Arteries of the Abdomen Artery Source Branches Supply to Notes PDF
Preview Arteries of the Abdomen Artery Source Branches Supply to Notes
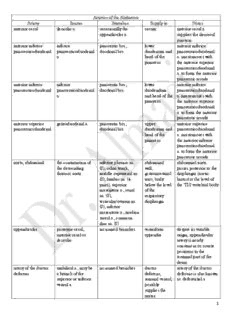
Arteries of the Abdomen Artery Source Branches Supply to Notes anterior cecal ileocolic a. occasionally the cecum anterior cecal a. appendicular a. supplies the ileocecal junction anterior inferior inferior pancreatic brs., lower anterior inferior pancreaticoduodenal pancreaticoduodenal duodenal brs. duodenum and pancreaticoduodenal a. head of the a. anastomoses with pancreas the anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal a. to form the anterior pancreatic arcade anterior inferior inferior pancreatic brs., lower anterior inferior pancreaticoduodenal pancreaticoduodenal duodenal brs. duodendum pancreaticoduodenal a. and head of the a. anastomoses with pancreas the anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal a. to form the anterior pancreatic arcade anterior superior gastroduodenal a. pancreatic brs., upper anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal duodenal brs. duodenum and pancreaticoduodenal head of the a. anastomoses with pancreas the anterior inferior pancreaticoduodenal a. to form the anterior pancreatic arcade aorta, abdominal the continuation of inferior phrenic aa. abdominal abdominal aorta the descending (2), celiac trunk, wall; passes posterior to the thoracic aorta middle suprarenal aa. gastrointestinal diaphragm (aortic (2), lumbar aa. (4 tract; body hiatus) at the level of pairs), superior below the level the T12 vertebral body mesenteric a., renal of the aa. (2), respiratory testicular/ovarian aa. diaphragm (2), inferior mesenteric a., median sacral a., common iliac aa. (2) appendicular posterior cecal, no named branches vermiform despite its variable anterior cecal or appendix origin, appendicular ileocolic artery is nearly constant in its course posterior to the terminal part of the ileum artery of the ductus umbilical a.; may be no named branches ductus artery of the ductus deferens a branch of the deferens, deferens is also known superior or inferior seminal vesical; as: deferential a. vesical a. possibly supplies the ureter 1 caudal pancreatic splenic a. numerous small aa. tail of the caudal pancreatic a. that supply the pancreas enters the tail of the pancreas pancreas near the hilum of the spleen; it may arise from the left gastro-omental a. cecal, anterior ileocolic a. may give off the anterior surface anterior cecal a. appendicular a. of the cecum supplies the ileocecal junction cecal, posterior ileocolic a. may give off the posterior posterior cecal a. appendicular a. surface of the supplies the ileocecal cecum junction celiac trunk abdominal aorta at left gastric a., splenic stomach, lower celiac trunk supplies the level of the T12- a., common hepatic a. esophagus, the foregut derivatives L1 intervertebral disc liver, upper duodenum, pancreas, spleen circumflex iliac, deep external iliac a. unnamed muscular iliacus muscle deep circumflex iliac a. branches and the lower courses along the iliac abdominal wall crest on the inner surface of the abdominal wall circumflex iliac, femoral a. unnamed muscular superficial superficial circumflex superficial branches fascia of lower iliac a. crosses the abdomen and upper thigh parallel to thigh the inguinal ligament colic, left inferior mesenteric a. ascending br., descending left colic a. descending br. colon anastomoses with the middle colic a and the sigmoid a.to form part of the marginal a. colic, middle superior mesenteric right br., left br. transverse middle colic a. colon anastomoses with the right colic a. and the left colic a. to form part of the marginal a. colic, right superior mesenteric ascending br., ascending right colic a. (or br. of) descending br. colon anastomoses with the ileocolic a. and the middle colic a. to form part of the marginal a. common hepatic celiac trunk gastroduodenal a., liver, upper common hepatic a. is proper hepatic a. part of the one of three brs. of the duodenum, celiac trunk (see also: part of the left gastric a., splenic pancreas, part a.) of the stomach common iliac abdominal aorta external iliac a., pelvis, lower abdominal aorta internal iliac a. limb bifurcates at the level of the L4 vertebral 2 body to form the right and left common iliac aa.; the common iliac artery bifurcates anterior to the sacroiliac articulation into its terminal brs. (external iliac a. and internal iliac a.) cremasteric inferior epigastric a. no named branches cremaster m., cremasteric a. is one of coverings of the the contents of the spermatic cord spermatic cord; it anastomoses with the testicular artery distally cystic right hepatic a. (or no named branches gall bladder cystic a. arises from superior mesenteric the right hepatic a. in a., proper hepatic a., ~72% of cases; other left hepatic a., possible origins are gastroduodenal a.) noted at left and are clinically relevant during gall bladder surgery dorsal pancreatic splenic a. right br., left br. neck of the right br.of the dorsal pancreas pancreatic a. anastomoses with the anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal a. in the prepancreatic arcade ductus deferens, umbilical a.; may be no named branches ductus artery of the ductus artery of a branch of the deferens, deferens is also known superior or inferior seminal vesical; as: deferential a. vesical a. possibly supplies the ureter epigastric, inferior external iliac a. cremasteric a. lower rectus inferior epigastric m. abdominis m., anastomoses with the pyramidalis m., superior epigastric m. lower within the rectus abdominal wall abdominis m. epigastric, superficial femoral a. cutaneous brs. superficial superficial epigastric a. fascia and skin is one of three of the lower superficial arteries that abdominal wall arise from the femoral a. (see also: superficial circumflex iliac a. and superficial external pudendal a.) epigastric, superior internal thoracic a. no named branches upper rectus superior epigastric a. is abdominis m., the direct continuation upper of the internal thoracic 3 abdominal wall a.; it s anastomoses with the inferior epigastric a. within the rectus abdominis m. esophageal descending thoracic no named branches lower 2/3rds of there are usually two aorta; left gastric a. the thoracic (sometimes 3) esophagus esophageal brs. off of the aorta; the left gastric a. gives esophageal brs. that ascend to supply the abdominal esophagus and lowest part of the thoracic esophagus; anastomoses occur between the esophageal brs. of the aorta and left gastric a. gastric, left celiac a. esophageal brs. superior part of left gastric a. the stomach anastomoses with the near the lesser right gastric a. on the curvature lesser curvature of the stomach; it also anastomoses with the esophageal brs. of the thoracic aorta gastric, right proper hepatic a. no named branches inferior part of right gastric a. the stomach anastomoses with the near the lesser left gastric a. on the curvature lesser curvature of the stomach gastric, short splenic a. no named branches fundus and short gastric aa. reach upper part of the stomach by passing the stomach through the near the greater gastrosplenic ligament; curvature they are usually 4-5 in number gastro-omental, left splenic a. gastric brs., omental mid-part of the left gastro-omental a. brs. stomach near anastomoses with the the greater right gastro-omental a. curvature; near the greater greater curvature of the omentum stomach; also known as: left gastroepiploic a. gastro-omental, right gastroduodenal a. gastric brs., omental lower part of right gastro-omental a brs. the pyloric anastomoses with the region of the left gastro-omental a. stomach, right near the greater part of greater curvature of the curvature of the stomach; also known 4 stomach, as: right gastroepiploic greater a. omentum gastroduodenal common hepatic a. supraduodenal aa., upper gastroduodenal a. retroduodenal aa., duodenum, supplies the lowest posterior superior upper part of portion of the foregut pancreaticoduodenal the head of the and its derivatives a., anterior superior pancreas; pancreaticoduodenal greater a., right gastro- curvature of the omental a. stomach on the right great anterior the spinal br. of the no named branches lower spinal great anterior radicular radicular lower posterior cord a. anastomoses with intercostal a., the anterior spinal a. at subcostal a., or upper lower thoracic or lumbar a., usually on upper lumbar spinal left cord levels hepatic, common celiac trunk gastroduodenal a., liver, upper common hepatic a. proper hepatic a. parts of the supplies some of the duodenum, foregut derivatives upper part of the pancreas, right side of the stomach hepatic, left proper hepatic a. segmental aa. left lobe of the left hepatic a. supplies liver, quadrate the liver parenchyma lobe of the and stroma; an liver, part of aberrant left hepatic a. the caudate may arise from the left lobe of the liver gastric a. hepatic, proper common hepatic a. right gastric, right & liver, lesser proper hepatic a. left hepatic curvature of the supplies the foregut stomach derivatives associated with the liver bud hepatic, right proper hepatic a. cystic a., segmental aa. right lobe of right hepatic a. the liver, part supplies the liver of the caudate parenchyma and lobe of the liver stroma ileocolic superior mesenteric colic br., anterior cecum, colic br. of the a. cecal br., posterior appendix, ileocolic a. participates cecal br., appendicular terminal in the formation of the a., ileal br. portion of the marginal a. ileum iliac, common abdominal aorta external iliac a., pelvis, lower abdominal aorta internal iliac a. limb bifurcates at the level of the L4 vertebral body to form the right and left common iliac aa.; the common iliac artery bifurcates 5 anterior to the sacroiliac articulation into its terminal brs. (external iliac a. and internal iliac a.) iliac, external common iliac a. inferior epigastric a., lower limb external iliac a. is deep circumflex iliac continuous with the a., femoral a. femoral a., the name change occurs at the inguinal ligament; the common iliac artery bifurcates anterior to the sacroiliac articulation iliac, internal common iliac a. anterior division gives pelvic viscera, common iliac artery rise to the : umbilical gluteal region, bifurcates anterior to a., obturator a., hip, medial the sacroiliac uterine a., vaginal a., thigh articulation to form inferior vesical a., the internal iliac a. and middle rectal a., the external iliac a. internal pudendal a., inferior gluteal a.; posterior division gives rise to the: iliolumbar a., lateral sacral a., superior gluteal a. iliolumbar internal iliac a., iliac br., lumbar br. iliacus m., lumbar br. of the posterior division psoas major iliolumbar a. sends a m., quadratus small spinal br. into lumborum m. the vertebral canal inferior epigastric external iliac a. cremasteric a. lower rectus inferior epigastric m. abdominis m., anastomoses with the pyramidalis m., superior epigastric m. lower within the rectus abdominal wall abdominis m. inferior mesenteric abdominal aorta at left colic a., sigmoid splenic flexure, branches of the the level of the L3 aa.(2-3), superior descending inferior mesenteric a vertebral body rectal a. colon, sigmoid anastomose in the colon, superior marginal artery part of rectum inferior pancreatic dorsal pancreatic, left no named branches lower part of inferior pancreatic a. br. the body of the may be imbedded in pancreas the substance of the gland inferior superior mesenteric anterior inferior lower inferior pancreaticoduodenal a. pancreaticoduodenal duodenum, pancreaticoduodenal a., posterior inferior head of the a. supplies both the pancreaticoduodenal pancreas anterior and posterior a. surfaces of the lower duodenum and lower 6 part of the head of the pancreas inferior phrenic abdominal aorta superior suprarenal diaphragm, inferior phrenic a. is aa. suprarenal the first abdominal gland branch of the aorta; it may arise from the celiac trunk inferior rectal internal pudendal a. no named branches anus, ischioanal inferior rectal a. fossa anastomoses with the middle rectal a. and the superior rectal a. inferior suprarenal renal a. numerous unnamed inferior aspect inferior suprarenal a. branches of the may anastomose with suprarenal the superior gland suprarenal a. intercostal, posterior highest intercostal posterior br., spinal intercostal posterior intercostal (upper 2 intercostal br., anterior br., muscles, spinal aa. supply the lateral spaces), descending collateral br., lateral cord and and posterior portions thoracic aorta (3rd- cutaneous br. vertebral of the intercostal 11th intercostal column, deep space; anterior spaces) back muscles, intercostal aa. supply skin and the anterior portions superficial of the intercostal fascia overlying spaces the intercostal spaces internal iliac common iliac a. anterior division gives pelvic viscera, common iliac artery rise to the : umbilical gluteal region, bifurcates anterior to a., obturator a., hip, medial the sacroiliac uterine a., vaginal a., thigh articulation to form inferior vesical a., the internal iliac a. and middle rectal a., the external iliac a. internal pudendal a., inferior gluteal a.; posterior division gives rise to the: iliolumbar a., lateral sacral a., superior gluteal a. intestinal superior mesenteric arterial arches jejunum, ileum intestinal aa. are 12-15 a. in number and are found in the mesentery lateral sacral internal iliac a., spinal brs. sacrum, sacral there are usually 2 posterior division nerve rootlets, lateral sacral aa. on meninges, each side, a superior adjacent one and an inferior muscles one left colic inferior mesenteric a. ascending br., descending left colic a. descending br. colon anastomoses with the middle colic a and the 7 sigmoid a.to form part of the marginal a. left gastric celiac a. esophageal brs. superior part of left gastric a. the stomach anastomoses with the near the lesser right gastric a. on the curvature lesser curvature of the stomach; it also anastomoses with the esophageal brs. of the thoracic aorta left gastro-omental splenic a. gastric brs., omental mid-part of the left gastro-omental a. brs. stomach near anastomoses with the the greater right gastro-omental a. curvature; near the greater greater curvature of the omentum stomach; also known as: left gastroepiploic a. left hepatic proper hepatic a. segmental aa. left lobe of the left hepatic a. supplies liver, quadrate the liver parenchyma lobe of the and stroma; an liver, part of aberrant left hepatic a. the caudate may arise from the left lobe of the liver gastric a. lumbar abdominal aorta anterior br., posterior psoas major the 4 lumbar arteries br., spinal br. m., psoas on each side arise minor m., from the posterior quadratus surface of the aorta at lumborum m., the level of vertebrae spinal cord and L1-L4; they course vertebral posterior to the psoas column, deep major m. back muscles marginal formed by colic brs. colon an important anastomoses of anastomosis for the branches of the large intestine ileocolic a., right colic a., middle colic a., left colic a., sigmoid a. median sacral abdominal aorta 5th lumbar aa. sacrum median sacral a. appears to be the continuation of the abdominal aorta in the median plane, although it is much smaller in size mesenteric, inferior abdominal aorta at left colic a., sigmoid splenic flexure, branches of the the level of the L3 aa.(2-3), superior descending inferior mesenteric a vertebral body rectal a. colon, sigmoid anastomose in the colon, superior marginal artery 8 part of rectum mesenteric, superior abdominal aorta at inferior inferior part of superior mesenteric a. the level of the lower pancreaticoduodenal the head of the supplies the midgut 1/3 of the L1 a., middle colic a., pancreas, distal derivatives; brs. of the vertebral body jejunal a., ileal a., right duodenum, superior mesenteric a. colic a., ileocolic a. jejunum, ileum, participate in cecum, formation of the appendix, marginal artery ascending colon, transverse colon middle colic superior mesenteric right br., left br. transverse middle colic a. colon anastomoses with the right colic a. and the left colic a. to form part of the marginal a. middle rectal internal iliac, anterior no named branches middle portion middle rectal a. division of the rectum anastomoses with the inferior rectal a and the superior rectal a. middle suprarenal abdominal aorta numerous unnamed medial side of middle suprarenal a. branches the suprarenal anastomoses with the gland superior suprarenal a. and the inferior suprarenal a. musculophrenic internal thoracic a. anterior intercostal aa. anterior musculophrenic a. diaphragm, supplies muscles that anterior aspects develop in the septum of intercostal transversum spaces 7-10 or 11 pancreatic, caudal splenic a. numerous small aa. tail of the caudal pancreatic a. that supply the pancreas enters the tail of the pancreas pancreas near the hilum of the spleen; it may arise from the left gastro-omental a. pancreatic, dorsal splenic a. right br., left br. neck of the right br.of the dorsal pancreas pancreatic a. anastomoses with the anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal a. in the prepancreatic arcade pancreatic, inferior dorsal pancreatic, left no named branches lower part of inferior pancreatic a. br. the body of the may be imbedded in pancreas the substance of the gland pancreatic, superior splenic a. no named branches superior part of superior pancreatic aa. the body of the are multiple small brs. 9 pancreas arising from the splenic a. pancreatica magna splenic a. numerous unnamed body of the pancreatic magna is brs. within the pancreas the largest pancreatic pancreas branch to arise from the splenic a.; it enters the pancreas at the junction of its middle 1/3 and left 1/3 pancreaticoduodenal, inferior pancreatic brs., lower anterior inferior anterior inferior pancreaticoduodenal duodenal brs. duodenum and pancreaticoduodenal a. head of the a. anastomoses with pancreas the anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal a. to form the anterior pancreatic arcade pancreaticoduodenal, gastroduodenal a. pancreatic brs., upper anterior superior anterior superior duodenal brs. duodenum and pancreaticoduodenal head of the a. anastomoses with pancreas the anterior inferior pancreaticoduodenal a. to form the anterior pancreatic arcade pancreaticoduodenal, superior mesenteric anterior inferior lower inferior inferior a. pancreaticoduodenal duodenum, pancreaticoduodenal a., posterior inferior head of the a. supplies both the pancreaticoduodenal pancreas anterior and posterior a. surfaces of the lower duodenum and lower part of the head of the pancreas pancreaticoduodenal, inferior pancreatic brs., lower posterior inferior posterior inferior pancreaticoduodenal duodenal brs. duodenum and pancreaticoduodenal a. head of the a. anastomoses with pancreas the posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal a. to form the posterior pancreatic arcade pancreaticoduodenal, gastroduodenal a. pancreatic brs., upper posterior superior posterior superior duodenal brs. duodenum and pancreaticoduodenal head of the a. anastomoses with pancreas the posterior inferior pancreaticoduodenal a. to form the posterior pancreatic arcade phrenic, inferior abdominal aorta superior suprarenal diaphragm, inferior phrenic a. is aa. suprarenal the first abdominal gland branch of the aorta; it may arise from the 10
Description: