Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) II. Algal taxonomy PDF
Preview Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) II. Algal taxonomy
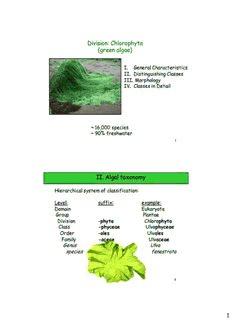
Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Distinguishing Classes III. Morphology IV. Classes in Detail ~ 16,000 species ~ 90% freshwater 1 II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix: example: Domain Eukaryote Group Plantae Division -phyta Chlorophyta Class -phyceae Ulvophyceae Order -ales Ulvales Family -aceae Ulvaceae Genus Ulva species fenestrata 2 1 DOMAIN Groups (Kingdom) 1.Bacteria- cyan obacteria (blue green algae) 2.Archae “Algae” 3.Eukaryotes 1. Alveolates- dinoflagellates 2. Stramenopiles- diatoms, heterokonyophyta 3. Rhizaria- unicellular amoeboids 4. Excavates- unicellular flagellates 5. Plantae- rhodophyta, chlorophyta, seagrasses 6. Amoebozoans- slimemolds 7. Fungi- heterotrophs with extracellular digestion 8. Choanoflagellates- unicellular 9. Animals- multicellular heterotrophs 3 Glaucophytes Plantae Rhodophyta Chlorophytes Chl b, Charophytes starch Land Plants 4 Adapted from Sadava 2014 2 Phylogenetics of Chlorophyta (morphological, molecular data) 5 classes: Chlorophyceae C h ol r Trebouxiophyceae o p Chl b, h y starch Ulvophyceae t a Prasinophyceae Encasement of egg Charophytes Charophyceae Embryo, cuticle Land plants 5 I. General Green Characteristics: 1) Pigments: ? 2) Chloroplast structure?: 3) Storage product? 4) Flagella? 6 3 Classes: Chlorophyceae = freshwater Trebouxiophyceae = freshwater, soil and marine Ulvophyceae = marine macroalgae Prasinophyceae = primarily marine flagellates, some freshwater; modern representatives of earliest green algae Charophyceae = freshwater; all terrestrial plants are derived from Charophycean class 7 II. Distinguishing among classes based on: 1. How flagella are attached/constructed: • basal bodies orientation • microtubule roots 2. Cell covering: • scales vs. cell wall 3. How cells divide: • aspects of mitosis and cytokinesis 8 4 II. Distinguishing among classes based on: 1. How flagella are attached/constructed: -basal bodies orientation -microtubule roots Flagella Basal Bodies Microtubule roots Cell anterior swimming direction 9 Flagella- complex cellular projections used for movement - bundle of nine fused pairs of microtubule doublets surrounding two central single microtubules "9+2" Basal bodies- attachment site of the flagella - containing a microtubules 9 triplet configuration forming a hollow cylinder Flagella Basal Bodies Microtubule roots Cell 10 5 Basal Bodies: ONE per flagellum, located at base of flagellum, anchoring into cell -pairs of basal bodies may be opposite parallel clockwise counterclockwise Flagella Basal Bodies Microtubule roots Cell 11 5 Flagella Microtubule roots: Basal Bodies -under the cell membrane at point of attachment of basal bodies Microtubule roots - may be cruciate or broadband Cell cruciate broad-band 12 6 II. Distinguishing among classes based on: 2. Cell covering- scales vs. cell wall Scales are made of complex Cell wall = usually cellulose polysaccharides secreted from golgi Chlorophyceae, trebouxiophyceae, prasinophyceae Ulvophyceae, charophyceae 13 II. Distinguishing among classes based on: 3. How cells divide: (aspects of mitosis and cytokinesis) • open vs. closed mitotic spindle • phycoplast vs. phragmoplast • furrowing vs. cell plate formation in center of cell closed metacentric centrioles Open -during Mt nuclear 14 envelope breaks down 7 II. Distinguishing among classes based on: 3. How cells divide: (aspects of mitosis and cytokinesis) • open vs. closed mitotic spindle • phycoplast vs. phragmoplast • furrowing vs. cell plate formation in center of cell furrowing furrowing Phycoplast: microtubules Phragmoplast: double parallel to dividing plane microtubules perpendicular -rare in algae to dividing plane -land plants 15 II. Distinguishing among classes based on: 3. How cells divide: (aspects of mitosis and cytokinesis) • open vs. closed mitotic spindle • phycoplast vs. phragmoplast • furrowing vs. cell plate formation in center of cell furrowing = most algae cell plate formation = a few algae and land plants 16 8 III. Morphology Chlorophyta: easiest division to identify visually • usually bright, grass-green color 17 III. Morphology Chlorophyta: easiest division to identify visually • usually bright, grass-green color Except - photo: Morgan Bond Snow algae Dunaliella Trentepohlia parasitic on Monterey Cypress 18 9 For classes: - any easy “rules” using external thallus morphology? - Prasinophyceans are all unicells, but… Charophyceans Chlorophyceae Ulvophyceae Ulvophyceae 19 Diversity in chloroplast shape: (unique to algae) “napkin ring-shaped parietal” “cup-shaped parietal” “stellate (star-shaped)” “axial (plate-like)” “ribbon-like” “reticulate (net-like)” “multiple discoid” 20 10
Description: