appendix a: design of mse wall PDF
Preview appendix a: design of mse wall
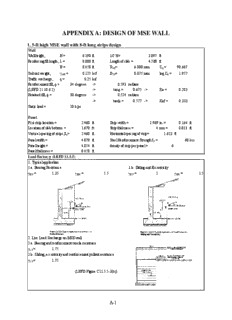
APPENDIX A: DESIGN OF MSE WALL 1. 5-ft high MSE wall with 8-ft long strips design Wall Wall height, H = 6.190 ft 1/2 H= 3.095 ft Reinforcing fill length, L = 8.000 ft Length of slab = 4.500 ft B = 8.458 ft D = 6.800 mm C = 90.667 60 u Soil unit weight, = 0.125 kcf D = 0.075 mm log C = 1.957 soil 10 u Traffic surcharge, q = 0.25 ksf Reinforcement fill, = 34 degrees -> 0.593 radians (LRFD 11.10.6.2) -> tan = 0.675 -> Ka = 0.283 Retained fill, = 30 degrees -> 0.524 radians -> tan = 0.577 -> Kaf = 0.333 f Static load = 10 kips Panel First strip location = 2.460 ft Strip width = 1.969 in. = 0.164 ft Location of slab bottom = 1.670 ft Strip thickness = 4 mm = 0.013 ft Vertical spacing of strips,S = 2.460 ft Horizontal spacing of strip= 1.623 ft v Panel width = 4.870 ft Steel Reinforcement Strength f = 60 ksi y Panel height = 4.854 ft density of strip per panel = 6 Panel thickness = 0.458 ft Load Factor, (LRFD 11.5.5) 1. Typical application 1.a. Bearing Resistance 1.b. Sliding and Eccentricity = 1.35 = 1.5 = 1 = 1.5 EV EH EV EH 2. Live Load Surcharge on MSE wall 2.a. Bearing and reinforcement tensile resistnace = 1.75 LS 2.b. Sliding, eccentricity and reinforcement pullout resistance = 1.75 LS (LRFD Figure C11.5.5-3(b)) A-1 Resistance Factor, (LRFD Table 11.5.6-1) Mechanically Stabilized Earth Walls Pullout resistance of tensile reinforcement, Static loading = 0.9 Combined static and impact loading = 1 Tensile Resistance of strip reinforcement, Static loading = 0.75 Combined static and impact loading = 1 1. External Stability 1.1 Static Mass Stability (LRFD Figure 11.10.5.2-1) 1.1.1 Vertical loads 1. Reinforced Soil V = × H × L soil V1= 0.125 (kcf) × 6.19 (ft) × 8 (ft) = 6.190 kips/ft × V1= 1.35 × V1= 8.357 kips/ft EV Moment arm of V1 = 4 ft M = 6.19 (kips/ft) × 4 (ft) = 24.760 ft-kips/ft v1 × M = 1.35 × M = 33.426 ft-kips/ft EV v1 v1 2. Traffic surcharge V2= 0.25 (ksf) × 8 (ft) = 2.000 kips/ft × V2= 1.75 × V2= 3.500 kips/ft LS Moment arm of V2 = 4 ft M = 2 (kips/ft) × 4 (ft) = 8.000 ft-kips/ft v2 × M = 1.750 × M = 14.000 ft-kips/ft LS v2 v2 ∑V = 8.19 kips/ft ∑Mv = 32.760 ft-kips/ft ∑V = 11.86 kips/ft ∑Mv = 47.426 ft-kips/ft A-2 1.1.2 Horizontal loads 1. Retained soil F1= 1/2 × soil × H2 × Kaf F1= 1/2 × 0.125 (kcf) × 38.316 (ft2) × 0.333 = 0.798 kips/ft × F1= 1.5 × F1= 1.197 kips/ft EH Moment arm of F1 = 6.19 /3 = 2.06 ft M = 0.798 (kips/ft) × 2.063 (ft) = 1.647 ft-kips/ft F1 × M = 1.5 × M = 2.471 ft-kips/ft EH F1 F1 2. Traffic surcharge F2= q × H × Kaf F2= 0.250 (ksf) × 6.190 (ft) × 0.333 = 0.516 kips/ft × F2= 1.5 × F2= 0.774 kips/ft LS Moment arm of V2 = 3.095 ft M = 0.51583 (kips/ft) × 3.095 (ft) = 1.597 ft-kips/ft F2 × M = 1.5 × M = 2.395 ft-kips/ft LS F2 F2 ∑F = 1.31 kips/ft ∑MF = 3.244 ft-kips/ft ∑F = 1.97 kips/ft ∑MF = 4.865 ft-kips/ft 1.1.3 Sliding (LRFD 11.10.5.3) Sliding without Load Factor= ∑V*tan = 8.190 ×tan 30 = 3.598 ∑FH = 1.314 Sliding with Load Factor = ∑EVV*tan= 11.857 ×tan 30 = 3.473 ∑EHFH = 1.971 1.1.4 Overturning (LRFD 11.10.5.3) Overturning w/o Load Factor= ∑Mv = 32.760 = 10.100 ∑MF 3.244 Overturning w/ Load Factor= ∑EVMv = 47.426 = 9.748 ∑EHMF 4.865 1.2 Bearing Capacity at Base Eccentricity w/o Load Factor= L - ∑M - ∑M v F 2 ∑V = 8 - 32.760 - 3.244 = 0.396 2 8.190 Eccentricity w/ Load Factor = L - ∑EVMv - ∑EHMF 2 ∑EVV = 8 - 47.426 - 4.865 = 0.410 2 11.857 ≤ B = 1.410 ft OK 6 A-3 w/o Load Facto r= ∑V = 8.19 = 1.136 ksf v (L-2e) 8 - 2 × 0.39604 v w/ Load Facto r= ∑EVV = 11.86 = 1.651 ksf (L-2e) 8 - 2 × 0.41035 2. Internal Stability 2.1 Static Load 2.1.1 Compute Kr (LRFD Figure 11.10.6.2.1-3) Kr = 1.7 × Ka = 1.7 × 0.28 = 0.48 at 0 ft EH Kr = 1.2 × Ka = 1.2 × 0.28 = 0.34 under 20 ft EH Use interpolation at other depth 2.1.2 Fisrt strip at h1= 2.46 ft h1 = 2.46 ft kr = 0.463 1. Vertical stress 1) Reinforced Soil = × H V1 soil V1 = 0.125 (kcf) × 2.460 (ft) = 0.308 kips/ft2 EV × V1 = 1.35 × = 0.415 kips/ft2 2) Traffic surcharge = 0.25 ksf V2 EV × V2 = 1.75 × 0.25 = 0.438 kips/ft2 a) ignoring tracffic surcharge b) including tracffic surcharge ∑v = 0.308 kips/ft2 ∑v = 0.558 kips/ft2 ∑EVv = 0.415 kips/ft2 ∑EVv = 0.853 kips/ft2 Horizontal stress, = ( k + ) (LRFD Eq. 11.10.6.2.1-1) H P v r H a) ignoring tracffic surcharge = k = 0.308 ksf × 0.463 = 0.142 ksf h v r = k = 0.415 ksf × 0.463 = 0.192 ksf EV h EV v r At per strip = 4.870 (ft) × 2.460 (ft) / 3 = 3.993 ft2 Tmax = H Sv = 0.142 ksf × 3.993 ft2 = 0.57 kips per strip EV Tmax = EV H Sv = 0.192 ksf × 3.993 ft2 = 0.77 kips per strip A-4 b) including tracffic surcharge = k = 0.558 ksf × 0.463 = 0.258 ksf h v r = k = 0.853 ksf × 0.463 = 0.395 ksf EV h EV v r Tmax = H Sv = 0.258 ksf × 3.993 ft2 = 1.03 kips per strip EV Tmax = EV H Sv = 0.395 ksf × 3.993 ft2 = 1.58 kips per strip 3. Resistance in friction of one strip against soil (LRFD Equation 11.10.6.3.2-1) 1) using L for static case e P = F* Le C b = 1.138 kips v P = 0.9 × 1.138 = 1.025 kips 2) using L for static + dynamic case P = F* L C b = 1.483 kips v P = 0.9 × 1.483 = 1.334 kips a) F* Kr = 2.000 at 0 ft Kr = tan = 0.675 under 20 ft f Use interpolation at other depth F* = 1.837 (LRFD Figure 11.10.6.3.2-1) b) = 1 (LRFD Table 11.10.6.3.2-1) c) = 0.125 (kcf) × 2.46 (ft) = 0.3075 ksf v d) L= L-H/3 = 8 - 0.3 × 6.19 = 6.143 ft e (LRFD Figure 11.10.2-1 and 11.10.10.1-2) e) C = 2 for stip (LRFD 11.10.6.3.2) f) b = 0.164 ft 4. Location of Maximum Tensile Force (LRFD Figure 11.10.10.1-2) If the height of reinforcement layer is above the H/2, the location of max. tensile force is located in 0.3H. 0.3H = 1.857 ft H/2 = 3.095 ft L = 1.857 ft max. A-5 2.1.3 Second strip at h2= 4.92 ft h1 = 4.920 ft Kr = 0.446 1. Vertical stress 1) Reinforced Soil = × H V1 soil V1 = 0.125 (kcf) × 4.920 (ft) = 0.615 kips/ft2 EV × V1 = 1.35 × = 0.830 kips/ft2 2) Traffic surcharge = 0.25 ksf V2 EV × V2 = 1.75 × 0.25 = 0.438 kips/ft2 a) ignoring tracffic surcharge b) including tracffic surcharge ∑v = 0.615 kips/ft2 ∑v = 0.865 kips/ft2 ∑EVv = 0.830 kips/ft2 ∑EVv = 1.268 kips/ft2 Horizontal stress, = ( k + ) (LRFD Eq. 11.10.6.2.1-1) H P v r H a) ignoring tracffic surcharge = k = 0.615 ksf × 0.446 = 0.274 ksf h v r = k = 0.830 ksf × 0.446 = 0.370 ksf EV h EV v r At per strip = 4.870 (ft) × 2.460 (ft) / 3 = 3.993 ft2 depth for A at the second layer = S = 2.460 ft t v Tmax = H Sv = 0.274 ksf × 3.993 ft2 = 1.095 kips per strip EV Tmax = EV H Sv = 0.370 ksf × 3.993 ft2 = 1.478 kips per strip b) including tracffic surcharge = k = 0.865 ksf × 0.446 = 0.386 ksf h v r = k = 1.268 ksf × 0.446 = 0.565 ksf EV h EV v r Tmax = H Sv = 0.386 ksf × 3.993 ft2 = 1.54 kips per strip EV Tmax = EV H Sv = 0.565 ksf × 3.993 ft2 = 2.26 kips per strip 3. Resistance in friction of one strip against soil (LRFD Equation 11.10.6.3.2-1) 1) using L for static case e P = F* Le C b = 2.445 kips v P = 0.9 × 2.44 = 2.200 kips A-6 2) using L for static + dynamic case P = F* L C b = 2.702 kips v P = 0.9 × 2.702 = 2.432 kips a) F* Kr = 2.000 at 0 ft Kr = tan = 0.675 under 20 ft f Use interpolation at other depth F* = 1.674 (LRFD Figure 11.10.6.3.2-1) b) = 1 (LRFD Table 11.10.6.3.2-1) c) = 0.125 (kcf) × 4.920 (ft) = 0.615 ksf v d) L= 7.238 ft (LRFD Figure 11.10.2-1 and 11.10.10.1-2) e e) C = 2 for stip (LRFD 11.10.6.3.2) f) b = 0.164 ft 4. Location of Maximum Tensile Force (LRFD Figure 11.10.10.1-2) If the height of reinforcement layer is above the H/2, the location of max. tensile force is located in 0.3H. 0.3H = 1.857 ft H/2 = 3.095 ft L = 0.762 ft max. 2.1.4 Reinforcement Tensile Strength 1) 75.00 years Design Life R= f × A = f × (Strip width × E ) y steel y c = 60.00 ksi × ( 1.969 in. × 0.102 ) in. = 12.016 kips R = 0.75 × 12.016 = 9.012 kips 2) 100.00 years Design Life R= f × A = f × (Strip width × E ) y steel y c = 60.00 ksi × ( 1.969 in. × 0.078 ) in. = 9.226 kips R = 0.75 × 9.226 = 6.919 kips For corrosion Losses E = E - E (LRFD Eq. 11.10.6.4.2a-1) c n s Zinc Coating Lift = 16 years Loass of carbon steel = 0.012 mm/yr. after zinc deplection 1) 75.00 years Design Life E = 4.00 mm - 1.416 mm = 2.584 mm = 0.102 