-1992 Change -1.5% 54,106 54,931 Total Enrollment -6.9% 42,232 45,348 Total Participants +8.0% 12,097 11,202 All ESL Levels: +3.8% 19,557 18,839 All ABE Levels: -30.9% 10,578 15,307 All ASE Levels: +14.2% 75.42 66.02 Average Attendance Hours: -19.7% 5,942 7,396 Total Separations: +27.6% 17,912 14,040 Completed Personal Ed. Plan: +4.3% $139.07 $133.37 State Cost / Participant: +25.4% $81.88 $65.28 Federal Cost / Participant: +9.92% $428.12 $389.50 Total Cost / Participant: While the number of adults attempting to enter ABE programs is rising, the number who have not are able to be served is declining. State, local and Federal funding sources kept pace with the demand. A new State program that allows economicallY-JTPA-rr- gible adults older than 21 to return to high school and generate "foundation aid" has reduced the adult secondary enrollment significantly. (The "foundation aid" payment Page 4 Minnesota's 1992-1993 ABE Performance Report Narrative available through ABE, if there for these adults is 14.3 times higher than what would be which to serve them.) were any extra ABE money with hours that each ABE participant per- Some good news is that the average number of more than 14 percent. The number of sisted in the program increased significantly prior to completing their personal educa- participants who separated from the program the number of participants who com- tion plans dropped by nearly 20 percent. And increased by nearly 30 percent, in spite of the re- pleted their personal education plans duced number of participants. of systems for coordinating and coopera- Continue encoleaging the development GOAL II: that could improve and/or expand the delivery ting with all availab:e resources and services services to adults throughout the State of individualized ABE and support and outreach educationally disadvantaged adults. with basic skills deficiencies, especially to monitoring and other site visits, in 2.a. We encourage, in the application process, du? ing development events, and during evaluations, ABE management seminars and ABE staff in the service area that may be of that all education, resource and service providers project. For the past two benefit to individual adult learners be involvad in the ABE community-wide local planning, coordination and years, we also have encouraged that education and support service advisory teams be organized consisting of all the job training agencies, providers, libraries, business and industry, welfare reform and etc., in the area. training in how to work collaboratively 2.b. Since 1979, we have provided resource fairs and administrators and instruc- with community services at least twice each year for ABE Adult Basic Education office In an attempt to "model" collaborative relations, the tors. (public assistance), works very closely with the State departments of Human Services Education Coordinating Board, Jobs and Training (JTPA), Corrections, with the Higher Vocational-Technical Education. the Community College System, and the State Board of Council, we attempt to coordinate 2.c. Through the Minnesota Interagency Adult Learning councils representing adult education related activities across State agencies and among increasing collaborative each racial/ethnic/linguistic group. Officially a mechanism for team-building grants to efforts, the Interagency Adult Learning Council has provided communities, community-based organizations and adult basic education programs benefit of adult learners. throughout the State to encourage collaboration for the Facilitators specializing in ABE 2.d. A group of Literacy Training Network ABE Training activities finished developing, piloting and wogram improvement and development stated in Objective 11.2, training folks to participate in ABE Peer Program Reviews. As successful existing integrated ABE this process is intended to utilize personnel from others to reproduce these effective programs in developing, modeling and helping implement successful adult designs so that more local program personnel are able to opportunities for learning techniques that improve or expand appropriate learning disadvantaged adults. Page 5 Minnesota's 1992-1993 ABE Performance Report Narrative The Peer Review Process is paid for with Section 353 funds to improve local programs. with their peers and But to ensure that local program personnel are direct and forthright from the with their own self-assessment process, copies of the written reports resulting will be coordinated visits are not sent to the State. The Peer Review Process, however, evaluations. with the Indicators of ABE Program Quality and the statewide ABE related 2.e. We are continuing to work on developing new interagency agreements on Colleges and Technical Colleges. The to welfare reform, food stamps, Community formal interagency agreement through which we provided adult refugee ESL and work- force education ended when Federal refugee resettlement dollars ended. (Our inter- ESL, so this action resulted in a loss of agency agreement also funded adult refugee $650,000 per year to local ABE programs.) 2.f. 1992- 1991- Separations Change 1992 1993 Due To: Transportation +65.9% 443 267 Problems Child Cwe + 3.0% 430 443 Difficulties Overall, separations prior to completing Personal Education Plans have decreased. Separations due to transportation and child care difficulties, however, have increased. it is no longer feasible to operate the many part- Part of this problem is due to funding: time, sparsely attended sites that we have had in rural areas throughout the State. Transportation and child care are much harder to arrange in rural areas. Another difficulty was due to the welfare reform changes: Minnesota had been operating under required to revert to the an exemption from Ishp Federal model; when the State was the Federal JOBS guidelines, many hundreds of adults who had been clients of PATHS, State's welfare reform effort, were no longer eligible, and lost their child care and transportation subsidies to attend ABE. basic GOAL lll: Continue providing for, and expanding thecluality and availability of, adult education staff development activities that better prepare program personnel to facilitate achieve the self-directive, practical, and personalized learning that best enables adults to their individual goals. 3.a. Through the Literacy Training Network, we provide 16 regional and three statewide ABE teacher training events for more than 900 adult educators and one statewide and three regional seminars for more than 200 adult education administrators, lead teachers, and site coordinators. In addition, through the Minnesota Literacy Council, America, ESL, and volunteers in the we provide Laubach, Literacy Volunteers of classroom training for volunteer tutors, volunteer coordinators and tutor trainers. Minnesota's 1992-1993 ABE Performance Report Narrative -- Page 6 3.b. Our promoting of practitioner-researchers emphasizes self- and peer reflection about ABE practices. We developed, and trained people to use, both ESL and ABE staff ob- servation instruments to formalize this reflective practice. Levels of Training have been drafted to guide adult education professionals in planning and providing for their own ' ,ation of staff continuing development. We participated in the Pelavin Associates el development activities, and the Minnesota Literacy Training Network system was chosen as the only statewide one of nine national models. 3.c. In addition, continuing education for ABE Training Facilitators has continued to investigate new and promising practices, including all the Pelavin Associates training modules, as well as to continue improving interpersonal skills needed for their own self- direction, for peer mentoring and for peer observations. 3.d. An outside evaluation of the statewide Literacy Training Network showed that adult educators and their managers were pleased with the training being provided, and felt that inservice education, plus the increased communication and information-sharing through the publication of CONNECTIONS, was improving the quality of ABE. The adult educators who do not participate in the regional or statewide LTN training claimed that their full-time non-ABE positions and their very limited ABE hours were to blame. GOAL IV: Continue encouraging the development, adoption and adaptation of innovative, effective and cost-efficient methods and techniques for providing appropriate and timely adult learning options, especially non-traditional opportunities that promise to involve educationally disadvantaged adults in developing and mastering personal self-sufficiency plans. 4.a. In addition to the Section 353 Special Projects, Staff Development activities, and networking, the Adult Basic Education office has sponsored participatory task-teams working on, looking at and experimenting with: learner-centered assessment; revision of the Levels of Training for adult educators; learner-centered evaluation; outcome- based education, and funding equity and simplification. And we have been working with local ABE providers to begin working on standardizing and computerizing data collection and reporting. 4.b. With the demise of Federal refugee resettlement funds, we have been sponsoring additional ESL, ESL-Family Literacy, and ESL-Workforce Education staff and program training events to cope with Minnesota's large and continuously growing refugee and immigrant populations. 4.c. Family Literacy, Workforce Education and ESL, separately and in combination, are the growth areas for ABE in Minnesota. Collaboration will continue with Even Start, Head Start, Early Childhood Family Education, business, industry, labor, welfare reform and other resources and services with which to help meet these growing needs. Page 7 Minnesota's 1992-1993 ABE Performance Report Narrative system, at both the local GOAL V: Continue developing and implementing a management programmatic and fiscal requirements and the state levels, that adequately addresses the and the Federal Adult Education Act. of the Minnesota State Plan for Adult Education project personnel, task teams of adult educators 5.a. We have been working with local ABE of Education to standardize and and other sections of the Minnesota Department Task teams have been simplify the student accounting and fiscal reporting systems. both the State's monitoring and working on a peer program review system to augment for staff development. One task evaluation functions, and to provide another avenue with the Minnesota Legislature to permit multi-year team was successful in working In addition, for the the 1992-1993 program year. program approval, beginning with sponsored public hearings on our Rules of past few years, and egain this year, we Thumb or performance standards. Finger, which are proposed to become Rules of have been working with othef 5.b. As already mentioned under other goals above, we collaborate in order to provide provider, resource and service agencies to coordinate and task team efforts are fully better services to learners. Our staff development and participatory, open, and led by front-line adult educators. during the Spring and early Summer of 5.c. A new statewide evaluation was conducted ;* used the Indicators of ABE Program Quality to 1993 by an outside evaluation group. designed to produce interview administrators, teachers and leorners in a methodology collection and analysis, of program review and more effective systems of data development process. evaluation, and of collecting "in-put" to the Indicator of St. Thomas for participants 5.d. Graduate credit become available through the University training events who complete an in Department of Education and LTN-sponsored ABE extra practitioner-research project paper. o n 3 9 , r 9 e - 1 B v , e 0 s w 3 n o e m n H u u ) ) L l J K . o g ( o c 3 n 2 3 t 9 ( 9 i 3 9 7 3 1 7 g 2 7 9 l 2 2 7 5 5 2 a 9 n 2 1 6 2 2 2 , , t 9 , o 0 , 2 , , 0 o , R 1 3 9 1 l 7 1 4 1 T e A , b I E s v Y a l u y c M e J t i l 4 0 0 i n 4 a 6 A M 8 8 n ) 9 2 2 6 a m K 9 1 2 u R 5 1 8 9 p O 1 6 3 m ( e , , , , G s 2 4 9 1 R F i m O H F n o R : f c r D P o O e E t h R o t 1 e 2 n E 3 2 4 n 9 2 l ) 1 3 0 8 a 2 1 V i 3 7 t 0 X 7 . 1 6 M 1 t ( , 4 2 d O i , 0 , , E 3 h 3 2 e 1 C W d S r D a M D g O N A e I r A R R e s l G E 1 9 i 4 8 8 a P 4 8 4 ) 0 P 5 8 m 0 r N O 9 8 I U 8 2 o 1 2 2 ( 6 2 , R O e 1 O , F h c P I R T t i i n D G A w a E C p N s R s U e i T O E H i N D f e R T I x i 6 5 l H O 0 T 2 . 7 t 1 E 5 O 1 a e S 3 1 6 n 9 7 0 8 O 1 0 M I A s - I 5 8 e P 2 T 1 2 T 3 4 4 2 N 5 d , d L E , A 2 L L 1 - i n I s R U 2 M U e C A a , g 0 g P U D E C , D 2 n a p O C 0 D p I A o A u T 0 P 2 1 l 2 l 5 N o 0 E 1 n a e 5 - 3 S n 6 9 D 7 ) 6 r 0 E . m o b 8 0 A Y G 9 9 i 5 C g I T 2 e f N g , T T , s 1 e M o ( B o 2 . L n i p D A A A F t r o U t u R O S s T T o i , o L D r t O T N n S S a a r c A A g N l F e O i k u N - n p N R n A c p T F I a O p e 4 0 1 o 6 a O E o 4 G p O 6 T P a l ) 7 6 9 1 8 i l I p a 4 P F 3 s t I B T I 9 R 2 2 N 1 5 a e M 1 T i N ( C , , , H , L A l h A 1 4 l I 2 A u e O I H s A C T p P v C I r S o U e U R S o O A p l I N D A e g V V W r N h E n P o e I c 8 i F l f D 3 A 6 0 6 h 9 n 4 a T i 9 ) 0 O s 6 4 0 f 7 c m 0 o E L 1 n 3 i 1 3 0 i 2 5 i c ( h o , r E U e t , , 4 a c e 1 w i 2 F C t D P n d i u n I n A o r F f i a o f t F l e l E . p a s 7 s O n d l 2 8 5 H 1 7 h n u I l e 2 a e 2 1 1 5 6 ' e o o l ) 2 1 T i 1 v 3 a D 5 7 3 e s i r , M e t 3 , S A g ( R a 1 l ( c c O n u p i o F n d u i h e t o c t r y r e n e 8 6 g o 2 9 b / l u 7 4 3 6 1 l a 3 7 e ) 2 e a f 1 1 n 4 s m C 3 4 v , n i t l a 1 c n ( a i o e i t a n a d F a r n p o N n e a i i I c t h h a n i n t t t c a r a 9 n e u a k c 2 r 7 i d 4 9 p s e o i 2 3 0 8 e 9 0 8 d a r ) l m f , 4 a 3 4 B e e l 1 o t A M n m d ( n r e u e A i r l b e c d A m f n e f T i t i u d n O e n u b E e L S o l e y h B e d E h c S t r v E l A t L a N l L E u f e e a B d r o b S o S L N n e e n e A h E s t E o d t t I o n l n s a a i M ) a l E c g d o t g A u i i e n a d e d n i e n o e ( o c t S F e c e i i i l h u i n n n l m n . m O t s o I t d n c i n a l l f r r a n E n i u r E i v e E n e g e g t o u d d L o d e t T e t e s F n A n ' A B B I B c r A n I ' I e e A A T p S T S
