Description of two new Carlia species (Reptilia: Scincidae) from north-east Australia, elevation of Carlia pectoralis inconnexa Ingram & Covacevich 1989 to full species status, and redescription of Carlia pectoralis (de Vis 1884) PDF
Preview Description of two new Carlia species (Reptilia: Scincidae) from north-east Australia, elevation of Carlia pectoralis inconnexa Ingram & Covacevich 1989 to full species status, and redescription of Carlia pectoralis (de Vis 1884)
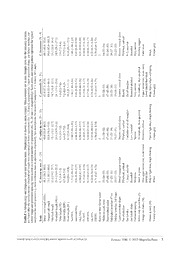
Zootaxa 3546: 1–28 (2012) ISSN 1175-5326 (print edition) www.mapress.com/zootaxa/ ZOOTAXA Article Copyright © 2012 · Magnolia Press ISSN1175-5334(online edition) urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3EFDDF27-88ED-4D0B-9668-4F9BE58547CA Description of two new Carlia species (Reptilia: Scincidae) from north-east Australia, elevation of Carlia pectoralis inconnexa Ingram & Covacevich 1989 to full species status, and redescription of Carlia pectoralis (de Vis 1884) CONRAD J. HOSKIN1,3 & PATRICK J. COUPER2 1School of Marine & Tropical Biology, James Cook University, Townsville, Queensland 4811, Australia. 2Queensland Museum, PO Box 3300, South Bank, Brisbane, Queensland 4101, Australia. 3Corresponding author. Email: [email protected] Abstract Scincid lizards belonging to the genus Carlia are found in eastern and northern Australia and in New Guinea and associated islands. These skinksare a particularly diverse component of the reptile fauna of north-east Australia. Carlia pectoralis (de Vis 1884) was formerly regarded as occurring over much of eastern Queensland, in north-east Australia. Here we show that it consists of four species: Carlia pectoralis,Carlia decora sp. nov.,Carlia rubigo sp. nov. and Carlia inconnexa Ingram & Covacevich 1989 (which was formerly described as a subspecies of C. pectoralis). Herein, we describe two new species, elevate C. p. inconnexa to full species status with a revised description, and redescribe C. pectoralis sensu stricto. The four species differ in aspects of scalation, morphology and colour pattern. Carlia decora sp. nov. occurs in vine thickets, rainforest margins and moist open forests in high rainfall coastal areas of mid-east and north- east Queensland. Carlia rubigo sp. nov. occurs in dry open forests of inland eastern Queensland and in some coastal areas of mid-eastern Queensland. Carlia pectoralis is distributed through open forests of south-east Queensland. Carlia inconnexa is restricted to rocky open forests on islands of ‘the Whitsundays’off mid-eastern Queensland. The addition of these three species brings the number of Australian Carlia to 22 species, 17 of which are found in Queensland. Key words: Carlia decora,Carlia rubigo,Carlia inconnexa, reptile, lizard, skink, Queensland, Whitsunday islands Introduction Carlia Gray 1845 is a diverse genus of skinks found in Australia, New Guinea and the Wallacea region of Southeast Asia. Carlia has at times also included members of the genus Lygisaurus de Vis 1884 (Cogger et al. 1983; Ingram & Covacevich 1988; Stuart-Fox et al. 2002) but genetic evidence does not support this generic assignment and Lygisaurus is currently recognised asa separate genus (Dolman & Hugall 2008). Genetic data also supports the recognition of Liburnascincus Wells & Wellington 1984, for several rock-adapted species formerly assigned to Carlia (Dolman & Hugall 2008). This leaves 39 currently recognised Carlia species: 19 in Australia, 1 in the Torres Strait between Australia and New Guinea, 13 in New Guinea, and 7 in Wallacea (Donnellan et al. 2009; Zug 2010). Only one species, C. storri Ingram & Covacevich 1989 is shared between these regions, occurring in north-east Australia and south-east New Guinea (Ingram & Covacevich 1989; Zug 2010). In Australia, Carlia spp. are restricted to eastern and northern parts of the country, with the highest diversity in the north-east (Ingram & Covacevich 1989; Couper et al. 2005; Donnellan et al. 2009; Wilson & Swan 2010). Ingram & Covacevich (1989) published a complete revision of Australian Carlia, describing two new species. Since then, an additional two species have been added, both resurrected from synonymy (Donnellan et al. 2009). Several other species that were described as Carlia during this period (Couper et al. 1994; Couper et al. 2005) were subsequently separated out with the resurrection of Lygisaurus (Dolman & Hugall 2008). Phylogenetic analyses of Carlia spp. support the status of all recognised species (Stuart-Fox et al. 2002; Dolman & Hugall 2008; Donnellan et al. 2009). Ingram & Covacevich (1989) recognised two subspecies of Carlia pectoralis: C. p. pectoralis for mainland populations and C. p. inconnexa for populations on islands of ‘the Whitsundays'off the coast of mid-east Accepted by L. Grismer: 16 Oct. 2012; published: 12 Nov. 2012 1 Queensland. This was based on tricarinate versus bicarinate dorsal scales and the dorsal patterns of breeding males. Unusually broad ranges were noticeable in several of the scale counts presented by Ingram & Covacevich (1989) for C. p. pectoralis hinting that the mainland populations may be polytypic. However, C. pectoralis has not been assessed in detail since Ingram & Covacevich's 1989 revision. Based on extensive fieldwork over the last decade, we have become aware of significant differences in colour pattern, morphology and scalation in Carlia pectoralis across its range. Here we quantify this variation and conclude that four species are present: Carlia pectoralis, the formerly recognised subspecies inconnexa, and two new species. We describe the new species, elevate inconnexa to species status giving a more detailed description, and redescribe C. pectoralis sensu stricto. The four species are diagnosable on aspects of morphology, scalation and colour pattern. They are also supported by genetic data that is not presented herein, representing monophyletic lineages that differ by over 10% from each other for protein- coding mtDNA (C. Hoskin, unpublished data). Materials and methods Specimens examined are held in the Queensland Museum (QMJ numbers) or the Australian Museum (R numbers). All measurements were taken using Mitutoyo electronic callipers and rounded to the nearest 0.1 mm. The following scale traits were counted: keels on the dorsal scales of the midbody; midbody scale rows; paravertebral scales, counted from the posterior margin of the hindlimb to the posterior edge of the parietal scales; supralabials; infralabials; supraciliaries; lamellae under the 4th toe, from claw sheath to junction of 3rd and 4th toes; lamellae under the 3rd finger, from claw sheath to the junction of the 2nd and 3rd fingers. The following scale traits were also scored: shape and contacts of the upper preocular scale (variation in this character was also assessed for multiple Carlia spp. and representatives of the closely related genera Lygisaurus and Liburnascincus—see Appendix for details); size of the palpebral disc; size of ear opening relative to size of palpebral disc; shape and orientation of the ear opening; number of ear lobules and their shape; degree of separation between the nasals; degree of separation between the prefrontals. Scales were generally counted/scored on the left side of the specimen. The following measurements were taken: snout to vent length (SVL); length of original tail (original versus regenerated tail determined by eye); interlimb distance, measured from axilla to groin; hindlimb length, from insertion to tip of longest digit, with limb stretched straight perpendicular to body (HLL); tibia length, measured from knee to heel with hindlimb compressed against body (TL); head width (HW), measured just anterior to the tympana at widest point of the head; head length (HL), from anterior edge of tympanum to snout. The following colour pattern traits were scored: the extent of the white mid-lateral line along flanks (females); evidence of a dorso-lateral pale line (females); position and extent of orange on flanks (males); colour of throat, neck and head; degree and extent of black edging to scales of throat, neck and head (males); colour of ventral and dorsal surfaces; degree of spotting or blotching on dorsal and lateral surfaces. The sex of adult specimens was determined by colour pattern—females lack breeding colours and have a white mid-lateral stripe from the nare to at least the forearm, whereas mature males lack the white stripe and show some indication of breeding colours and markings on the flanks, neck, throat and head. Systematics The skinks discussed herein can readily be assigned to Carlia Gray 1845 by the following character states: limbs well-developed with manus reduced to four digits; lower eyelid with a transparent palpebral disc; supranasal scales absent; rostral–frontonasal suture as wide as, or wider than the frontal; frontoparietal scales fused; interparietal small and distinct; ear-opening with enlarged lobules; dorsal body scales strongly keeled; males with conspicuous breeding colours on flanks (Ingram & Covacevich 1989; Cogger 2000; Dolman and Hugall 2008; Wilson and Swan 2008). Other ‘Carlia group’ genera (Dolman and Hugall 2008), Liburnascincus Wells and Wellington 1984 and Lygisaurus de Vis 1884, can be excluded from further consideration. Liburnascincus spp. have dorsoventrally flattened bodies, long sprawling limbs and the males lack breeding colours, whilst Lygisaurus spp. have smooth to weakly striate dorsal scalation. 2 · Zootaxa 3546 © 2012 Magnolia Press HOSKIN & COUPER Carlia decora sp. nov. Elegant Rainbow Skink (Figs 1A & B, 2A, 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A, 9A, 10A–C.) Holotype. QMJ90875, female, Alligator Ck, Mt Elliot, Bowling Green Bay National Park (19°26'07"S, 146°56'48"E, 50 m), north-east Queensland, C. J. Hoskin, 6 October 2011. Paratypes. J42498-500 Townsville Common (19°16'S, 146°49'E); QMJ90878-79 Riverside Gardens, Townsville (19°19'14"S, 146°44'30"E); J48391 Townsville, James Cook University Campus (19°20'S, 146°46'E); QMJ90876-77 Alligator Ck, Mt Elliot (19°25'54"S, 146°56'37"E); J86515 Deadman's Creek, Proserpine (20°30' 14"S, 148°33'23"E); J86516 Deadman's Ck, Proserpine (20°30'15"S, 148°33'22"E); J86449 Deadman's Creek, Proserpine (20°30'6"S, 148°33' 21"E); J63912 Cathu SF, Horse Ck (20°48' 51"S, 148°34'11"E); J74809 Brampton Is (20°49'S, 149°17'E); J74805 Cape Hillsborough NP (20°54'30"S, 149°00'30"E); J74807, J74812 Cape Hillsborough NP (20°55'30"S, 149°02' 30"E); J53395 Boulder Ck, campsite, via Mt Charlton (21°01'S, 148°43'E); J81405 East Point, Mackay (21°09'S, 149°13'E). Additional material. J79829 Curacoa Island (18°40'S, 146°33'E); J42502, J42504 Bluewater, ca. 20 km N Townsville (19°11'30"S 146°33'30"E); J79565 Pallarenda (19°12'S, 146°46'E); J42497 Townsville (19°16'S, 146°49'E); J79270, J79297-98, J79375 Townsville Common (19°16'S, 146°49'E); J48393 Townsville, James Cook University Campus (19°20'S, 146°46'E); J89137 Whitehaven Whitsunday Is (20°17'47"S, 149°3'13"E); J86754 Mount Macartney, Eungella (20°47'58.4"S 148°32'31.2"E); J79888-89 Cape Hillsborough NP, Smalley's Beach (20°54'S, 149°00'E); J74806, J74808 Cape Hillsborough NP (20°55'30"S, 149°02'30"E); J53396 Boulder Ck, campsite, via Mt Charlton (21°01'S, 148°43'E); J59968 Walkerston, 3 km W of the Peak Downs Hwy (21°13'S, 149°0'30"E); J60072-73 Sarina Beach, 9 km E of Sarina (21°23' 10"S, 149°18'30"E). Diagnosis. A moderate-sized Carlia (max SVL 49 mm) that can be distinguished from all its congeners by a combined suite of characters. Interparietal scale free. Dorsal scales tricarinate and hexagonally-shaped. Palpebral disc large. Ear aperture vertically elliptic (usually angled back) with a single large, rounded lobule on the anterior margin (Fig. 8A). Supraciliaries usually five. Prefrontals usually moderately separated (Fig. 9A). Upper preocular usually well developed and contacting posterior edge of 2nd loreal scale (if not contacting loreal, then broadly triangular in shape) (Figs. 10A–C). Breeding male with a pale blue throat and distinct orange upper lateral stripe that extends from forelimb to hindlimb; sometimes a less distinct orange lower lateral stripe is also present; black speckling present on neck and jawline but usually no, or limited, black-edging to scales on throat (Figs 1A, 2A, 4A, 5A). Adult female with a distinct, black-edged, white mid-lateral stripe that always extends to the groin (Figs 1B, 6A, 7A). Both sexes with an immaculate white or cream ventral surface. Etymology. From the Latin decora (feminine), meaning ‘beautiful'. In recognition of the beautiful form and colour pattern of this species. The species epithet is treated as a noun in apposition. Description of holotype (Fig. 7A). QMJ90875, female. Measurements (mm): SVL 38.2; tail 71.6; interlimb 19.2; HLL 18.9; TL 5.9; HW 6.0; HL 8.6. Scalation: Dorsal scale keels 3; midbody scale rows 30; paravertebrals 47; supralabials 7; infralabials 6; supraciliaries 5, subdigital lamellae (4th toe) 24; subdigital lamellae (3rd finger) 19. Upper preocular in contact with posterior edge of 2nd loreal scale; palpebral disc large; ear smaller than palpebral disc, vertically elliptic with one large rounded lobule on anterior margin; postsupralabial divided; nasals widely spaced; prefrontals moderately spaced. Colour pattern of holotype in preservative. Dorsum brown; top of head tawny brown. Indistinct, silvery dorso-lateral line, most prominent at the shoulders. Distinct, white mid-lateral line, bordered above and below by a thin black edging. Tawny brown upper flanks between mid-lateral and dorso-lateral lines. Lower flanks smudged greyish, merging to white belly. Ventral surfaces immaculate white. Tail brown with irregular fine black markings. Prominent white spot at posterior base of hindleg. Legs brown with dark mottling. Fine white line from nare, under eye, through tympanum, and continuous with mid-lateral line. Description of type series. Body robust with keeled dorsal scales. Head barely distinct from neck. Snout rounded in profile. Limbs moderate; four fingers; five toes. Adult measurements and proportions: see Table 1. Scalation: Rostral in broad contact with frontonasal. Postsupralabial divided. Nasals widely spaced. Prefrontals large and usually in moderate separation (moderate separation 74%, narrow separation 26%) (Fig. 9A). Supraoculars 4; 1 and 2 in contact with frontal; 2, 3 and 4 in contact with frontoparietal. Frontoparietals fused, forming a single shield. Interparietal distinct. Enlarged nuchal scales 2. Loreals 2. Preoculars 2. Presubocular THREE NEW CARLIA SPECIES FROM NORTH-EAST AUSTRALIA Zootaxa 3546 © 2012 Magnolia Press · 3 single. Supraciliaries 5 (very rarely 6 or 7). Upper preocular well developed and contacting posterior edge of 2nd loreal scale (66%) or, if not contacting loreal, then broadly triangular in shape (33%) (Fig. 10A–C). Lower eyelid movable, with clear window; palpebral disc large, occupying more than half of lower eyelid. Ear aperture smaller than palpebral disc; usually vertically elliptical (68%) but sometimes rounded (32%); with 1 large rounded lobule on anterior margin (Fig. 8A). Supralabials 7, with the fifth positioned below the eye. Infralabials 6. Three scales between the nasal scale and the presubocular. Midbody scale rows 26–30 (mean = 29); dorsal scales with tricarinate keels. Paravertebral scale rows 46–50 (mean = 47). Subdigital lamellae under 3rd finger 17–22 (mean = 20). Subdigital lamellae under 4th toe 22–31 (mean = 27). FIGURE 1. Photos of: (A) C. decora sp. nov., male, Pallarenda; (B) C. decora sp. nov., female, Townsville; (C) C. rubigo sp. nov., male, Magnetic Island; (D) C. rubigo sp. nov., female, Magnetic Island; (E) C. pectoralis, male, Murgon area; (F) C. pectoralis, female, Carnarvon Range; (G) C. inconnexa, QMJ89138, male, Whitsunday Island; (H) C. inconnexa, female, Whitsunday Island. No photo in life is available for a male C. inconnexa. The photo in (G) was flipped to match the orientation of the other panels. Photo credits: Conrad Hoskin (A, B), Steve Wilson (C–F, H), Jeff Wright (G). 4 · Zootaxa 3546 © 2012 Magnolia Press HOSKIN & COUPER es for the majority of traits pe, ear lobule number, ear attern represent the typical C. inconnexa (N = 9) 49.7 (46.6–52.4) 90.0 (82.0–103.2) 23.2 (20.8–24.4) 24.9 (20.2–27.2) 7.9 (7.2–8.6) 7.7 (7.1–8.6) 11.0 (10.1–12.3) 1.88 (1.68–2.22) 0.47 (0.45–0.50) 0.51 (0.45–0.58) 0.16 (0.15–0.18) 0.16 (0.15–0.17) 0.22 (0.21–0.24) 0.70 (0.69–0.72) 2 34 (32–34) 51 (49–53) 29 (27–31) 22 (21–23) Narrow vertical sliver Elliptical, vertical 1–2, anterior Rounded Very narrow Mottled, ragged Faint wash Black Cream-grey ogy is shown as mean (range). Measurements are in mm. Sample sizewer specimens (14, 11, 9 and 4, respectively). Upper preocular shapecimens (42, 50, 38 and 15, respectively). Scale states and colour ped). See descriptions for details of variation. F = female; M = male. sp. nov. C. rubigo (N = 21) C. pectoralis (N = 21) 40.0 (33.9–44.2) 42.8 (37.3–47.0) 64.0 (56.3–73.6) 61.9 (53.5–68.4) 19.1 (16.3–22.7) 19.7 (16.8–22.1) 20.3 (18.9–21.8) 21.1 (19.6–23.6) 6.3 (5.5–7.0) 6.6 (5.2–7.6) 6.4 (5.7–7.2) 7.2 (6.0–8.3) 9.1 (7.8–10.0) 10.2 (8.7–11.1) 1.60 (1.39–1.91) 1.46 (1.19–1.54) 0.48 (0.43–0.53) 0.46 (0.42–0.53) 0.50 (0.46–0.57) 0.49 (0.46–0.54) 0.16 (0.15–0.17) 0.15 (0.14–0.17) 0.16 (0.14–0.18) 0.17 (0.15–0.19) 0.23 (0.20–0.25) 0.24 (0.22–0.26) 0.70 (0.64–0.74) 0.71 (0.65–0.77) 3 3 31 (30–32) 31 (28–32) 47 (45–48) 47 (45–50) 27 (23–29) 25 (23–28) 19 (17–21) 19 (18–21) Narrow vertical sliver Narrow vertical sliver Elliptical, vertical Round 1 anterior or on all margins On all margins Low, rounded Rounded–pointed Narrow Very narrow To midbody, then speckled To midbody, then speckled Extensive, diffuse Upper lateral line, weak–mod. lower lateral line/chest Pale or light blue, black flecking Blue, heavy black scalloping Cream-grey Cream-grey ostic scale and pattern traits. MorpholOriginal tail length was measured on fg were scored on a larger number of sst common state in specimens examin sp. nov. C. decora (N = 23) 44.2 (38.2–48.6) 75.1 (64.1–89.6) 22.6 (19.2–25.7) 21.4 (18.9–23.2) 6.7 (5.9–7.4) 6.7 (6.0–7.8) 9.6 (8.6–10.9) 1.71 (1.35–2.12) 0.51 (0.48–0.55) 0.50 (0.47–0.55) 0.15 (0.14–0.18) 0.15 (0.14–0.17) 0.22 (0.20–0.24) 0.71 (0.67–0.76) 3 29 (26–30) 47 (46–50) 27 (22–31) 20 (17–22) Broad triangular wedge Elliptical, vertical 1, large, anterior Rounded Moderate Bold, to groin Thin upper lateral line, weak lower lateral line Pale or light blue, black flecking White diagnmes. pacine. mo TABLE 1. Morphology and are listed after the species nalobule shape and prefrontal scondition for each species (i. Trait Snout–vent length (SVL) Original tail length Interlimb length Hindlimb length (HLL) Tibia length (TL) Head width (HW) Head length (HL) Tail/SVL Interlimb/SVL HLL/SVL TL/SVL HW/SVL HL/SVL HW/HL Keels on mid–dorsal scales Midbody scale rows Paravertebral scales thSubdigital lamellae 4 toe Subdig. lamellae 3rd finger Upper preocular shape Ear orientation Ear lobules Ear lobule shape Prefrontal spacing White mid–lateral line (F) Orange on flanks (M) Throat & neck (M) Ventral colour THREE NEW CARLIA SPECIES FROM NORTH-EAST AUSTRALIA Zootaxa 3546 © 2012 Magnolia Press · 5 Colour pattern in preservative. Males (Figs 3A, 4A, 5A): Dorsal surfaces brown, with paired paravertebral dark markings (and occasionally white flecks) present on some individuals, particularly on the posterior half of the body and tail. Iridescent sheen to scales. Top of head generally lighter brown; often with fine black dots. Flank light brown with a thin orange upper lateral line from above forelimb to above hindlimb; sometimes a faint orange lower lateral line. Ventral surfaces immaculate white, cream or creamy yellow. Throat, neck and jawline blue or white. Throat generally unmarked but sometimes with grey or black flecking or fine edging to scales; occasionally grey or dark smudging. Neck and jawline generally marked with fine dark flecks or dark scale edging. Limbs brown on top, pale below. Prominent white spot at posterior base of hindleg. Females(Figs 6A, 7A):Dorsal surfaces brown, with paired paravertebral dark markings and white flecks present on some individuals. Iridescent sheen to scales of some individuals. Top of head generally lighter brown; often with fine black dots. Bold, white mid-lateral line, edged with black, always extends full length of flank to groin. Sometimes also a faint, silvery dorso-lateral line, particularly evident at shoulders. Upper flanks coppery, bronze or tawny. Lower flanks coppery or brown and merging with pale underside. White line from nare, under eye, through tympanum, and continuous with white mid- lateral line. Ventral surfaces immaculate white, cream or grey. Limbs brown on top, pale below. Prominent white spot at posterior base of hindleg. Colour pattern in life (Figs 1A, 1B, 2A). Dorsum of both sexes brown with paravertebral row of black and pale dots, generally becoming more distinct posteriorly. Ventral surfaces immaculate white or cream. Breeding males with uniform pale blue or white throats and fine dark speckling along edge of jawline. A sharply defined orange or red upper lateral stripe encompasses two scale rows and extends from just in front of the forelimb to groin. At maximum breeding extent a ragged, orange lower lateral line is also present, the throat can be sky blue, and grey speckling on the neck and throat can be quite pronounced in some individuals. Occasionally, fine grey or black edging is present on scales of the throat. Adult females have a white mid-lateral stripe, with well-defined dark edges, extending from nostril or eye to groin. The upper flanks, above the white mid-lateral line, are usually tawny brown. In many females a narrow, coppery dorsolateral stripe is also discernable, particularly at the shoulders. FIGURE 2. Comparison of males in full breeding condition: (A) C. decora sp. nov., Townsville; (B) C. rubigo sp. nov., Magnetic Island; (C) C. pectoralis, Woodgate National Park; (D) C. inconnexa, QMJ89134, Whitsunday Island. Photos: Conrad Hoskin (A, B), Steve Wilson (C), Jeff Wright (D). Comparison. Only likely to be confused with C. vivax de Vis 1884, members of the C. pectoralis group (C. pectoralis, C. rubigo sp. nov. and C. inconnexa), and female C. jarnoldae Covacevich & Ingram 1975. Carlia decorasp. nov. is most closely related to C. vivax (C. Hoskin, unpublished data) and females of the two species are superficially similar. The two species also share some key traits, such as an upper preocular that contacts the 2nd 6 · Zootaxa 3546 © 2012 Magnolia Press HOSKIN & COUPER loreal or is a broad triangular wedge, and a vertically elliptical ear opening with a single large, rounded lobule on the anterior margin. However, C. decora sp. nov. can be readily distinguished from C. vivax by tricarinate versus bicarinate mid-dorsal scales, respectively. Tricarinate mid-dorsal scales also separates C. decora sp. nov. from C. inconnexa (predominately bicarinate), and the latter is also a larger skink with higher midbody, paravertebral and subdigital lamellae scale counts (Table 1). The male and female colour patterns also differ obviously between C. decora sp. nov. and C. inconnexa (Table 1, Figs 1–7; see C. inconnexa Comparison section). Carlia decora sp. nov. differs from C. pectoralis and C. rubigo sp. nov. in a variety of ways. The upper preocular scale in C. decora sp. nov. is broadly triangular (and usually contacts the loreal) versus a narrow vertical sliver in C. pectoralis and C. rubigo sp. nov. (Fig. 10). The prefrontals are generally moderately separated in C. decora sp. nov. versus narrowly separated or in point contact in C. pectoralis and C. rubigo sp. nov. (Fig. 9). Carlia decora sp. nov. generally has one large, rounded anterior ear lobule whereas C. rubigo sp. nov. often has low, rounded lobules present on other margins and C. pectoralis generally has lobules present on all margins of the ear (and these lobules are often pointed) (Fig. 8). Additionally, the ear opening of C. pectoralis is usually rounded, versus typically vertically elliptical in C. decora sp. nov. (Fig. 8).Carlia decora sp. nov. is a more elongate (> interlimb/SVL) skink than C. pectoralis and C. rubigo sp. nov., and is larger (average and max SVL) than C. rubigo sp. nov. (Table 1). Female C. decora sp. nov. have a bold white, dark-edged mid-lateral line that always extends to the groin, whereas this stripe rarely extends as a distinct white line onto the posterior half of the flank in C. pectoralis and C. rubigo sp. nov. (Figs 1, 6). Additionally, in female C. decora sp. nov. the upper flanks are generally tawny brown and there is often some indication of a pale dorso-lateral line at the shoulders (Figs 1, 6). The colour pattern of breeding males differs between Carlia decora sp. nov.,C. pectoralis and C. rubigo sp. nov. (Figs 1–5). Breeding male C. decora sp. nov. have a thin orange upper lateral line and occasionally also a less distinct, ragged orange lower lateral line. The throat is pale or light blue and grey or black flecking is generally restricted to the jawline and side of the neck and rarely extends obviously onto the throat. In male C. pectoralis,the lower lateral orange line is often more obvious and the orange regularly extends onto the chest, and the scales of the neck and throat are typically heavily edged with black (i.e. black scalloping). The flanks of male C. rubigo sp. nov. arediffusely washed with orange or copper colouration, rather than the orange being restricted to upper and lower lateral lines. The ventral surfaces of male and female C. decora sp. nov. are typically immaculate white or cream, versus tinged with grey in C. pectoralis and C. rubigo sp. nov. Female C. decora sp. nov. and C. jarnoldae are superficially similar in that both have a white mid-lateral line that always extends to the groin. This line is broader on C. jarnoldae and bordered above by a more obvious dark band. Additionally, C. decora sp. nov. is larger (mean SVL 44 mm vs. 38 mm), generally has 5 supraciliaries (vs. usually 7), has vertically elliptical ear opening (vs. horizontally elongate) and with a large, rounded lobule on anterior margin (vs. a small pointed lobule on anterior margin and smaller pointed lobules on other margins). Genetics. Carlia decora sp. nov. is approximately 16% divergent (900 bp ND4 mtDNA) from C. rubigo sp. nov., C. inconnexa and C. pectoralis. Carlia decora sp. nov. is genetically most similar to Carlia vivax (approximately 13% divergence) (C. Hoskin, unpublished data). A representative ND4 mtDNA sequence for this species from the type locality is JX291972 (GenBank accession number). Distribution. Carlia decora sp. nov. is found in high rainfall coastal areas of mid-east and north-east Queensland from approximately Sarina in the south to Mt Molloy in the north (Fig. 11). The distribution is centred on two areas: the Sarina-Mackay-Proserpine region and the Townsville region (Mt Elliot, Townsville city area, Bluewater Range). There are no records from the drier forests that separate these two regions. Carlia decora sp. nov. is also known from some offshore islands in these regions (e.g. Brampton Is., Whitsunday Is., and Curacoa Is. in the Palm Islands).The most northerly record of C. decora sp. nov. (Mt Molloy, north-west of Cairns) is a considerable distance from the records in the Townsville region. The lack of records in the intervening area is interesting because wet forests are fairly continuous through this region, and generally well surveyed. This may represent a genuine disjunction in the distribution (perhaps due to competing species in the Wet Tropics wet forests) or C. decora sp. nov. may be distributed through this area patchily or at low density. Habitat and habits. Carlia decora sp. nov. is found in riparian forest, vine thickets, rainforest margins, seasonally moist open forests and town gardens. It generally occurs in thicker vegetation amongst a matrix of open woodland and is particularly abundant in vine thickets and in the ecotone between riparian rainforest and grassy Eucalyptus woodland (Fig. 12A). It occurs in areas with thick leaf litter and other ground cover (low vegetation, rocks, logs, etc.). It is a common garden skink in Townsville. Carlia decora sp. nov. is an active, ground-dwelling skink that retreats rapidly to thick leaf litter and dense vegetation when disturbed. THREE NEW CARLIA SPECIES FROM NORTH-EAST AUSTRALIA Zootaxa 3546 © 2012 Magnolia Press · 7 FIGURE 3. Comparison of typical dorsal pattern of males: (A) C. decora sp. nov., QMJ74807, Cape Hillsborough National Park; (B) C. rubigo sp. nov., QMJ76659, Magnetic Island; (C) C. pectoralis, QMJ63390, Wongi State Forest; (D) C. inconnexa, QMJ89138, Whitsunday Island. The photo in (A) was flipped to match the orientation of the other panels. Photos: Jeff Wright. 8 · Zootaxa 3546 © 2012 Magnolia Press HOSKIN & COUPER FIGURE 4. Comparison of typical lateral pattern of males: (A) C. decora sp. nov., QMJ90878, Townsville; (B) C. rubigo sp. nov., QMJ90885, Magnetic Island; (C) C. pectoralis, QMJ63390, Wongi State Forest; (D) C. inconnexa, QMJ89138, Whitsunday Island. Photos: Jeff Wright. THREE NEW CARLIA SPECIES FROM NORTH-EAST AUSTRALIA Zootaxa 3546 © 2012 Magnolia Press · 9 FIGURE 5. Comparison of typical ventral pattern of males: (A) C. decora sp. nov., QMJ90878, Townsville; (B) C. rubigo sp. nov., QMJ90885, Magnetic Island; (C) C. pectoralis, QMJ63390, Wongi State Forest; (D) C. inconnexa, QMJ89138, Whitsunday Island. Photos: Jeff Wright. 10 · Zootaxa 3546 © 2012 Magnolia Press HOSKIN & COUPER