in. c 2) 100.00 years Design Life E = 4.00 mm - 2.016 mm = 1.984 mm = 0.078 in. c 2.1.5 Summary 1) Pullout - ignoring traffic surcharge Rein. Layer Z T T P P NO. (ft) (kips) (kips) (kips) (kips) 1 2.46 0.569 0.768 1.138 1.025 2 4.92 1.095 1.478 2.445 2.200 A-7 2) Tensile - ignoring traffic surcharge 75 year Design Life 100 year Design Life Rein. Layer Z T T R R R R NO. (ft) (kips) (kips) (kips) (kips) (kips) (kips) 1 2.46 0.569 0.768 12.016 9.012 9.226 6.919 2 4.92 1.095 1.478 2.2 Including Impact Load load Br (length of s f 45+(/2) 45+(/2) tan(45+(/2)) Cr l1 (kips) (ft) (degrees) (degrees) radian (ft) (ft) 10 4.50 34 62 1.082 1.881 0.000 8.463 2.2.1 Tensile stress 5 ft.-> ∑F = 2 kpf Rein. Layer Layer l1 A T T hmax t impact impact NO. (ft) (ft) (ksf) (ft2) (kips) (kips) bottom of sla 1.670 8.463 0.473 1 2.460 7.673 0.429 3.993 1.711 1.711 2 4.920 5.213 0.291 3.993 1.163 1.163 * Summary of Total 75 year 100 year Rein. Layer Z T T Total T R R impact NO. (ft) (kips) (kips) (kips) (kips) (kips) 1 2.46 0.569 1.711 2.280 12.016 9.226 2 4.92 1.095 1.163 2.257 12.016 9.226 A-8 2.2.2 Pullout stress 20 ft.-> ∑F = 0.5 kpf Rein. Layer Layer l1 A T T hmax t impact impact NO. (ft) (ft) (ksf) (ft2) (kips) (kips) bottom of sla 1.670 8.463 0.118 1 2.460 7.673 0.107 3.993 0.428 0.428 2 4.920 5.213 0.073 3.993 0.291 0.291 * Summary of Total Rein. Layer Z T T Total T P impact NO. (ft) (kips) (kips) (kips) (kips) 1 2.46 0.569 0.428 0.997 1.483 2 4.92 1.095 0.291 1.386 2.702 A-9 2. 5-ft high MSE wall with 16-ft long strips design Wall Wall height, H = 6.190 ft 1/2 H= 3.095 ft Reinforcing fill length, L = 16.000 ft Length of slab = 4.500 ft B = 16.458 ft D = 6.800 mm C = 90.667 60 u Soil unit weight, = 0.125 kcf D = 0.075 mm log C = 1.957 soil 10 u Traffic surcharge, q = 0.25 ksf Reinforcement fill, = 34 degrees -> 0.593 radians (LRFD 11.10.6.2) -> tan = 0.675 -> Ka = 0.283 Retained fill, = 30 degrees -> 0.524 radians -> tan = 0.577 -> Kaf = 0.333 f Static load = 10 kips Panel First strip location = 2.460 ft Strip width = 1.969 in. = 0.164 ft Location of slab bottom = 1.670 ft Strip thickness = 4 mm = 0.013 ft Vertical spacing of strips,S = 2.460 ft Horizontal spacing of strip= 2.435 ft v Panel width = 4.870 ft Steel Reinforcement Strength f = 60 ksi y Panel height = 4.854 ft density of strip per panel = 4.000 Panel thickness = 0.458 ft Load Factor, (LRFD 11.5.5) 1. Typical application 1.a. Bearing Resistance 1.b. Sliding and Eccentricity = 1.35 = 1.5 = 1 = 1.5 EV EH EV EH 2. Live Load Surcharge on MSE wall 2.a. Bearing and reinforcement tensile resistnace = 1.75 LS 2.b. Sliding, eccentricity and reinforcement pullout resistance = 1.75 LS (LRFD Figure C11.5.5-3(b)) A-10
Description: