Elephant Crop Raiding Problems and Their Solutions at Kui Buri National Park, Southwestern Thailand PDF
Preview Elephant Crop Raiding Problems and Their Solutions at Kui Buri National Park, Southwestern Thailand
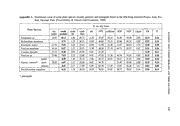
NAT. HIST. BULL. SIAM Soc. 53(1): 87-109,2 005 ELEPHANT CROP RAIDING PROBLEMS AND THEIR , SOLUTIONS AT KUI BURI NATIONAL PARK SOUTHWESTERN THAILAND Maltana Srikrachang',2 and Sompoad Srikosama飽ra' ABSTRACT Measures to stop elephant crop r剖d泊gin an agro-泊dus凶alcrop area紅'eassessed,us ing 出eda飽 fromdocumen旬ryresearch,fi eld observation and reports 合omthe park agency. Expansion of commercial p凪.eapplegrowing in al owland valley of favorable elephant habitat has pushed elephants into su加rdinateupland areas,w hich町 nowincluded in Kui Buri National Park. Due to the close proximity of croplands to the national park,el ephants from the p訂'kcome out and raid the croplands. When pineapple w鎚 expensive,4e lephants were killed. Immediate actions to solve血isproblem were made under the HMth e King's Initiated Project by allocating ap 副 ofcroplands for elephant habitat improvement. Thee leph初旬 havenot be叩 poachedand killed since,b ut th出 herdshave split into several smaller groups如 d dispersed,ca using mo陀 frequentconflicts. Crop raiding occurs in bo白 dryand wet seasons, 組dis related to the dis凶bution,availability,an d nu佐itionalvalue of fodder in the forests and in由ecroplands,as well鎚 wateravailability. Simple electric fences and chasing by p釘k rangers and farmers are present meas脚 sto limit movement of巴le抑制Sto cultivated areas. However,出.eeffort is just a蜘 por町 onedue to increasing of侃 ele抑制tpopulation and 恥 verylong park boundary in contact with croplands. Appropriate multiple counterm聞 ures withp釘ticipationof local stakeholders is the recommended longterm solution.百ley紅巳ωrry泊g out land-use p加mingand establishing schemes to provide permanent benefits to the rural community by using the elephants in the conflict area. Keywords: Asian elephant,c rop raiding,K ui Buri National Park,百ailand 別τRODUCTION Crop raiding by elephants is currently血.emost impo此antproblem泊 theconservation and management of elephants泊百1ailand.However,el ephants have special sta旬sdue to 血.eirrole加官凶nationalhistory (UMPHANWONG,19 94),so 白紙血eyare under血epatronage of出e百1aiRoyal Family,w hich plays av ery important role in solving this problem.官le problem is difficult to solve due to complex factors associated with the interaction of people and elephant ecology (O'CONNELL Ef AL., 2000). Factors studied by previous researchers include competition for land and water sources (KANGWANA,1 995; KIIRu, 1995;百IOUL回S& SAKWA 1995; TCHAMBA,1 995),in creases in白earea of cultivation (DE SILVA,1 998; TCHAMBA,1 995),n atural preference of crops by elephants (SUKUMAR, 1989),e lephant optimal foraging strategy (SUKUMAR,1 990),t he aggressiveness of male IDep釘tmentof Biology,Fa culty of Science,Ma llidol University,R ama 6R oad,B an依.ok10400,T hailand 2Wildlife Research Division,De partment of National Park,Wi ldlife and Plant Conservation,Ph allolyothin Road, Bangkok 10900,百lailand Received 14 February 2005; accepted 8J une 2005. 87 88 MATTANA SRIKRACHANG AND SOMPOAD SRIKOSAMATARA W+E 。 m 5,000 5 10 Krn ~ villages .r凶ervOlrs 同headquarterandr angers 凶 on Figllre 1. Map of Kui Buri National Park showingb oundary and both Kui CanalV all巴ysthat加eexcluded from thep ark and mainlyg row pineappl巴asan agro-indllstrialc rop fOl巴xport ELEPHANT CROP RAIDING PROBLEMS AND THEIR SOLUTIONS 89 elephants in finding mates (SUKUMAR,1 991),c hanges in rainfall (SAM ETA L., 1998) and increase in numbers of wild elephant due to improved protection of habitats and poaching control,a nd loss of their fear of people (KANGWANA,1 995; TCHAMBA,1 995; NAUGHTON- TREVES,19 98; PRASAD & REDDY,20 02). Localized soil degradation forces people to plant crops in scattered pattems at greater distances from villages where they are more vulnerable to elephant raids (LAHM,1 996). In addition,th e severity of this problem also depends on human densities (BARNES ET AL., 1991; NEWMARK ET AL., 1994),s ocio-economic improvement and raised expectations of the affected farmers and their attitude toward the elephants (BANDARA & TrSDELL,20 03; MADDEN,20 04) etc. Nos ingle factor may ∞mpletely explain the phenomenon of crop raiding by elephants,bu t several of the above factors may play significant roles under particular circumstances (NATH & SUKUMAR,1 998). Crop raiding by elephants at Kui Buri National Park was studied to understand the phenomenon in an agro-industrial landscape. Other questions asked concemed出epattem of eleph1tcrop raiding and the time of the serious incidents. And finally,w hat were the 創 outcomes after “solutions" to the problem were implemented under the special project initiated by His Majesty the King. STUDY SITE AND METHODS Study Area Kui Buri National Park (KBNP) lies within 11040'ー12010'Nand 99・20'-99050'Ein Prachuap Khiri Khan Province,so uthwestem Thailand. It has been protected as aN ational Park since 1990,b ut was gazetted in 1999 with at otal area of 969 km乙or79% of the present forest cover of the province (CHARUPPAT,19 98). This park is an important watershed eafor the Kui canal system and its tributaries,wh ich run through the valleys. The park 紅 was established by excluding the Kui canal valleys,w hich became croplands and villages. Thepsentlandscape of the park comprises three forest remnants and almost all boundaries 陀 in the north,ea st and south are adjacent to croplands (Fig. 1). Thew est side borders forest in Myanmar and ap art of the northem boundary is adjacent to a官1aiMilitary Security Area. Small vi11ages of Karen people are settled in the northem part of the park. Them ean annual rainfall of the Kui Buri district during 1990ー2000recorded by the Meteorological Department was 857 mma nd mean annual temperature was 28C (23.7・-32C).官1efirst 0 0 wet season lasts from late April to September. Superabundant rain falls in September to October (Fig. 2). Vegetation of the park is roughly classified as 30% mixed deciduous forest and 70% evergreen forest (Kur BURI NATIONAL PARK,1 999). Before the 1970s,th e valleys were dense forest and elephants were abundant. Elephant captures泊出isarea were legal,us ing the kraal or Kheddah method (capture of elephant herds by driving them into al arge stockade) (SRIKRACHANG,20 04). It was also ar efuge for communists (KANGWAN,20 00). After 1969,th e百1aigovemment encouraged settlement of remote紅'easto eliminate communism.百1eProvincial Administrative Organization rented 35 km2 of白isvalley from the Royal Forest Department for 30 ye紅s(1979 to 2009) for settlement of 3v illages (Ban Ruam Thai,B anY a n Su and Ban Phu Bon). On 31 July 2002,K ui Buri District recorded that there were 1,975,8 41 and 151 people in those villages,re spectively,a nd their populations were rather stable during the subsequent four 90 MATTAt、IASRIKRACHANG ANDS OMPOADS RIKOSAルIATARA 300 200 100 E E 』主 80 ロ i': 30 >- Eeι〉』sBb 60 〈" 2『 <( 40 20常 → o ヨ司 20 1iハU muE 。 n EZ u (の)・ Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Figure2 . Cilll1ated iagram ofK ui Bllri NationalP ark indicatingp eriodo f drought(I ight gray) and period of rainfa llsuperabundance (black). Thel l1eana nnualra infa llof IheK ui Buri districtis 8 57 mm.D ata obtainedf roll1 Ampho巴KuiBllri arem onthlya verages during 1990-2000. Source: Meteorological D巴parlll1enl Figure3 . Pineapplefi 巴Ilcs,ll1ango ancl jackfrllil orcharclsi n theK ui Canalv alley. ELEPHANT CROP RAID町GPROBLEMS AND THEIR SOLUTIONS 91 ye s.People now grow mainly pineapples to supply 11 factories in the province. Other 訂 economic plants are mango,j ackfruit,e ucalyptus (Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnhよ casuarina (Casuarina junghuhniana Miq.),s ugarcane,b anana,p ara-rubber,et c (Fig. 3). Four reservoirs (Huai Luek,S om Rong,Y an Su and Yang Chum) were constructed to support the agricultural activities and household utilization (KUI BURI NATION札 PARK, 1999).百leefforts to eliminate communism and expansion of cultivated釘'eashave also driven away the elephants from their preferred habitat. In addition,t he elephants were poached heavily,a nd the population estimate for 1990 was very low (SRIKRACHANG, 1992). METHODS Historical information associated with elephant crop raiding in this eacomes from 紅 documentary research.百lefrequency of crop raiding by wild elephants w邸 studiedfor three crop harvest periods during September 1999 to December 2000,wh ich was soon after 出estart of the project “Conservation and Restoration of Kui Buri Forest" initiated by His Majesty the King. Under this project,a t otal of about 108 million baht (USD 2.9 million) was allocated through the Royal Development Project Board for the following activities: reforestation 52.7%,re servoir construction 30%,so il and water conservation 11.2%,pa rk management 3.6%,l and development 0.9%,c heck dam building 0.8%,li fe quality and agricul佃ralpractice improvement 0.7%叩dele仲間tfood plant growth 0.1 % (0町ICEOF THE ROYAL DE四 LOP阻 NTPROJECT BOARD,1 999). 官lemonthly incidence and locations of crop raiding were collected合omthe farmers' complaints,re ports of investigation of the park rangers,an d observations of the first author. It is very difficult to know the group sizes of elephants raiding the fields because the incidents usually occurred du巾 g血enight. Therefore,e lephant herd sizes and locations where they moved out from出eforest edge to feed in the grassland泊血eeve凶ngwere observed and noted. However,s ome clear numbers of elephant raiders in croplands during the night were also recorded. Some known locations of elephant resting areas and birth areas in出eye紅s2000 and 2002 were recorded. RESULTS General Situation Pineapple: An important agroindusb抱1product of Thailand 聞 百lailandis白eworld's largest pineapple producer佃 dexporter (FALVEY,20 00). About 2.6 million tons of pineapple,o r 22% of the world's production and 39% of Asia's production,a re produced in Thailand (OFFICE OF AGRICUL'百成ALECONOMICS,1 994). Canned pineapple and pineapple juices are major products (OFFICE OF AGRIC瓜,TURAL ECONOMICS,20 01). In 1994,ca nned pineapple export peaked at 0.7 million tons,re presenting 46% of the world's production with 0.1 million tons of pineapple juice in血esame ye低 The export incomes from由iscrop during 1990ー2000were about 8,400-16,000 million baht per year (OFFICE OF AGRICULTURAL ECONOMICS,2 001). 92 N1Al寸ANASRIKRACHANG AND SoルIPOADSRIKOSAMATARA 1973 1974 1978 ]991 1998 ↑ present 口 remainingforestc over w E • cultivated land and settlemenl S • Kui BuriN P Scal巴 0 4 8km Figure 4. Changes of Kui Buri ReservedF orest in Prachuap Khiri Khan Province since 1973. Rapid conversion of th巴KuiCanal vall巴ysOCCUIT巴dsince 1978,w heng ov巴rllmentpromotedt hee xpansiono f pi口巴appl巴 plantationsa nd settlem巴ntalongt he canalsa nd their tributaries.So urce:T he Royal For巴stDepartm巴nt ELEPHANT CROP RAID町GPROBLEMS AND TI也IRSOLUTIONS 93 Pineapple has developed as am ajor agro・indu紺ysince 1967 ('百fONG-PRASERT,1983). At白紙 time,the Thai govemment also had developed ap olicy to eliminate communism from many remote forests by encourag泊gsettlement and providing由epeople with agricultural area. Prachuap Khiri Khan Province was one of the target areas for出ispolicy (KANGWAN,20 00). Thisp olicy led to ad ecline of forest area泊 thisprovmce 合om79% (5,038 km2) in 1961 to 28% in 1978 and 19% (1,228 km2)i n 1998 (CHARUPPAT,1 998), as shown in Fig. 4. Prachuap Khiri Khan Province b amethe producer of about 40--60% 回 ofthe coun町'spineapple (ALPHA悶 SEARCH,2001). In addition,出e百1aigovemment had supported investments to establish 11 fruit-canning factories ne釘 growingareas泊血is provin回 (OFFICEOF AG則CUL抗JRALECONOMICS,20 01). Therefore,th e elephant habitat白血eKui canal valley became invaded more and more due to uncontrolled forest encroachment and illegal logging as well as lack of appropriate development for白isagro-indus剖alcrop. When pineapple prices泊creased,farmers expanded their growing areas.百世scaused price declines in the following ye紅s,佃dfarmers abandoned the more remote plots close to the forest edges. Wild elephants could visit those croplands without conflict with people. When the crop prices became high again,th e farmers came back to expand the pineapple growing area,ca using more severe conflict with elephants. Elephant Crop Raiding Bそforeproject implementation Kui Buri Forest was protected and managed as an ational p釘kafter 1990 by出eRoyal ∞ Forest Depar佃1en.tCrop raiding by small groups of eleph組t(5-10 animals) curred du出19the night in the世yand frrst wet se部on(February-June) of 1991 near血eeas飽m and southem boundaries of the largest pkremn t.Thee lephants visited cropl dsne 釘 叩 佃 釘 the forest edge to合加kwater and take ab a由 inthe reservoirs (Huai Luek and Yan Su) and man-made ponds and to eat grass,p泊 eapples(ripe合uitsand leaves),an d visit m泊eral licks.官1efarmers tolerated the minor damage when the pineapple prices were dropp泊g during that periodσ'ig.6). Thes ituation has worsened since 1995,be cause crop raiding has been caused by large elephant herds and p泊eappleprices have risen (Fig. 6). Before ag roup of elephants comes out from the forest in the evening,叩 elephantgroans very loudly 2--6 times.τ'hen,t hey move out toge出.erin large compact herds (composed of several far凶ly山首ts)ω血er,回ervo出. Thec alves usually are泊由.ecenter of the herds or close to血e仕mothers(Fig. 5). About 70--80 elephants were often observed at Huai Luek reservoir,w hen they were drinking and taking ab ath in出eevenings of the dry months. However,th e large herds usually split aptinto smaller groups when they foraged in croplands during the night. Observations 釘 during 5-9 July 1997 (血efrrst wet season) indicated that the elephants ate both grasses and pineapples泊 thecroplands.τ'hee lephants moved back into the forest before dawn. CHUKAEW (1999) reported血at,p釘'askirmishes along the border between My紅m紅 military and minority Karen people during dry seasons of 1995 and 1996 caused the elephants to move to血eThai side. Many people also believe白atshortage of fodder and water so町'ces 泊 theforest during dry periods was the major cause. 94 MAITANA SRIKRACHANG AND SOMPOAD SRIKOSAMATARA Pineapple price: A critical factor Thes ituatinb ecame severe in the large Kui cana1 valley when pineapples were 'O expensive泊 1997and 1998σi'g. 6). F'Our elephants were killed by farmers. One ma1ea nd ne fema1ed ied n2 2 and 23 May 1997. Pst mrtem examinatini ndicated at e 'O 'O 'O 'O 'O 出 出 elephants ate pisnwhich might have been put inside pineapples. A carcass f ne 'O 'O, 'O 'O elephant 'Ofu nkn'Owns ex w出 f'Ound'On2 6 Janu創y1998 (dry se邸'On).Itapp訂ent1yc'Onsumed p'Ois'Oned p加eapplesand died 'On出eway back泊t'Othe f'Orest. On 20 March 1998 (世y seasn)an adult ma1ee lephant was shta nd bumt in the suthem valley. When pineapples 'O , 'O 'O became expensivesme farmers cmplained atthe elephants damaged abut 30 rai (5 , 'O 'O 血 'O hectares) ra but 100 tns fp .eapplesin ne night. This meant atthe farmers might 'O 'O 'O 'O 泊 'O 出 lse 40000ι600000 baht (USD 10500-16000) at as ingle raid by the elephants. When 'O , , , , pineapple prices were expensive again during 2002-2003 (Fig. 6), ne tuskless ma1ew as 'O sht n9 M arch 2003 and ne female died n1 0 June 2003 in ac rpland due tunknwn 'O'O 'O 'O 'O 'O 'O causes because autpsy was ntm ade. 'O 'O Solutions under HMth e King's project After the deaths ft he elephantsslutins t eeleph tprblem were frmulated 'O , 'O 'O 'O出 釦 'O 'O in May 'Of1 997 in am eeting led by Princess Rangsin'Opd'OlY ugala,( HisM ajesty's c'Ousin and an elephant lver) with the c peratin ft he First Army and the Ryal Frest 'O 'O'O 'O 'O 'O 'O Departmentbased nt he belief atshrtage ff da nd water inside the pkhad caused , 'O 血 'O 'O 'O'O 釘 crpr aiding by elephants in is Elephant habitat imprvement has been undertaken 'O 出 紅白. 'O in the nrthem crpl dva1leyespecia1ly enlargement fpnds and minera1licks. Ele仲間t 'O 'O 叩 , 'O 'O l'Overs b'Ought fruits such as bananas,j ac防 uit,p加eapples,gu町 aand sugarcane,l eft them ne thefrest edges tfeed the elephants. This me urehas been carried ut cntinuusly 紅 'O 'O 錨 'O 'O 'O t'O血epr回l entd町泊g血ecrop raiding se部'On(合Yt'O frrst wet seas'On) (Figs. 7a nd 8). Elephant f dp lants (bananabamb sugarcaneetc) have been plantedwith rws f 'O'O , 'O'O, , , 'O 'O dense,出'Omythicket 'OfS i Siad Nam (Acacia sp.) t'O prevent elephants合omentering the pl印刷i'Ons.When the trees gr'Owu p and have fewer th'Oms,t he elephants eat them. Additi'Ona1 measures by park rangers,m i1itary pers'Onnel and farmers include gu訂d泊g白ecr'Ops and chasing the elephants from the croplands. His Ma吋~邸esty's Pr,守吋oIjecはt implemented since May 1998 泊a白e釘ram a1ee l句eph佃 twa儲s曲shω'Otand bumt ∞0'n却2oMarch 1998. Ab'Out 凶16km♂22 'Oft he cr'Opμl釦 d泊血en'O抗rt恥h1聡e百m1va11ey wa酎s,r隠et旬um吋edpe宜mn叩anentlyt'O the pr吋,ectf'Orr ef'Orestati'On,s 'Oil and water c'Onservati'On,a nd elephant habitat impr'Ovement. Because the Kui cana1 and its tributaries have bec'Ome dry 'Orst 'Opped fI'Owing after being lng-term crop grwing eas9s ma11re servirsmany pnds and hundreds fc heck dams 'O 'O 釘 , 'O , 'O 'O were built tkeep water a11y e rund. ther 3r eservirs were cnstructed in 2004. 'O 紅 'O An'O 'O 'O S'Ome f'Orage cr'Ops企'Omthe Dep紅臨時nt'OfL ivest'Ock Devel'Opment have been s'Own fr'Om helicpters. Abut 30 artificia1 minera1 licks were a1screated. Checkpints were set up 'O 'O 'O 'O as statins fra n“elephant driving team" tprtect crps and elephant lives. Rangers and 'O 'O 'O 'O 'O farmers ehired tgudcrps and chase the elephants away frm the plantatins during 紅 'O 紅 'O 'O 'O 出epeak 'Ofth e cr'Opr aid泊gseas'On.百leref'Ore,n'Ot'O nly have wild elephants benefited fr'Om the pr'Oject,b ut a1s'O l'Oca1 pe'Ople have received inc'Ome fr'Om白evari'Ous activities 'Of出e prject. In additintw r gerstatinsPa Yang and Hup MaS angwere established 'O 'O, 'O 如 'O , , 泊 1998 and 2004respectivelyin b Kuicana1 valleys tprovide safety frt he elephants. , , 'O血 'O 'O ELEPHANT CROP RAIDING PROBLEMS AND THEIR SOLUTIONS 95 Figure 5. A group of a 22 elephants drinking water at Huai Luek reservoir on an evening in March 1998. The calves were close to their mothers. Picture drawn from a photo. 6 5 / r '@ ~ 4 e /) u0..' ·q 3 / I 0.. / '"a' ·~ 0.. '!!. 2 "' .8 ·~~/// 0.. 0 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 Figure 6. Pineapple prices in Thailand during 1991 and 2003, an important factor influencing the severity of man-elephant conflict at Kui Buri NP. Four wild elephants were killed by fanners when the pineapple prices were high in 1997 and 1998, and another two elephant deaths occurred in 2003. Source: Office of Agricultural Economics. 96 MAl寸ANASRIKRACHANG AND SOMPOAD SRIKOSAMATARA Figure 7. Duringd rys eason,P rinc巴ssRangsinopdolY ugalak indlyp rovided ab udg巴Itob uy food for wild elephants KuiBuri NP 川 Figure8 . Ana dult tuskerca 11leo ut 500na flerja ckfruitsw eret hrown onIh eg round nearP a YangR angerS tation (24 D巴ce11lber2 004)
