Contributions to the study of the comparative morphology of teeth and other relevant ichthyodorulites in living supraspecific taxa of Chondrichthyan fishes. Part. A: Selachii. N°2c: Order : Carcharhiniformes Families: Proscylliidae, Hemigaleidae, Pseudotr PDF
Preview Contributions to the study of the comparative morphology of teeth and other relevant ichthyodorulites in living supraspecific taxa of Chondrichthyan fishes. Part. A: Selachii. N°2c: Order : Carcharhiniformes Families: Proscylliidae, Hemigaleidae, Pseudotr
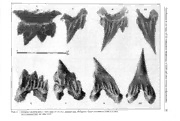
BULLETIN DE L'INSTITUT ROYAL DES SCIENCES NATURELLES DE BELGIQUE, BIOLOGIE, 61: 73-I20, 1991 BULLETIN VAN HET KONINKLIJK BELGISCH INSTITUUT VOOR NATUURWETENSCHAPPEN, BIOLOGIE, 61: 73-120, 1991 Contributions to the study of the comparative morphology of teeth and other relevant ichthyodorulites in living supraspecific taxa of Chondrichthyan fishes Editor : M_ STEHMANN Part A: Selachii. No. 2c: Order: Carcharhiniformes Families : Proscylliidae, Hemigaleidae, Pseudotriakidae, Leptochariidae and Carcharhinidae o_c_ by J_ HERMAN, M_ HOVESTADT-EULER and HOVESTADT Abstract Kurzfassung The description of micro-teeth within the Carcharhiniformes is hereby Die Beschreibung der Mikrozahne innerhalb der Carcharhiniformes completed by presentation of generic representatives for the remaining wird hiermit vervollstandigt durch die Behandlung von Gattungsver families Proscylliidae, Hemigaleidae, Pseudotriakidae, Leptochariidae tretem der restlichen Familien Proscylliidae, Hemigaleidae, Pseudo and Carcharhinidae. Detailed descriptions of the tooth morphology triakidae, Leptochariidae und Carcharhinidae. Deren Zahnmorphologie are given, as well as $EM-photographs. The tooth morphology of the wird im einzelnen beschrieben, begleitet von REM-Photos. Die Zahn genera herein concerned is compared with those published of the other morphologie der hier behandelten Gattungen wird verglichen mit den carcharhiniform families in two previous issues of this series, in order jenigen der anderen carcharhiniformen Familienvertreter, die bereits to elucidate the interrelationships within this shark order also from in zwei vorhergehenden Beitragen dieser Serie behandelt wurden, urn an odontological point of view. The dental histology for the carcharhi die Verwandtschaftsbeziehungen innerhalb dieser Haiordnung auch niform genera is commented on, and their dental vascular types are unter odontologischen Gesichtspunkten zu erhellen. Die Zahn re-examined. The results are summarized in a differential diagnosis histologie der carcharhiniformen Gattungen wird kommentiert, und for all carcharhiniform genera and families. Dental morphology, histo die verschiedenen Formen des Zahngefal3systemes sind emeut unter logy and vascularisation results allow to provide an odontological key sucht worden. Aile Ergebnisse sind in einer Differentialdiagnose fiir to all supraspecific taxa of this order and to suggest a number of aile Gattungen und Familien der Carcharhinifom1es zusammengefal3t. systematical adjustments. The glossary for the series, as published so Die somit vollstandigen Ergebnisse zur Zahnmorphologie, -histologie far, has been complemented and updated. und -geftil3versorgung ermoglichten die Aufstellung eines zahnmor Key-words : Elasmobranchii, Selachii, Proscylliidae, Hemigaleidae, phologischen Bestimmungsschliissel fiir aile supraspezifischen Taxa Pseudotriakidae, Leptochariidae, Carcharhinidae, Odontology. dieser Haiordnung und Vorschlage fiir eine Reihe von moglichen Anderungen der Klassifikation. Das Glossar fiir bisher veroffentlichte Beitrlige der Serie wurde vervollstandigt und auf den aktuellen Stand Resume gebracht. Schliisselworter : Elasmobranchii, Selachii, Proscylliidae, Hemigalei dae, Pseudotriakidae, Leptochariidae, Carcharhinidae, Odontologie. La description de Ia morphologie dentaire des genres appartenant aux Proscylliidae, Hemigaleidae, Pseudotriakidae, Leptochariidae et Car charhinidae complete !'etude odontologique des Carcharhiniformes a laquelle deux fascicules precedemment publies (Triakidae et Scyliorhi Introduction nidae) ont ete consacres. a Lorsque leurs dimensions l'autoriserent, ces dents ont ete figurees !'aide de cliches M.E.B. To complete Part 2 on Carcharhiniformes of this series, L'histologie dentaire des Carcharhiniformes est commentee et leurs this fascicle will deal with the following families : Pro modes de vascularisation dentaire sont reexamines. scylliidae, Hemigaleidae, Pseudotriakidae, Leptocharii Les donnees que fournissent conjointement morphologie, histologie et vascularisation dentaires permettent d'etablir une clef odontologique dae and Carcharhinidae. The tooth morphology of their pour !'ensemble des taxons supraspecifiques de cet ordre, et de formu supraspecific taxa is described and eventually illustrated ler un certain nombre de propositions de reajustements systematiques. by SEM-photographs. For Triakidae and Scyliorhinidae, Le glossaire qui interesse !'ensemble de cette serie de publications a see Part 2a (HERMAN et al., 1988) and 2b (HERMAN et ete revu et sensiblement augmente. Mots-cles : Elasmobranchii, Selachii, Proscylliidae, Hemigaleidae, al., 1991) respectively. The dimensions of teeth of the Pseudotriakidae, Leptochariidae, Carcharhinidae, Odontologie. following genera were too large to produce SEM- 74 J. HERMAN, M. HOVESTADT-EULER and D.C. HOYESTADT photographs, and consequently their illustration is thus BIGELOW & SCHROEDER (1948), CAOENAT & BLACHE beyond the scope of this series. However, their morpho (1981) and CoMPAGNO (1984, 1988) as is shown in the logy is well known and illustrated in previous works, table below : such as BAss, o'AuBREY & KlsTNASAMY (1973, 1975), BIGELOW & CADENAT & BASS & al. COMPAGNO SCHROEDER BLACHE Genus 1948 1973 1975 1981 1984 1988 Hemipristis pl. 5 f. 3.1 I sogomphodon f. 73 p. 511 pl. 19 Carcharhinus pl. 10 p. 488 Glyphis p. 509 f. 3.1 Lamiopsis p. 512 pl. 19 Nasolamia p. 516 Negaprion pl. 4 p. 518 Prionace f. 47, 48 pl. 6 f. 167 p. 522 Galeocerdo f. 44 pl. 7 f. 164 p. 504 pl. 19 Sphyrna f. 85, 86 pl. 12 p. 554 Eusphyra p. 540 Teeth of a subadult specimen of lsogomphodon are illus and Scyliorhinidae were published in previous fascicles trated additionally. of this series (Part A : 2a and 2b). The systematic arrangement of the order Carcharhinifor The teeth of the following 113 specimens of 36 species mes following below is based on tooth morphology. A were examined : key and a systematic diagram are provided to assist other Carcharhinus albimarginatus investigators and promote further considerations. 1 sex unknown A major revision of Carcharhiniformes was recently Carcharhinus amboinensis presented by CoMPAGNO (1988), and the nomenclature 1 sex unknown of all the taxa mentioned in the present paper is accord Carcharhinus brachyurus ing to this work. 1 sex unknown The original literature reference of each specific taxon Carcharhinus brevipinna will be given in the descriptive part, respectively, and 1 sex unknown 1 female not be repeated in the bibliography. Carcharhinus falciformis 1 sex unknown 1 female 2 males Carcharhinus galapagensis Systematics and materials 1 sex unknown Carcharhinus leucas ORDER:CARCHARHINWORMES 1 sex unknown sensu COMPAGNO (1988) Carcharhinus limbatus 4 sex unknown 1 male The order comprises eight families : Triakidae, Scylio Carcharhinus longimanus rhinidae, Proscylliidae, Leptochariidae, Pseudotriakidae, 1 sex unknown Hemigaleidae, Sphyrnidae and Carcharhinidae. Carcharhinus melanopterus 1 female The tooth morphology descriptions and illustrations, as Carcharhinus plumbeus well as separate systematic evaluations on the Triakidae 1 sex unknown Contributions to the study of the comparative morphology of teeth and other relevant ichthyodorulites 75 Carcharhinus sealei 1 male REMARK Carcharhinus signatus 1 female Carcharhinus sorrah 3 males Odontological features also allow grouping into families Chaenogaleus macrostoma 2 females and subfamilies. However, this scheme differs rather Ctenacis fehlmanni (holotype) 1 female widely from that of CoMPAGNO (1988). Eridacnis barbouri 1 female 1 male The authors will here not draw any nomenclatorially Eridacnis radcliffei 1 male valid conclusions from their odontological results. Being Eridacnis sinuans 1 male aware of dealing with one complex of characters only, Collum attenuatus 1 male they will present their odontological results and leave Hemigaleus microstoma I male it to following revising authors to incorporate also odon Leptocharias smithii 4 females 3 males tological points of view in a full systematic review with Loxodon macrorhinus 3 females 1 male possible taxonomic and nomenclatorial changes. Negaprion acutidens 1 sex unknown Paragaleus pectoralis 2 females 2 males Prionace glauca 8 females 6 males Description of the odontological morphotypes Proscyllium habereri 1 female 1 male Pseudotriakis aerates (holotype) 1 male Pseudotriakis microdon 4 females 6 males Family: Proscylliidae FowLER, 1941 Rhizoprionodon acutus 5 females 5 males Scoliodon terranovae 1 female I male This family, after CoMPAGNO (1988), includes the two Sphyrna lewini 2 sex unknown 1 female 2 males subfamilies : Sphyrna mokarran 2 sex unknown Proscylliinae Sphyrna tudes 1 male Sphyrna zygaena 10 females 7 males Genus Proscyllium HILGENDORF, 1904, type species Triaenodon obesus 1 female Proscyllium habereri. Genus Eridacnis SMITH, 1913, type species Eridacnis The revision of CoMPAGNO (1988) resulted in the fol radcliffei. lowing arrangement of families and subfamilies : Genus Ctenacis CoMPAGNO, 1973, type species Ctenacis Family : ScvuoRHINIDAE fehlmanni. Subfamily : Atelomycterinae Schroederichthyinae Golluminae Scyliorhininae Pentanchinae : Tribe : Galeini Pentanchini Genus Gollum CoMPAGNO, 1973, type species Gollum Family : PROSCYLLIIDAE attenuatus. Subfamily : Proscylliinae Golluminae The teeth of species of the family Proscylliidae in gene Family : PsEuDOTRIAKIDAE ral have a well developed principal cusp flanked by up Family : LEPTOCHARIIDAE to three cusplets. Family : TRIAKlDAE The root is mostly secondarily anaulacorhizid, often Subfamily : Triakinae secondarily hemiaulacorhizid and rarely holaulacor Galeorhininae : Tribe : Iagini hizid. Galeorhinini Family : HEMIGALEIDAE HETERODONTY Subfamily : Hemigaleinae H emipristinae A weak dignathic heterodonty can be present by relati Family : CARCHARHlNIDAE vely higher cusplets and a shorter principal cusp in lower Subfamily: Galeocerdinae teeth. A weak sexual heterodonty is sometimes present Scoliodontinae by a slightly higher principal cusp and more cusplets in Carcharhininae: Tribe: Rhizoprionodontini females. A gradient monognathic heterodonty is always lsogomphodontini present by little broader lateral teeth with a more inclin C archarhinini ed or oblique principal cusp. The lateral teeth and those Triae nodontini toward the commissure are mostly smaller than the ante Family : SPHYRNIDAE rior ones. .. 76 J. HERMAN, M. HOVESTADT-EULER and D.C. HOYESTADT Genus : Ctenacis CoMPAGNO, 1973 The root is secondarily anaulacorhizid, showing two relatively long and narrow lobes forming an angle at The type species of this monotypic genus is Ctenacis the root base. The dimensions of the teeth are plurimilli fehlmanni (SPRINGER, 1968). Two upper teeth of the metrical in range. holotype were available for examination. The outer face of the principal cusp is weakly convex, presenting a few well developed striae, which run from Ctenacis fehlmanni (SPRINGER, 1968) crown base halfway to the apex of the principal cusp. (Plate 1) A reticulated ornamentation is present between the striae on the crown base. The inner face of the principal cusp Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, and cusplet is strongly convex, also presenting striae, 81 : 613-624. which run from crown base toward apex of the principal The teeth of this species have a broad based, relatively cusp. short principal cusp. The principal cusp is oriented more The outer face of the root is rather low, presenting an or less obliquely toward the commissure, and one also irregular series of about five well developed but small short and broad based, distal cusplet is present. foramina. The root varies between holaulacorhizid and secondarily The inner face shows a ridge, which has about the same anaulacorhizid and has two lobes, that are relatively long shape as the angle of the root lobes. It divides the inner and narrow and form an angle at the root base. The face of the root into two sections, and its central part dimensions of the teeth are plurimillimetrical in range. is more or less protuberant. A foramen is present in the The outer face of the principal cusp and cusplet is weak centre of the ridge. ly convex, presenting well developed striae, that run from crown base toward apex of the principal cusp and Genus: Proscyllium HILGENDORF, 1904 cusplet. A reticulated ornamentation is present between the striae on the crown base. This genus is monotypic with the type species Proscyl The inner face of the principal cusp and cusplet is lium habereri Hilgendorf, 1904. strongly convex, also presenting striae, that run from crown base toward apex of the principal cusp and cus Proscyllium habereri HILGENDORF, 1904 plet. The outer face of the root is rather high, presenting an (Plates 4, 5) irregular series of about five well developed but small foramina. Sitzungsberichte der Gesellschaft fiir Naturforschende The inner face shows a ridge, having about the same Freunde Berlin, Jahrgang 1904 (2): 39-41. shape as the angle of the root lobes. It divides the inner The teeth of this species have a broad based, relatively face of the root into two sections, and its central part short principal cusp. The principal cusp is oriented more is more or less protuberant. A foramen is present in the or less obliquely toward the commissure, and two or centre of the ridge. sometimes three also short and broad based distal cus plets are present. Genus : Eridacnis SMITH, 1913 The root is secondarily hemiaulacorhizid, showing two relatively long and narrow lobes forming an obtuse angle This genus comprises three species : Eridacnis barbouri at the root base. The dimensions of the teeth are pluri (BIGELOW & ScHROEDER, 1944), Eridacnis sinuans millimetrical in range. (SMlTH, 1957) and the type species Eridacnis radcliffei The outer face of the principal cusp and cusplet is weak SMITH, 1913. ly convex, presenting. well developed striae, which run from crown base toward apex of the principal cusp and Eridacnis radcliffei SMITH, 1913 cusplet. A reticulated ornamentation is present between (Plates 2, 3) the striae on the crown base of the posterior teeth. The inner face of the principal cusp and cusplet is Proceedings of the United States National Museum, 45 strongly convex, also presenting striae, which run from (200) : 599-600. crown base toward apex of the principal cusp and cus The teeth of this species have a broad based, relatively plet. short principal cusp. The principal cusp is oriented The outer face of the root is rather high, presenting an sometimes a little obliquely toward the commissure, and irregular series of about five well developed foramina. one also short and broad based distal and mesial cusplet The inner face shows a ridge, which has about the same is present in anterior upper teeth. Cusplets are absent shape as the angle of the root lobes. It divides the inner on upper anterior, lower anterior and latero-anterior face of the root into two sections and its central part is teeth. The posterior teeth have up to three mesial cus more or less protuberant. A foramen is present in the . plets and sometimes another distal one. centre of the ridge and root base. I I Contributions to the study of the comparative morphology of teeth and other relevant ichthyodorulites 77 Genus : Gollum CoMPAGNO, 1973 those toward the commissure are mostly smaller than the anterior ones and can have up to seven cusplets. The type species of this monotypic genus is Gollum attenuatus (GARRICK, 1954). Genus : Pseudotriakis BRITO CAPELLO, 1867 Gollum attenuatus (GARRICK, 1954) The genus is, after CoMPAGNO (1988), monotypic with (Plates 6, 7) the type species Pseudotriakis mierodon BRITO CAPELLO, 1867. Pseudotriakis aerates JoRDAN & SNYDER, 1904 Transactions of the Royal Society of New Zealand, 82 has been synonymised with Pseudotriakis mierodon. In (3) : 695-702. spite of this fact the teeth of the holotype of Pseudotria The teeth of this species have a broad based, relatively kis aerates will be illustrated (Plate 10 ). short principal cusp. The principal cusp is oriented more or less obliquely toward the commissure and flanked by a well developed mesial and distal cusplet on anterior Pseudotriakis mierodon BRlTO CAPELLO, 1867 teeth, sometimes a poorly developed second mesial cus (Plates 8, 9) plet on lateral teeth along with loss of distal cusplets. But up to six or seven distal cusplets exist on posterior Jornal de Sciencias mathematicas, physicas e naturales, and commissural teeth. Lisboa, 1 (4): 316 + 321. The root is secondarily hemiaulacorhizid, showing two The teeth of this species have a broad based, relatively relatively long and narrow lobes forming an angle. The short principal cusp, which is more distinct in the lower dimensions of the teeth are plurimillimetrical in range. jaw. The principal cusp points more or less obliquely The outer face of the principal cusp and cusplet is toward the commissure and is commonly flanked by weakly convex, presenting well developed, but fine one, also short and broad based cusplet. Next to each striae, which run from crown base toward apex of the cusplet, on the extreme edges, a poorly developed principal cusp and cusplet. A reticulated ornamentation second cusplet is present, which is more distinct on is present between the striae on the crown base. The upper lateral teeth. crown base overhangs a rather high basal depression The root varies between holaulacorhizid and secondarily below its entire length. anaulacorhizid and shows two relatively long and nar The inner face of the principal cusp and cusplet is row lobes forming a sharp angle at the root base. The strongly convex, also presenting well developed, fine dimensions of the teeth are plurimillimetrical in range. striae, which run from crown base toward apex of the The outer face of the principal cusp and cusplet is weak principal cusp and cusplet. The outer face of the root ly convex, presenting well developed, short basal costu is rather high, presenting an irregular series of about les. The crown more or less overhangs the root. Striae five well developed foramina. on principal cusp and cusplets and a reticulated orna The inner face shows a ridge, that has about the same mentation are absent. The inner face of the principal shape as the angle of the root lobes. It divides the inner cusp and cusplet is strongly convex, also presenting well face or the root into two sections and its central part is developed, fine striae running from crown base toward more or less protuberant. A foramen is present in the apex of the principal cusp and cusplets. Their density centre of the ridge. is rather high with about eleven to seventeen striae on the principal cusp and five to seven on the cusplets. A Family: Pseudotriakidae GILL, 1893 basal ornamentation is absent. The outer face of the root is rather high, presenting a This family is monotypic with the genus Pseudotriakis. series of about three to five well developed foramina, The teeth in the family Pseudotriakidae in general have of which those in the centre are often merged. a well developed principal cusp flanked by up to three The inner face shows a ridge having about the same cusplets on each side. shape as the angle of the root lobes. It divides the inner The root is holaulacorhizid to secondarily anaulacor face of the root into two sections, and its central part hizid. is strongly protuberant. On each root lobe, two to three foramina are present on the root part toward the crown HETERODONTY on the mesial and distal part. Foramina are absent near the crown-root junction. A central foramen is often pre A weak dignathic heterodonty may be shown by relati sent in the centre of the ridge, which is sometimes more vely higher cusplets and a shorter principal cusp in lower or less elongated toward the root base, forming partly teeth. No sexual heterodonty has been observed. A a groove or sometimes even a complete median groove. gradient monognathic heterodonty is always present by On the basal part, usually some randomly scattered fora little broader lateral teeth. The lateral teeth and mina are present. '' 78 J. HERMAN, M. HOVESTADT-EULER and D.C. HOVESTADT Family: Leptochariidae GRAY, 1851 less protuberant. Foramina are absent near the crown root junction. A foramen is sometimes present in the This family is monotypic with the genus Leptocharias centre of the ridge, which is sometimes more or less SMITH, 1838. elongated toward the root base. An additional central foramen is often present at the basal part. HETERODONTY LATERAL TEETH A slight dignathic heterodonty is shown by a relatively higher principal cusp in lower teeth. Sexual heterodonty The crown has a high principal cusp, which is inclined is presented by anterior teeth with a longer principal toward the commissure. The mesial cutting edge is cusp and a sigmoidal mesial cutting edge in males. sometimes weakly sigmoidal in males and straight in Except for the parasymphysial rows, a disjunct mono females. A well developed mesial and distal cusplet is gnathic heterodonty is presented by anterior teeth, with present in both upper and lower teeth, with sometimes a high principal cusp strongly oriented obliquely toward a poorly developed second cusplet at the extreme mesial the commissure and much smaller lateral and posterior part. teeth with a slightly oblique principal cusp. The root is secondarily anaulacorhizid and shows two long and broad lobes, which are angled at the base. Genus : Leptocharias SMITH, 1838 The dimensions of the teeth are plurirnillimetrical in range. This genus is monotypic with the type species Leptocha The outer face of the principal cusp and cusp lets is rather rias smithii (MOLLER & HENLE, 1839). convex. It presents strongly developed striae running from crown base toward apex. A reticulated ornamenta Leptocharias smithii (MOLLER & HENLE, 1839) tion is absent. (Plates 11, 12) The inner face of the principal cusp is strongly convex, presenting short, poorly developed basal costules. A Systematische Beschreibung der Plagiostomen : 56. basal ornamentation is absent. The disjunct monognathic heterodonty requires to des The outer face of the root is rather low, with a central cribe anterior and lateral teeth separately. foramen. The inner face shows a ridge of about the same shape ANTERIOR TEETH as the angle of the root lobes. It divides the inner face of the root into two sections. Its central part is more or The crown has a very high principal cusp, which is less protuberant. Foramina are absent near the crown strongly inclined toward the commissure. The mesial root junction. A foramen is sometimes present in the cutting edge is slightly sigmoidal in males and straight centre of the ridge. Numerous foramina are scattered in females. A poorly developed mesial and distal cusplet over the root Jobes. is present in upper teeth, but mostly absent in lower teeth. Family: Hemigaleidae HASSE, 1879 The root varies between secondarily hemiaulacorhizid and secondarily anaulacorhizid and shows two lobes, This family includes, after CoMPAGNO (1988), two sub which are relatively short but broad and sharply angled families : at the base. The dimensions of the teeth are plurimillimetrical in Hernigaleinae range. The outer face of the principal cusp and eventual cus Genus Hemigaleus BLEEKER, 1852, type species Hemi plets is rather convex. It presents poorly (on anteriors) galeus microstoma. or well developed (on laterals to commissurals) striae Genus Chaenogaleus GILL, 1862, type species Chaeno running from crown base toward apex in upper teeth, galeus macrostoma. are quite absent in lower teeth. A reticulated ornamen Genus Paragaleus BunKER, 1935, type species Paraga tion is absent. leus pectoralis. The inner face of the principal cusp is strongly convex, presenting short, well developed basal costules. A basal Hernipristinae ornamentation is absent. The outer face of the root is rather low. Foramina are Genus Hemipristis AGASSIZ, 1843, type species Hemi absent. pristis serra. The inner face shows a ridge of about the same shape as the angle of the root lobes. It divides the inner face The teeth of species of the family Hemigaleidae in gene of the root into two sections. Its central part is more or ral have, except for the parasymphysial rows, a broad II Contributions to the study of the comparative morphology of teeth and other relevant ichthyodorulites 79 based principal cusp with sometimes 7 or more distal root into two obtusely angled root lobes. A blunt ridge cusplets in upper teeth and a rather slender principal is present on the lobes near the crown-root junction, cusp in lower teeth. dividing the lobes into an upper and lower part. Fora The root is always strictly holaulacorhizid. mina are present within the median groove and on the root lobes near the crown-root junction. · HETERODONTY LOWER TEETH A strong dignathic heterodonty is present in all genera. Sexual heterodonty, as well as ontogenetic heterodonty The lower teeth have a suberect principal cusp. The has not been observed. Except for the parasymphysial smooth mesial and distal cutting edges are arched. Cus rows, the monognathic heterodonty is gradient in both plets are absent. The crown becomes more asymmetrical upper and lower jaws in Hemigaleinae, and gradient in and shorter toward the commissural teeth. upper but disjunct in lower jaws in Hemipristinae. The outer face of the principal cusp is smooth and slightly convex. Striae, costules or ornamentation are Genus: Hemigaleus BLEEKER, 1852 absent. The inner crown base is arched or somewhat angled. This genus is monotypic with the type species Hemiga The inner face of the principal cusp is fairly convex. leus microstoma BLEEKER, 1852. Striae, costules or ornamention are absent. The outer face of the root is low and shows a series of Hemigaleus microstoma BLEEKER, 1852 ten or more foramina. The inner median groove is visible (Plates 13, 14) at the central root base. The inner face of the root presents a broad and rather · Verhandelingen Bataviaans Genootschap voor Kunst en deep median groove, which divides the root into two Wetenschap, 24 : 46. angled lobes. The dentition presents a fair dignathic heterodonty. The A blunt ridge is present on the lobes near the crown teeth of the upper jaw have a rather broad based crown, root junction. It divides the lobes into upper and lower which is strongly inclined toward the commissure in parts. anterior teeth, even stronger inclined in lateral teeth and Some foramina are present within the median groove. finally loosing distal cutting edge by extreme inclination in posterior teeth. Genus: Chaenogaleus GILL, 1862 The teeth of the lower jaw have a principal cusp, which is always suberect and never inclines toward commis The genus is monotypic with the type species Chaenoga sure. The principal cusp of posterior teeth is low. leus macrostoma (BLEEKER, 1852). The root of both upper and lower teeth is strictly holaula corhizid. The dimensions of the teeth are plurimillimetri Chaenogaleus macrostoma (BLEEKER, 1852) cal in range. (Plates 15, 16) UPPER TEETH Verhandelingen Bataviaans Genootschap voor Kunst en Wetenschap, 24: 46. The upper teeth have the principal cusp strongly inclined The dentition is dignathic heterodont. The teeth of the toward the commissure. The long and smooth mesial upper jaw have a rather broad based crown, which is cutting edge is weakly sigmoidal. The distal cutting edge strongly inclined toward the commissure in anterior is very short and toward the crown base replaced by a teeth, even stronger inclined in lateral teeth. series of six or seven cusplets gradually reduced in The teeth of the lower jaw have a principal cusp, which height. The root is broad and rather low. The outer face is always suberect in anterior teeth, slightly inclined of the principal cusp and cusplets is rather flat and toward the commissure in lateral teeth, and again sub smooth. Striae, costules or ornamentation are absent. erect but lower in posterior teeth. The inner face of the principal cusp and cusplets is The root of both upper and lower teeth is strictly holaula weakly convex and smooth. Striae, costules or ornamen corhizid. The dimensions of the teeth are plurimillimetri tation are absent. cal in range. The outer face of the root is moderately high, and the root lobes present a series of numerous foramina. At UPPER TEETH the central root base, the basal part of the inner median groove is visible. The upper teeth have a principal cusp, which is strongly The inner part of the root presents a distinct median inclined toward the commissure. The mesial cutting groove, which is broad and rather deep, running from edge is long, smooth and weakly sigmoidal. The distal crown-root junction toward the root base. It divides the cutting edge is very short and toward the crown base 80 J. HERMAN, M. HOYESTADT-EULER and D.C. HOVESTADT replaced by a series of five or six cusplets gradually The dentition presents a fair dignathic heterodonty. The reduced in height. The root is broad and rather low. teeth of the upper jaw have a rather broad based crown, The outer face of the principal cusp and cusp lets is rather which is strongly inclined toward the commissure in flat and smooth. Striae, costules or ornamentation are anterior teeth, even stronger inclined in lateral teeth, and absent. loosing the distal cutting edge by extreme inclination in The inner face of the principal cusp and cusplets is posterior teeth. weakly convex and smooth. Striae, costules or ornamen The teeth of the lower jaw have a principal cusp, which tation are absent. The outer face of the root is moderately is always suberect but becoming lower toward the com high. At the central root base, the basal part of the inner missure. median groove is visible. The root of both upper and lower teeth is strictly holaula The inner part of the root presents a distinct median corhizid. The dimensions of the teeth are plurimillimetri groove, which is broad and rather deep, running from cal in range. crown-root junction toward the root base. It divides the root into two obtusely angled lobes. A blunt ridge is UPPER TEETH present on the lobes near the crown-root junction, divid ing the lobes into upper and lower parts. Foramina are Except for the parasymphysial row, the upper teeth have present within the median groove and on the root lobes a principal cusp strongly inclined toward the commis near the crown-root junction. sure. The mesial cutting edge is long, normally smooth and weakly sigmoidal (sometimes a cusplet-like irregu LOWER TEETH larity may be present at the base). The distal cutting edge is very short and toward the crown base replaced The lower teeth have a suberect, rugh principal cusp. by a series of four to seven cusplets gradually reduced The smooth mesial and distal cutting edges are strongly in height. arched at the base, forming mesial and distal extensions The root is broad and rather low_ of the cutting edges. Cusplets are absent. The crown The outer face of the principal cusp and cusplets is rather becomes more asymmetrical and shorter toward the flat and smooth. Striae, costules or ornamentation are commissural teeth. absent. The outer face of the principal cusp is smooth and The inner face of the principal cusp and cusplets is slightly convex. Striae, costules or ornamentation are weakly convex and smooth. Striae, costules or ornamen absent. The inner crown-base is more or less arched. taton are absent. The inner face of the principal cusp is fairly convex. The outer face of the root is moderately high. At the Striae, costules or ornamentation are absent. central root base, the basal part of the inner median The outer face of the root is low and shows a series of groove is visible. ten or more foramina. The inner median groove is visible The inner part of the root presents a distinct median at the central root base. groove, which is broad and rather deep, running from The inner face of the root presents a broad and rather crown-root junction toward the root base. It divides the deep median groove, which divides the root into two root into two obtusely angled lobes. A blunt ridge is angled, rather narrow lobes. present on the lobes near the crown-root junction, which A blunt ridge is present on the lobes near the crown is protuberant in the centre of the root. It divides the root junction, which is protuberant in the centre of the lobes into upper and lower parts. Foramina are present root. It divides the lobes into upper and lower parts. within the median groove and on the root lobes near Some foramina are present witrun the median groove. the crown-root junction. Genus: Paragaleus BuoKER, 1935 LOWER TEETH The lower teeth have a suberect, high principal cusp. The genus comprises, after CoMPAGNO (1988), three The mesial and distal cutting edges are strongly arched species : Paragaleus tengi (0-tEN, 1963), Paragaleus at the base, forming mesial and distal extensions of the leucolomatus CoMPAGNO & SMALE, 1985 and the type cutting edges. Distal cusplets are present in very lateral species Paragaleus gruveli BuoKER, 1935 (= Paraga teeth. The crown becomes more asymmetrical and short leus pectoralis (GARMAN, 1906)). er toward the commissural teeth. The outer face of the principal cusp is smooth and Paragaleus pectoralis (GARMAN, 1906) slightly convex. Striae, costules or ornamentation are (Plates 17, 18) absent. The inner crown base is almost straight. The inner face of the principal cusp is fairly convex. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology, Har Striae, costules or ornamentation are absent. vard College, 46 (11) : 203. The outer face of the root is low and shows a series of Contributions to the study of the comparative morphology of teeth and other relevant ichthyodorulites 81 ten or more foramina. The inner median groove is visible The outer face of principal cusp and cusplets is flat. at the central root base. Striae, costules and ornamentation are absent. The inner face of the root presents a broad and rather The inner face of principal cusp and cusplets is rather deep median groove, which divides the root into two convex. Striae, costules and ornamentation are absent. weakly angled, rather narrow lobes. The outer face of the root presents a series of numerous A blunt ridge is present on the lobes near the crown foramina. At the central basal part, the inner median root junction, which is protuberant in the centre of the groove is visible. root. It divides the lobes into upper and lower parts. The inner part of the root presents a shallow median Some foramina are present within the median groove. groove, which runs from just below the crown-root junc tion toward the root base. The upper central part of the Family : Carcharhinidae JoRDAN & EvERMANN, 1896 root is slightly protuberant. One or two foramina are present within the median groove. This family comprises, after CoMPAGNO (1988), the sub families Galeocerdinae, Scoliodontinae and Carcharhini Tribe: Rhizoprionodontini CoMPAGNO, 1988 nae. Galeocerdinae do not have microteeth and are therefore This tribe comprises, after CoMPAGNO (1988), the genera neither described nor illustrated here. Loxodon and Rhizoprionodon. Subfamily : Carcharhininae JoRDAN & EvERMANN, 1896 Genus: Loxodon MOLLER & HENLE, 1838 This subfamily comprises four tribes, of which only This genus is monotypic, with the type species Loxodon Rhizoprionodontini and Triaenodontini are described macrorhinus MOLLER & HENLE, 1839. and illustrated below, because microteeth are missing in taxa of the other two tribes. HETERODONTY Tribe: Triaenodontini BoNAPARTE, 1838 Teeth are weakly dignathic heterodont. Sexual hetero donty is present by a more sigmoidal mesial cutting This tribe comprises the single genus Triaenodon. edge in males. Ontogenetic heterodonty has not been observed. Except for the symphysial upper rows, a gra Genus: Triaeno_don MOLLER & HENLE, 1837 dient monognathic heterodonty is present by slightly broader and more inclined lateral teeth. The teeth toward This genus is monotypic with the type species Triaeno the commissure are lower and rather strongly inclined. don obesus (ROPPELL, 1837), sensu CoMPAGNO (1988). Loxodon macrorhinus MOLLER & HENLE, 1839 HETERODONTY (Plates 21, 22) This genus has weakly dignathic heterodont teeth. Sexual or ontogenetical heterodonty has not been observed. Systematische Beschreibung der Plagiostomen. 61. Except for the symphysial and first anterior rows, a Both upper and lower anterior teeth have a rather inclin gradient monognathic heterodonty is present by slightly ed principal cusp, which becomes more inclined in late broader and oblique lateral teeth. Teeth in rows toward ral and posterior teeth. Cusplets are absent, and a distal the commissure are lower and rather strongly inclined. blade is always present, which joins the distal cutting edge in a notch. Both mesial and distal cutting edges Triaenodon obesus (ROPPELL, 1837) are smooth. The root is neo-holaulacorhizid, with two (Plates 19, 20) obtusely angled lobes. The dimensions of the teeth are plurimillimetrical in range. In : Fische des Rothen Meeres, Neue Wirbeltiere zu der The outer face of principal cusp is flat. Numerous short Fauna von Abyssinien gehorig, 11 : 64. costules are present on the crown base, but striae and Both upper and lower anterior teeth have a high, sub ornamentation are absent. erect but broad principal cusp, which becomes more The inner face of p1incipal cusp and cusplets is slightly oblique in lateral teeth and more inclined in posterior convex. Striae, costules and ornamentation are absent. teeth. A firm mesial and distal cusplet is always present The outer face of the root presents a series of numerous at the basal part of each cutting edge. Both mesial and foramina. At the central basal part, the inner median distal cutting edges are smooth. groove is visible. The root is neo-holaulacorhizid, with two angled lobes. The inner part of the root presents a relatively broad The dimensions of the teeth are plurimillimetrical in and deep median groove running from crown-root junc range. tion toward the root base. The root lobes are rather flat. 82 J. HERMAN, M. HOVESTADT-EULER and D.C. HOVESTADT One rather large foramen is present within the median Genus: Scoliodon MOLLER & HENLE, 1837 groove. This genus is monotypic with the type species Scoliodon laticaudus MOLLER & HENLE, 1838. Genus: Rhizoprionodon WHJTLEY, 1929 HETERODONTY This genus comprises 7 species : Rhizoprionodon acutus (ROPPELL, 1835), Rhizoprionodon [a/andei (VA LENCIEN Teeth are strongly dignathic heterodont in males and NES, 1839), Rhizoprionodon longurio (JORDAN & GLL weakly heterodont in females. Sexual heterodonty is BERT, 1882), Rhizoprionodon o/igo/inx SPRINGER, 1964, presented by a more sigmoidal suberect principal cusp, Rhizoprionodon porosus (POEY, 1861), Rhizoprionodon which is twisted in its vertical axis in anterior lower taylori (OGLLBY, 1915) and Rhizoprionodon terranovae teeth of males only. Ontogenetic heterodonty has not (RICHARDSON, 1836). been observed. Except for anterior lower rows in males and the symphysial upper rows and parasymphysial rows HETERODONTY in both sexes, a gradient monognatic heterodonty is present by slightly broader and more inclined lateral Teeth are weakly dignathic heterodont. Sexual hetero teeth. The teeth toward the commissure are lower and donty is present by a more sigmoidal mesial cutting rather strongly inclined. edge in males. Ontogenetic heterodonty has not been observed. Except for the symphysial upper rows, a gra Scoliodon laticaudus MOLLER & HENLE, 1838 dient monognathic heterodonty is present by slightly (Plates 27, 28) broader and more inclined lateral teeth. The teeth toward the commissure are lower and rather strongly inclined. Systematische Beschreibung der Plagiostomen. 27. Both upper and lower anterior teeth have a rather inclin ed principal cusp in males, which becomes more inclin Rhizoprionodon acutus (ROPPELL, 1837) ed in lateral and posterior teeth. Cusplets are absent, (Plates 23 to 26) and a distal blade is always present. Both mesial and distal cutting edges as well as distal blade are smooth. In : Fische des Rothen Meeres, Neue Wirbeltiere zu der The root is neo-holaulacorhizid with two obtusely Fauna von Abyssienien gehorig, 11 : 65. angled, or, in lower anteriors of males, subquadrangu Both upper and lower anterior teeth have a rather inclin larly shaped lobes. The dimensions of the teeth are ed, but more or less suberect principal cusp, becoming plurimillimetrical in size. more inclined in lateral and posterior teeth. A mesial The outer face of principal cusp is weakly convex. cusplet is absent, but a poorly developed cusplet arising Striae, costules and ornamentation are absent. from a distal blade is always present. Both mesial and The inner face of principal cusp and cusplets is slightly distal cutting edges, as well as the distal cusplet are convex. Striae, costules and ornamentation are absent. weakly serrated. The root is neo-holaulacorhizid, with The outer face of the root presents a series of numerous two obtusely angled lobes. foramina. At the central basal part, the inner median The teeth are plurimillimetical in size. groove is visible. The outer face of principal cusp is flat. Numerous short, The inner part of the root presents a relatively broad, very fine costules are present on the crown base, but shallow median groove running from crown-root junc striae and ornamentation are absent. tion toward the root base. The root lobes are rather flat. The inner face of principal cusp and cusplets is slightly One rather large foramen is present within the median convex. Striae, costules and ornamentation are absent. groove. The outer face of the root presents a series of numerous foramina. At the central basal part, the inner median LATERAL LOWER TEETH OF MALES groove is visible. The inner part of the root presents a relatively broad The principal cusp is twisted in its vertical axis, and and shallow median groove running from crown-root mesial and distal cutting edges are sigmoidal but junction toward the root base. The root lobes are rather smooth. Cusplets, as well as distal blade are absent. flat. One rather large foramen is present within the The root is neo-holaulacorhizid. The root lobes are sub median groove. quadrangularly shaped. The outer face of the principal cusp is strongly convex. Striae, costules and ornamentation are absent. Subfamily: Scoliodontinae WHITLEY, 1934 The inner face of the principal cusp is strongly convex. Striae, costules and ornamentation are absent. This subfamily comprises the single genus Scoliodon. The outer face of the root has a weak central depression.
