chapterwise previous years' biology papers cbse pmt;aipmt;neet-12th PDF
Preview chapterwise previous years' biology papers cbse pmt;aipmt;neet-12th
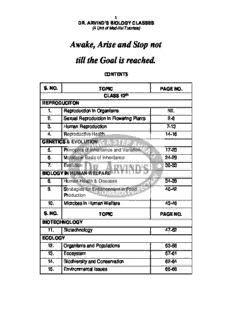
1 DR. ARVIND’S BIOLOGY CLASSES (A Unit of Med-Xel Tutorials) Awake, Arise and Stop not till the Goal is reached. CONTENTS S. NO. TOPIC PAGE NO. CLASS 12th REPRODUCITON 1. Reproduction in Organisms NIL 2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants 2-6 3. Human Reproduction 7-13 4. Reproductive Health 14-16 GENETICS & EVOLUTION 5. Principles of Inheritance and Variation 17-23 6. Molecular Basis of Inheritance 24-29 7. Evolution 30-33 BIOLOGY IN HUMAN WELFARE 8. Human Health & Diseases 34-39 9. Strategies for Enhancement in Food 40-42 Production 10. Microbes in Human Welfare 43-46 S. NO. TOPIC PAGE NO. BIOTECHNOLOGY 11. Biotechnology 47-52 ECOLOGY 12. Organisms and Populations 53-56 13. Ecosystem 57-61 14. Biodiversity and Conservation 62-64 15. Environmental Issues 65-68 2 DR. ARVIND’S BIOLOGY CLASSES (A Unit of Med-Xel Tutorials) REPRODUCTION 7. In which one of the following pollination is autogamous? a) Geitonogamy b) Xenogamy SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING c) Chasmogamy d) Cleistogamy PLANTS Ans. (d) 8. What would be the number of chromosomes CBSE PRELIMS – 2009 of the aleurone cells of a plant with 42 chromosomes in its root tip cells? 1. Vegetative propagation in mint occurs by: a) 42 b) 63 c) 84 d) 21 a) Rhizome b) Sucker Ans. (b) c) Runner d) Offset 9. Wind pollination is common in: Ans. (b) a) Legumes b) Lilies c) Grasses d) Orchids CBSE PRELIMS – 2010 Ans. (c) Hint: Wind pollination - Grasses; corn 2. Apomictic embryos in Citrus arise from: Most of the land plants use insects or a) Diploid egg wind for pollination. b) Synergids The wind and water pollinated flowers are c) Maternal sporophytic tissue in ovule not very colourful and do not produce d) Antipodal cells nectar. Lilies and orchids are colourful Ans. (c) flowers, so are mostly insect pollinated. 3. Wind pollinated flowers are: Legumes are self pollinated usually. a) Small, producing nectar and dry pollen b) Small, brightly coloured, producing large number of pollen grains CBSE PRELIMS – 2012 c) Small, producing large number of dry pollen grains 10. Even in absence of pollinating agents seed- d) Large, producing abundant nectar and setting is assured in pollen a) Zostera b) Salvia Ans. (c) c) Fig d) Commellina 4. Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to Ans. (d) the stigma of another flower of the same 11. An organic substance that can withstand plant is called: environmental extremes and cannot be a) Autogamy b) Xenogamy degraded by any enzyme is c) Geitonogamy d) Karyogamy a) Sporopollenin b) Lignin Ans. (c) c) Cellulose d) Cuticle Ans. (a) CBSE PRELIMS – 2011 12. Both autogamy and geitonogamy are prevented in: a) Cucumber b) Castor c) Maize d) Papaya 5. Filiform apparatus is a characteristic feature Ans. (d) of: Hint: a) Suspensor b) Egg - Cucumber has male and female flowers c) Synergid d) Zygote both on the same plant. Ans. (c) - Castor has male and female flowers 6. Nucellar polyembryony is reported in separate but on same plant species of: - Maize has male and female inflorescences a) Citrus b) Gossypium (spikelets) borne separately but on same plant c) Triticum d) Brassica - Papaya is dioecious plant. So both autogamy Ans. (a) and geitonogamy are prevented in it. 3 DR. ARVIND’S BIOLOGY CLASSES (A Unit of Med-Xel Tutorials) CBSE MAINS – 2010 CBSE MAINS – 2012 17. Plants with ovaries having only one or a few 13. Examine the figures (A – D) given below and select the right option out of 1 – 4, in which ovules, are generally pollinated by: all the four structures A, B, C and D are a) Birds b) Wind identified correctly c) Bees d) Butterflies Ans. (b) Structures 18. Which one of the following statements is wrong? a) Pollen grains in some plants remain viable for months b) Intine is made up of cellulose and pectin c) When pollen is shed at two-celled state, double fertilization does not take place d) Vegetative cell is larger than generative cell Ans. (c) 19. What is the function of germ pore? a) Initiation of pollen tube b) Release of male gametes c) Emergence of radicle d) Absorption of water for seed germination Ans. (a) NEET – 2013 A B C D 20. Meiosis takes place in: a) Rhizome Sporangiophore Polar cell Globule a) Gemmule b) Megaspore b) Runner Archegoniophore Synergid Antheridium c) Meiocyte d) Conidia c) Offset Antheridiophore Antipodals Oogonium Ans. (c) d) Sucker Seta Megaspore Gemma cup 21. Perisperm differs from endosperm in : mother a) Being a diploid tissue cell b) Its formation by fusion of secondary Ans. (c) nucleus with several sperms 14. Vegetative propagation is Pistia occurs by c) Being a haploid tissue a) Stolen b) Offset d) Having no reserve food c) Runner d) Sucker Ans. (a) Ans. (b) 22. Monoecious plant of Chara shows occurrence of: CBSE MAINS – 2011 a) Upper antheridium and lower oogonium on the same plant 15. In angiosperms, functional megaspore b) Upper oogonium and lower antheridium develops into: on the same plant a) Embryo sac b) Ovule c) Antheridiophore and archegoniophore on c) Endosperm d) Pollen sac the same plant Ans. (a) d) Stamen and carpel on the same plant 16. What is common between vegetative Ans. (b) reproduction and Apomixis? 23. Which one of the following statements is a) Both are applicable to only dicot plants correct? b) Both bypass the flowering phase a) Endothecium produces the microspores c) Both occur round the year b) Tapetum nourishes the developing pollen d) Both produces progeny identical to the parent c) Hard outer layer of pollen is called intine Ans. (d) d) Sporogenous tissue is haploid Ans. (b) 4 DR. ARVIND’S BIOLOGY CLASSES (A Unit of Med-Xel Tutorials) AIPMT – 2014 • Apogamy – Formation of sporophyte from gametophyte without involving the 24. Geitonogamy involves: formation and fusion of gametes. a) Fertilization of a flower by the pollen from • Cleistogamy – the flowers are intersexual a flower of another plant belonging to a and remain closed causing self- distant population. pollination, they do not need pollinators. b) Fertilization of a flower by the pollen from • Geitonogamy – the pollen grains of one another flower of the same plant. flower are transferred to stigma of c) Fertilization of a flower by the pollen from another flower belonging to either same the same flower. • plant or genetically similar plant. This is d) Fertilization of a flower by the pollen from similar genetically to autogamy which is a flower of another plant in the same self-pollination. population 30. In ginger vegetative propagation occurs Ans. (b) through: 25. Function of filiform apparatus is to a) Offsets b) Bulbils a) Guide the entry of pollen tube c) Runners d) Rhizome b) Recognize the suitable pollen at stigma Ans. (d) c) Stimulate division of generative cell 31. Which one of the following statements is not d) Produce nectar true? Ans. (a) a) Pollen grains of some plants cause 26. Pollen tablets are available in the market for: severe allergies and bronchial afflictions a) Ex situ conservation in some people b) In vitro fertilization b) The flowers pollinated by flies and bats c) Breeding programmes secrete foul odour to attract them d) Supplementing food c) Honey is made by bees by digesting Ans. (d) pollen collected from flowers 27. Which one of the following is wrong about d) Pollen grains are rich in nutrients and Chara? they are used in the form of tablets and a) Globule is male reproductive structure syrups b) Upper oogonium and lower round Ans. (c) antheridium Hint: Option (c) is totally wrong as honey is c) Globule and nucule present on the same plant made by bees from nectar collected from d) Upper antheridium and lower oogonium flowers. Ans. (d) Option (b) is to be taken as correct as some authors say that flowers pollinated AIPMT – 2015 by bats have fruity odour and some others say they may have a disagreeable odour like that of sour milk. 28. Transmission tissue is characteristic feature of: 32. The hilum is a scar on the a) Solid style b) Dry stigma a) Fruit, where it was attached to pedicel c) Wet stigma d) Hollow style b) Fruit, where style was present Ans. (a) c) Seed, where micropyle was present 29. Which one of the following may require d) Seed, where funicle was attached pollinators, but is genetically similar to Ans. (d) autogamy? 33. Which of the following are the important a) Xenogamy b) Apogamy floral rewards to the animal pollinators? c) Cleistogamy d) Geitonogamy a) Nectar and pollen grains Ans. (d) b) Floral fragrance and calcium crystals Hint: Xenogamy - Cross pollination between c) Protein pellicle and stigmatic exudates two flowers of genetically different d) Colour and large size of flower flowers. Ans. (a) 5 DR. ARVIND’S BIOLOGY CLASSES (A Unit of Med-Xel Tutorials) AIPMT RETEST – 2015 41. Which of the following statements is not correct? a) Insects that consume pollen or nectar 34. The wheat grain has an embryo with one without bringing about pollination are large, shield-shaped cotyledon known as: called pollen/nectar robbers a) Epiblast b) Coleorrhiza b) Pollen germination and pollen tube c) Scutellum d) Coleoptile growth are regulated by chemical Ans. (c) components of pollen interacting with those of the pistil 35. Filiform apparatus is characteristic feature of: c) Some reptiles have also been reported as a) Generative cell b) Nucellar embryo pollinators in some plant species c) Aleurone cell d) Synergids d) Pollen grains of many species can Ans. (d) germinate on the stigma of a flower, but 36. In angiosperms, microsporogenesis and only one pollen tube of the same species megasporogenesis: grows into the style a) Occur in anther Ans. (d) b) Form gametes without further divisions 42. Seed formation without fertilization in c) Involve meiosis flowering plants involves the process of: d) Occur in ovule a) Budding Ans. (c) b) Somatic hybridisation 37. Which of the following pairs is not correctly c) Apomixis matched? d) Sporulation Mode of reproduction Example Ans. (c) a) Offset Water hyacinth 43. Which one of the following statements is not true? b) Rhizome Banana a) Exine of pollen grains is made up of c) Binary fission Sargassum sporopollenin d) Conidia Penicillium b) Pollen grains of many species cause severe allergies Ans. (c) c) Stored pollen in liquid nitrogen can be 38. Coconut water from a tender coconut is: used in the crop breeding programmes a) Immature embryo d) Tapetum helps in the dehiscence of b) Free nuclear endosperm anther c) Innermost layers of the seed coat Ans. (d) d) Degenerated nucellus NEET-2; 2016 Ans. (b) 39. Male gametophyte in angiosperms produces: 44. In majority of angiosperms a) Egg has a filiform apparatus a) Two sperms and a vegetative cell b) There are numerous antipodal cells b) Single sperm and a vegetative cell c) Reduction division occurs in the c) Single sperm and two vegetative cells megaspore mother cells d) Three sperms d) A small central cell is present in the Ans. (a) embryo sac Ans. (c) AIPMT – 2016 Hint: In angiosperms the synergids have 40. The coconut water from tender coconut filiform apparatus, but in some even the represents: egg cell has filiform apparatus. There are 3 a) Fleshy mesocarp antipodal cells. The central cell is large in b) Free nuclear proembryo size which has two polar nucleii. 45. Pollination in water hyacinth and water lily is c) Free nuclear endosperm brought about by the agency of d) Endocarp a) Water b) Insects or wind Ans. (c) c) Birds d) Bats Ans. (b) 6 DR. ARVIND’S BIOLOGY CLASSES (A Unit of Med-Xel Tutorials) 46. The ovule of an angiosperm is technically equivalent to a) Megasporangium b) Megasporophyll c) Megaspore mother cell d) Megaspore Ans. (a) 47. Study the four statements (A-D) given below and select the two correct ones out of them: (i) Definition of biological species was given by Ernst Mayr. (ii) Photoperiod does not affect reproduction in plants. (iii) Binomial nomenclature system was given by R.H. Whittaker (iv) In unicellular organisms, reproduction is synonymous with growth. The two correct statements are a) (ii) and (iii) b) (iii) and (iv) c) (i) and (iv) d) (i) and (ii) Ans. (c) NEET- 2017 50. Flowers which have single ovule in the ovary and are packed into inflorescence are usually pollinated by: a) Water b) Bee c) Wind d) Bat Ans. (c) 51. Functional megaspore in an angiosperm develops into: a) Ovule b) Endosperm c) Embryo sac d) Embryo Ans. (c) 52. Double fertilization is exhibited by: a) Gymnosperms b) Algae c) Fungi d) Angiosperms Ans. (d) 53. A dioecious flowering plant prevents both: a) Autogamy and xenogamy b) Autogamy and geitonogamy c) Geitonogamy and xenogamy d) Cleistogamy and xenogamy Ans. (b) 54. Attractants and rewards are required for a) Anemophily b) Entomophily c) Hydrophily d) Cleistogamy Ans. (b) 7 DR. ARVIND’S BIOLOGY CLASSES (A Unit of Med-Xel Tutorials) HUMAN REPRODUCTION 5. Given below is a diagrammatic sketch of a portion of human male reproductive system. CBSE PRELIMS – 2009 Select the correct set of the names of the parts labelled A, B, C, D: 1. Which one of the following is the correct matching of the events occurring during menstrual cycle? (a) Development Secretory phase and of corpus increased secretion of luteum progesterone. (b) Menstruation Breakdown of myometrium and ovum not fertilized. (c) Ovulation LH and FSH attain peak A B C D level and sharp fall in the a) Vas Seminal Bulboure- Prostate secretion of progesterone. deferens vesicle thrall gland (d) Proliferative Rapid regeneration of b) Ureter Seminal Prostate Bulboure- phase myometrium and maturation vesicle thral gland of Graafian follicle. c) Ureter Prostate Seminal Bulboure- Ans. (a) vesicle thral gland 2. The correct sequence of spermatogenetic d) Vas Seminal Prostate Bulboure- stages leading to the formation of sperms in deferens vesicle thrall gland a mature human testis is: a) Spermatid-spermatocyte-spermatogonia- Ans. (d) 6. A change in the amount of yolk and its sperms distribution in the egg will affect: b) Spermatogonia-spermatid-spermatocyte- a) Number of blastomeres produced sperms b) Fertilization c) Spermatocyte-spermatogonia-spermatid- c) Formation of zygote sperms d) Pattern of cleavage d) Spermatogonia-spermatocyte-spermatid- Ans. (d) sperms 7. Seminal plasma in humans is rich in: Ans. (d) 3. Foetal ejection reflex in human female is a) Glucose and certain enzymes but has no induced by: calcium a) Fully developed foetus and placenta b) Fructose and certain enzymes but poor b) Differentiation of mammary glands in calcium c) Pressure exerted by amniotic fluid c) Fructose, calcium and certain enzymes d) Release of oxytocin from pituitary d) Fructose and calcium but has no Ans. (a) enzymes 4. Which one of the following is the most likely Ans. (c) root cause why menstruation is not taking Hint: Seminal plasma is the term used for place in regularly cycling human female? semen. Calcium is present in prostatic a) Maintenance of high concentration of secretion. sex-hormones in the blood stream b) Retention of well-developed corpus luteum c) Fertilisation of the ovum d) Maintenance of the hypertrophical endometrial lining Ans. (c) 8 DR. ARVIND’S BIOLOGY CLASSES (A Unit of Med-Xel Tutorials) CBSE PRELIMS – 2010 14. The signals for parturition originate from: a) Fully developed foetus only 8. Vasa efferentia are the ductules leading from: b) Placenta only a) Epididymis to urethra c) Placenta as well as fully developed foetus b) Testicular lobules to rete testis d) Oxytocin released from maternal pituitary c) Rete testis to vas deferens Ans. (c) d) Vas deferens to epididymis 15. The second maturation division of the Ans. (c) mammalian ovum occurs: Hint: The path followed by sperms is a) In the Graafian follicle following the first seminiferous tubules tubuli recti rete maturation division testis Vasa efferentia epididmis b) Shortly after ovulation before the ovum vas deferens ejaculatory duct makes entry into the Fallopian tube urethra. None of the above options is c) Until after the ovum has been correct. The best option seems to be (c). penetrated by a sperm 9. The first movements of the foetus and d) Until the nucleus of the sperm has fused appearance of hair on its head are usually with that of the ovum observed during which month of pregnancy? Ans. (c) a) Third month b) Fourth month 16. Which one of the following statements about c) Fifth month d) Sixth month morula in humans is correct? Ans. (c) a) It has more cytoplasm and more DNA 10. Which one of the following statements about than an uncleaved zygote human sperm is correct? b) It has almost equal quantity of cytoplasm a) Acrosome serves no particular function as an uncleaved zygote but much more b) Acrosome has a conical pointed structure DNA used for piercing and penetrating the egg c) It has far less cytoplasm as well as less resulting in fertilization DNA than in an uncleaved zygote c) The sperm lysins in the acrosome dissolve d) It has more or less equal quantity of the egg envelope facilitating fertilization cytoplasm and DNA as in uncleaved zygote d) Acrosome serves as a sensory structure Ans. (b) leading the sperm towards the ovum Ans. (c) CBSE PRELIMS – 2011 11. Seminal plasma in human males is rich in: a) Ribose and potassium 17. If for some reason, the vasa efferentia in the b) Fructose and calcium human reproductive system get blocked, the c) Glucose and calcium gametes will not be transported from: d) DNA and testosterone a) Testes to epididymis Ans. (b) b) Epididymis to vas deferens Hint: Fructose is mainly present in secretions of c) Ovary to uterus seminal vesicles and calcium in prostatic d) Vagina to uterus secretions. Ans. (a) 12. Sertoli cells are found in: 18. The testes in humans are situated outside a) Pancreas and secrete cholecystokinin the abdominal cavity inside a pouch called b) Ovaries and secrete progesterone scrotum. The purpose served is for: c) Adrenal cortex and secrete adrenaline a) Maintaining the scrotal temperature d) Seminiferous tubules and provide lower than the internal body temperature nutrition to germ cells b) Escaping any possible compression by Ans. (d) the visceral organs 13. The part of Fallopian tube closest to the ovary is: c) Providing more space for the growth of a) Ampulla b) Isthmus epididymis c) Infundibulum d) Cervix d) Providing a secondary sexual feature for Ans. (c) exhibiting the male sex Ans. (a) 9 DR. ARVIND’S BIOLOGY CLASSES (A Unit of Med-Xel Tutorials) 19. The figure given below depicts a a) Survival of sperm depends on the pH of diagrammatic sectional view of the female the medium and is more active in reproductive system of humans. Which one alkaline medium set of three parts out of I-VI have been b) Viability of sperm is determined by its motility correctly identified? c) Sperms must be concentrated in a thick suspension d) Sperm is viable for only up to 24 hours Ans. (d) CBSE MAINS – 2010 24. Signals from fully developed foetus and placenta ultimately lead to parturition which a) (II) Endometrium, (III) Infundibulum, (IV) requires the release of Fimbriae a) Estrogen from placenta b) (III) Infundibulum, (IV) Fimbriae, (V) Cervix b) Oxytocin from maternal pituitary c) (IV) Oviducal funnel, (V) Uterus, (VI) Cervix c) Oxytocin from foetal pituitary d) (I) Perimetrium, (II) Myometrium, (III) d) Relaxin from placenta Fallopian tube Ans. (b) Ans. (b) 25. In human female the blastocyst a) Forms placenta even before implantation CBSE PRELIMS – 2012 b) Gets implanted into uterus 3 days after ovulation 20. In a normal pregnant woman, the amount of c) Gets nutrition from uterine endometrial total gonadotropin activity was assessed. secretion only after implantation The result expected was: d) Gets implanted in endometrium by the a) High level of circulating HCG to stimulate trophoblast cells endometrial thickening Ans. (d) b) High levels of FSH and LH in uterus to 26. Secretions from which one of the following are stimulate endometrial thickening rich in fructose, calcium and some enzymes? c) High level of circulating HCG to stimulate a) Male accessory glands estrogen and progesterone synthesis b) Liver d) High level of circulating FSH and LH in c) Pancreas the uterus to stimulate implantation of the d) Salivary glands embryo Ans. (a) Ans. (c) 21. Signals for parturition originate from CBSE MAINS – 2011 a) Oxytocin released from maternal pituitary b) Placenta only 27. What happens during fertilisation in humans c) Fully developed foetus only after many sperms reach close to the ovum? d) Both placenta as well as fully developed a) Secretions of acrosome helps one sperm enter foetus cytoplasm of ovum through zona pellucida Ans. (d) b) All sperms except the one nearest to the 22. The Leydig cells as found in the human body ovum lose their tails are the secretory source of: c) Cells of corona radiata trap all the sperms a) Intestinal mucus b) Glucagon except one c) Androgens d) Progesterone d) Only two sperms nearest the ovum Ans. (c) penetrate zona pellucida 23. Which one of the following statements is false Ans. (a) in respect of viability of mammalian sperm? 10 DR. ARVIND’S BIOLOGY CLASSES (A Unit of Med-Xel Tutorials) 28. About which day in a normal human NEET – 2013 menstrual cycle does rapid secretion of LH (popularly called LH-surge) normally occurs? 31. What is the correct sequence of sperm a) 14th day b) 20th day formation? c) 5th day d) 11th day a) Spermatogonia, spermatozoa, spermatocyte, spermatid Ans. (a) b) Spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatid, spermatozoa c) Spermatid, spermatocyte, spermatogonia. CBSE MAINS – 2012 spermatozoa d) Spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatozoa, 29. The secretory phase in the human menstrual spermatid cycle is also called: Ans. (b) a) Luteal phase and lasts for about 13 days 32. Which one of the following is not the function b) Follicular phase and lasts for about 13 days of placenta? It: a) Facilitates removal of carbon dioxide and c) Luteal phase and lasts for about 6 days waste material from embryo. d) Follicular phase and lasting for about 6 days b) Secretes oxytocin during parturition. Ans. (a) c) Facilitates supply of oxygen and 30. Identify the human development stage nutrients to embryo. shown below as well as the related right place d) Secretes estrogen. of its occurrence in a normal pregnant Ans. (b) woman, and select the right option for the two 33. Product of sexual reproduction generally together. generates: a) New genetic combination leading to variation b) Large biomass c) Longer viability of seeds d) Prolonged dormancy Ans. (a) 34. Menstrual flow occurs due to lack of: a) Oxytocin b) Vasopressin c) Progesterone d) FSH Options: Ans. (c) Developmental stage Site of occurrence a) Blastocyst Uterine wall AIPMT – 2014 b) 8-celled morula Starting point of Fallopian tube 35. The shared terminal duct of the reproductive c) Late morula Middle part of Fallopian and urinary system in the human male is: tube a) Vasa efferentia b) Urethra d) Blastula End part of Fallopian tube c) Ureter d) Vas deferens Ans. (a) Ans. (b) Hint: The embryo with 8-16 blastomeres is 36. The main function of mammalian corpus luteum is to produce: called a morula, and is present in the end a) relaxin only part of fallopian tube. Morula forms the b) estrogen only blastocyst as it reaches the uterine c) progesterone cavity and then blastocyst implants in d) human chorionic gonadotropin the endometrium. Thus, the options (b), Ans. (c) (c), (d) are all wrong.
Description: