A membrane penetrating peptide aptamer inhibits STAT3 function and suppresses the growth of STAT3 addicted tumor cells. PDF
Preview A membrane penetrating peptide aptamer inhibits STAT3 function and suppresses the growth of STAT3 addicted tumor cells.
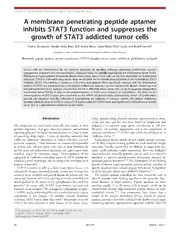
JAK-STAT1:1,44–54;January/February/March2012;G2012LandesBioscience A membrane penetrating peptide aptamer inhibits STAT3 function and suppresses the growth of STAT3 addicted tumor cells Corina Borghouts, Natalia Delis, Boris Brill, Astrid Weiss, Laura Mack, Peter Lucks and Bernd Groner* Georg-Speyer-Haus;InstituteforBiomedicalResearch;FrankfurtamMain,Germany Keywords: peptide aptamer, protein transduction, STAT3 phosphorylation, tumor inhibition, glioblastoma xenografts Cancer cells are characterized by the aberrant activation of signaling pathways governing proliferation, survival, angiogenesis,migrationandimmuneevasion.TheseprocessesarepartiallyregulatedbythetranscriptionfactorSTAT3. Thisfactorisinappropriatelyactivatedindiversetumortypes.Sincetumorcellscanbecomedependentonitspersistent activation,STAT3isafavorabledrugtarget.Here,wedescribethefunctionalcharacterizationoftherecombinantSTAT3 inhibitor, rS3-PA. This inhibitor is based on a 20 amino acid peptide which specifically interacts with the dimerization domainofSTAT3.Itisintegratedintoathioredoxinscaffoldandfusedtoaproteintransductiondomain.Proteingelblot © 2012 Landes Bioscience. and immunofluorescence analyses showed that rS3-PA is efficiently taken up by cells via an endocytosis independent mechanism. Intracellularly, it reduces the phosphorylation of STAT3 and enhances its degradation. This leads to the downregulationofSTAT3targetgeneexpressiononthemRNAandproteinlevels.Subsequently,tumorcellproliferation, survival and migration and the induction of angiogenesis are inhibited. In contrast, normal cells remain unaffected. SystemicadministrationofrS3-PAatdosesof7.5mg/kgreducedP-STAT3levelsandsignificantlyinhibitedtumorgrowth upto35% inaglioblastoma xenograft mousemodel. Do not distribute. Introduction colon, prostate, lung, pancreas, pituitary, gastrointestines, ovary, cervix and skin and has also been found in lymphomas and The comparison of normal and tumor cells with respect to their leukemias.9 It activates target genes contributing to cell pro- genomicsequences,1theirgeneexpressionpatterns2andactivated liferation, cell survival, angiogenesis and to the suppression of signalingpathways3hasledtotheidentificationofalargenumber immune surveillance.10-12 STAT3 also fulfills the definition of an of promising drug targets. A class of signaling molecules that “addiction factor.”13 confer an “addiction” phenotype to tumor cells have received Transcription factors usually do not exhibit enzyme activities, particularattention.4Thesemoleculesaretemporarilydispensable nordothey comprisebindingpockets forsmallmolecularweight in normal cells, whereas tumor cells react to their inhibition by molecules. For this reason they are difficult to target with syn- growth arrest and induction of apoptosis, and appear particularly thetic, small molecular weight compounds. However, biological suited as targets for innovative drugs.5 Downregulation of the macromolecules, especially peptides, can be used as competitive expression of “addiction-conferring” genes by RNA interference inhibitors to prevent protein-protein interactions required for servedasaproof-of-principleandencouragedthedevelopmentof particular protein functions.14,15 The delimitation of the binding targeted compounds. domain of known target-interaction partners and the selection of STAT3 is present in cells as a latent transcription factor. It is specificsequences fromrandompeptidelibrariescanbeexploited activated by receptorassociated tyrosine kinases andmediates the to derive peptides which exert inhibitory functions.16,17 actionofmanycytokinesandgrowthfactors.Innormalcells,the The peptide aptamer technology has been extensively used to extent and duration of STAT3 signaling is strictly controlled and identify peptides with binding specificities for particular func- downregulated by the action of e.g., phosphatases, Socs and Pias tional domains of target proteins. Peptide aptamers are short proteins.6 In tumor cells, STAT3 is persistently activated and peptides, usually 12 to 20 amino acids in length, which can be functionsasanoncogene.Thesphingosine-1-phosphatereceptor- selected from random, high-complexity peptide libraries in yeast- 1,S1PR1,anditsenhancingeffectsontyrosinekinasesisamajor two-hybrid screens.18,19 Our experiments have shown that a contributor to this process.7 In addition, somatic mutations variant of the human thioredoxin (hTrx), devoid of cysteine activating STAT3 have been discovered.8 Persistently activated residues,providesafavorablescaffoldforthedisplayofsuchtarget STAT3 has been detected in solid tumors of the breast, brain, interacting peptides. Appropriately appended scaffolds allow the *Correspondenceto:BerndGroner;Email:[email protected] Submitted:09/06/11;Revised:12/05/11;Accepted:12/05/11 http://dx.doi.org/10.4161/jkst.18947 44 JAK-STAT Volume1Issue1 RESEARCHPAPER presentation of the peptide in a constrained conformation, the Europe). The different peptide aptamer variants were fused to production as recombinant proteins and the cellular delivery of the Gal4-activation domain (pGAD-T7, Clontech-Takara Bio specific peptide aptamers.20,21 Europe) to create the prey constructs. To improve the recom- Here,wefurthermodifiedtheSTAT3-specificpeptideaptamer binant expression of the peptide aptamer, the pFlag vector hTrxDcys-DD3.8Dcys20 to optimize its functional properties. A (Sigma-Aldrich) was used. A NLS, generated by annealing two tagged version, rS3-PA, was derived and detailed analyses of its complementary oligonucleotides (5'- aaa aag cct cca aag aag aag cellular uptake into cultured cells and the molecular mode of agg aaggaattcttt-3'and5'-aaagaattccttcctcttcttctttggaag STAT3 inhibition were conducted. We found that rS3-PA ctt ttt -3') was inserted between the Hind III/EcoR I restriction efficiently enters cells, causes the reduction of STAT3 phosphor- sites of pFlag. The sequence encoding the peptide aptamer ylation and enhances the proteasomal degradation of P-STAT3. insertedintothehTrxscaffold,wasamplifiedfromplasmidpET- ThisresultsinSTAT3targetgeneinhibitionandimpairedtumor hTrxDD3–3.8Dcys20 using primers with EcoR I restriction sites cell proliferation, migration and survival. Finally, i.v. administra- (5'- aaa gaa ttc atg ggt aag cag atc gag -3' and 5'- aaa gaa ttc gac tion of rS3-PA into mice showed that the systemic application taa ttc att aat ggt -3'). Insertion of the product in pFlag-NLS of rS3-PA inhibits STAT3 activation in vivo and retarded the vector resulted in construct pFlag-hTrxDcys-DD3.8Dcys encod- growth kinetics of transplanted glioma cells. ing rS3-PA (see Fig.1C). Materials and Methods Reagents. Recombinant IL-6, INFc chloro- ©quine, he2paran 0sulfates1, mitom2ycin C,Lanti-andes Bioscience. Actin,anti-Flagand-Tubulinwereobtained from Sigma-Aldrich. STAT3 and STAT5 antibodieswerefromSantaCruz.P-STAT1, P-STAT5,P-STAT3Y705,His-tagandc-Myc antibodies were purchased from CellSignal- ing. Anti-Survivin was obtained from Acris Do not distribute. Antibodies and anti-Lamin B1 was obtained from Abcam. MG-132 was purchased from Calbiochem. Cell lines. Human (MZ-54, MZ-18 and U-373) and murine high-grade glioma cell lines (Tu-9648, Tu-2449), human breast cancer celllines (SK-BR-3,MDA-MB-468), the A431 epithelial cancer cell line, the murinebreastcancercellline4T1,theK562 leukemia cell line and immortalized fibro- blasts NIH-3T3, were cultivated in DMEM with 10% FCS. Primary human umbilical veinendothelialcells(HUVEC)werekindly provided at passage 2 by Carmen Döbele (Institute of Cardiovascular Regeneration, Figure1.StructureandbindingspecificityofrecombinantpeptideaptamerrS3-PA.(A)YTH Frankfurt, Germany) and grown in EGM interactionanalysisofthepeptideaptamerrS3-PAwithmembersoftheSTATfamily.Yeastcells (endothelialbasalmediumwithsupplements (Y187)wereco-transformedwithbaitandpreyconstructs.Interactionoftheseproteinswas and10%FCS).Theimmortalizedbreastcell quantifiedinstandardbgalactosidaseassays(displayedinMillerUnits).(B)Interactionofbaitand preyfusionproteinsdescribedin(A)alsoresultsinthegrowthofcoloniesonplateslacking line MCF-10A cells was grown in DMEM/ histidine.(C)SchematicpresentationofpeptideaptamerDD340aminoacids(A)insertedinto F12 medium supplied with 5% FCS, thehTrxscaffold(upperconstruct).ModificationsperformedtogeneratepFlag-hTrxDcys- 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 U/ml streptomy- DD3.8DcysencodingrS3-PAareshown(middleconstruct).rS3-PAencodesa20merpeptide cin, 2 mM L-glutamine, 20 ng/ml human fragmentofDD3devoidofcysteines.ThepeptideaptamerpresentinrS3-PAcorrespondstothe EGF, 100 ng/ml cholera toxin, 10 ng/ml sequenceN-VRHSALHMAVGPLSWPARVS-C.Thebaitusedtoselectthispeptideaptamer insulin and 500 ng/ml hydrocortisone. comprisestheSTAT3sequence655to755.21Secondarystructurepredictionprogramsfromthe Expasywebsite(e.g.,Porter,NtSurfP,JPred)wereusedandacomparisonoftheresultssuggests Plasmid construction. For yeast-two- thatthe20aminoacidpeptideaptamersequenceconsistslargelyofaa-helicalstructureinits hybrid (YTH) analyses, the different mem- N-terminalregionandacoiled-coilstructureinitsC-terminalregion.Thepredictionforthe bersoftheSTATtranscriptionfactorfamily, 655–755aminoacidsequenceofSTAT3suggeststhatitislargelycomposedofacoiled-coil without their C-terminal transactivation do- domainwithapossiblea-helicalinsertatposition76–84.ThepFlag-hTrxDcyscontrolconstruct wasgeneratedbyRsrIIdigestionremovingtheaptamersequences(lowerline).NLS,nuclear mains,werefusedtotheGal4-DNA-binding localizationsignal;9R,nineargininePTD. domain (pGBK-T7, Clontech-Takara Bio www.landesbioscience.com JAK-STAT 45 Protein purification. BL21 codonPlus (DE3)-RP competent loaded onto a polyacrylamide gel. Protein gel blots were cells (Stratagene) were transformed with the recombinant performed according to standard procedures. expression plasmids (Fig.1C). A 5 ml culture of the cells in standardTBmediumwasgrownfor8hat37°C.Thisculturewas Results used to inoculate a 2 L TB culture with ampicillin and chloramphenicol which was grown for 16 h at 37°C. Cells were Development of rS3-PA, a recombinant peptide aptamer with harvested at an OD of 3.5–5 and lysed under denaturing binding specificity for STAT3. We previously identified the 600 conditions using urea buffer (8 M urea, 500 mM NaCl in PBS, 40 amino acid peptide aptamer bTrx-DD3. This molecule was pH7.5).Proteinswerepurifiedusingaffinitychromatographyon selected to specifically bind to the SH2 domain of STAT3 as an FPLC system (GE Healthcare) as described earlier.21 showninYTHassaysandco-immunoprecipitationexperiments.21 Immunofluorescence microscopy. Cells were grown on cover- In a subsequent study, the original bacterial bTrx scaffold was slips and treated for 30 min with peptide aptamers. Slides were replaced by the human hTrx scaffold.20 We verified the binding prepared for microscopy as described earlier.20 Anti-Flag M2 specificityofthismoleculewithrespecttoitsinteractionwiththe (mouse) andanti-EEA1 (rabbit)antibodieswerediluted 1:100in other members of the STAT family of transcription factors in blocking buffer (0.5% gelatin from cold water fish skin, 0.1% YTH assays. Aptamer hTrx-DD3 was cloned in a GAL4 prey ovalbumin in PBS) and incubated overnight. Anti-mouse Alexa- constructandthegenesencodingtheSTATfamilymemberswere Fluor-568 and anti-rabbit Alexa-Fluor-488 coupled secondary cloned in GAL4 bait constructs. The transactivation domains of antibodies were used in a 1:100 dilution for detection. Nuclei the STAT proteins were omitted. The interaction of the Stat werestainedwith1mMToPRO-3iodide(MolecularProbes).To proteins with the aptamer was investigated using β-galactosidase ©visuali ze 2the ER0, cells1were w2ashed wiLth 0.2aM ancetic adcid andeasssays (F igB.1A) oir doetermisned bcy groiwtheof thne yeasct celles on . stained with 100 mg/ml Concanavalin A-Alexa-Fluor-488. plates lacking histidine (Fig.1B). We found that the DD3 Confocallaserscanningmicroscopywasusedtovisualizethecells. aptamerbindsefficientlytoSTAT3,butnottoSTAT1,2,4,5A mRNA analyses. Total RNA was isolated from cell lysates and 6. using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) and the SuperScript II Subsequently, the three cysteines present in hTrx as well as Reverse Transcriptase kit (Invitrogen) was used for synthesis of one cysteine present in the peptide aptamer sequence were cDNA.ToamplifytranscriptsofSTAT3targetgenesinTu-9648 replacedby serines and the40aminoacid aptamerwasdelimited Do not distribute. cells, the following primers were used: CyclinD1 5'- tgg aac ctg to 20 amino acids, resulting in the hTrxDcys-DD3.8Dcys gccgccatg-3'and5'-gtggccttggggtcgacg-3',Bcl 5'-agtttg construct.20 This modified peptide aptamer exhibits very similar XL gatgcgcgggag-3'and5'-gccacagtcatgcccgtc-3',Survivin5'- binding affinity and specificity for the SH2 domain of STAT3 tggcagctgtacctcaag-3'and5'-tcaagaattcactgacgg-3',Actin when compared with the original DD3 peptide aptamer (Fig.1A 5'- atg gcc act gcc gca tcc -3' and 5'- tcc aca tct gct gga agg -3'. andB).Finally, theT7promoterwasreplaced byatacpromoter PCRproductsweregeneratedat58°Cannealingtemperatureand and the N-terminal His- and S-tags of hTrxDcys-DD3.8Dcys 20 cycles for semi-quantitative analysis. were replaced by a nuclear localization signal and a Flag-tag. Cell viability assays. Two thousand cells were seeded in 96- TheFlag-tagfacilitatestheintracellulardetectionofthemolecule. well plates and the next day, the medium was removed. One This construct has been named rS3-PA (Fig.1C). A construct micromolar of the peptide aptamers (or PBS as control) were lacking the aptamer sequence, pFlag-hTrxDcys, was prepared diluted in 100 ml medium and added to the cells every 24 h. for control experiments. Upon bacterial expression and affinity Proliferation of the cells was measured on day 3 by adding purification via its His-tag, we obtained yields of about 25 mg 50 ml XTT solution (Roche). After 4 h, substrate turnover was rS3-PA per ml of culture and concentrations of 1.5–2.0 mg/ml. determined in a plate reader at 490 nm. Both rS3-PA and hTrxDcys-DD3.8Dcys were taken up from the Mousexenografttransplantations.FemaleNMRInu/numice medium and retained by the cultured cells very similarly (data (Charles River) were kept in individual ventilated cages. Experi- not shown).Intracellular uptake ismediatedbytheninearginine ments were performed according to German government guide- protein transduction domain (PTD). lines (Regierungspräsidium Darmstadt). Tu-9648 cells (3 (cid:1) 106) Peptide aptamer rS3-PA is taken up by cultured cells in an were injected into the right flanks of 6-week-old nude mice. endocytosis independent fashion. Protein transduction depends Mice were treated daily by tail vein injection with 150 ml of upon interactions between the positively charged PTD and recombinant proteins (7.5 mg/kg rS3-PA, 7.5 mg/kg hTrx) or negatively charged heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HS) present temozolomide (60 mg/kg) or with 150 ml PBS. Tumor volumes on the cell surface. Internalization can involve a form of fluid and body weights were measured every second day and volumes phaseendocytosis,calledmarcropinocytosis,oroccurthroughthe were calculated using the formula: (length (cid:1) p (cid:1) width2)/6. direct penetration of the cellular membrane. We used inhibitors Preparation of tissue lysates. Mouse organs or tumors were affecting different steps of the endocytosis process to investigate dissected and dissociated in 5 ml standard RIPA buffer/g tissue the mechanism of internalization of rS3-PA (Table 1). The using an Ultra-Turrax (IKA, Staufen, Germany). Samples were compoundswereaddedtothemediumofthecells30minbefore incubated on ice for 20 min and sonified. After centrifugation rS3-PA.After4hthecellswerewashedwithaceticacidtoremove (15,000 rpm, 20 min, 4°C) supernatants were stored at −20°C. the proteins associated with the cell surface. We found that Forproteingelblotanalysis,100mgofproteinofeachsamplewas none of the endocytosis inhibitors affected rS3-PA uptake when 46 JAK-STAT Volume1Issue1 compared with the non-treated cells (Table 1). Only heparan stimulation, are not affected by rS3-PA. A strong and specific sulfates (HS) exerted an effect on the intracellular accumulation effect on P-STAT3 signaling was observed in these cells (not of rS3-PA in NIH-3T3, 4T1 and Tu-9648 cells (Table 1 and shown). Fig.2A). The addition of HS, however, is known to sequester We observed also that rS3-PA accumulated in the cytoplasm PTD fusion proteins in the medium without directly affecting and the nucleus of non-induced HepG2 cells as a function of uptake processes.22 time. In IL-6 treated cells, rS3-PA accumulated to a maximal Uptake of rS3-PA into cells was also visualized by immuno- level within 1 to 2 h, but then decreased steadily until the fluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). Thirty end of the observation period at 6 h (Fig.3A). This suggests min after exposure of the cells to rS3-PA, the molecule can that the stability of rS3-PA is a function of the presence of be found evenly distributed in the cytoplasm as well as in the P-STAT3 and the presence of P-STAT3 is related to the nucleus (Fig.2B, panel 1). rS3-PA does not accumulate in degradationofrS3-PA.WetransducedHepG2cellsandTu-9648 dotted structures which would be characteristic for endosomal cells with rS3-PA in the presence of a proteasome inhibitor. uptake. To confirm this conclusion, endosomes were visualized MG-132 prevented the downregulation of rS3-PA as well as with an early endosome-specific antibody (anti-EEA1), and Flag- the degradation of P-STAT3 (Fig.3B and C). These results hTrxDcys or rS3-PA proteins were detected with an anti-Flag suggest that at least three molecular mechanisms are involved antibody.WeobservedthatthesignalsforrS3-PAandFlag-hTrx in the inhibition of STAT3 function by rS3-PA: it interferes did not co-localize with the signals for the endosomes (Fig.2B, with dimer formation, it inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation and it panels 5, 9 and 10). This indicates that the uptake of rS3-PA is causes the proteasomal degradation of the P-STAT3-rS3-PA independentoftheendosomalpathwayandfavorstheaccumula- complex. ©tion o f fu2nction0al rS3-1PA in 2the cyt oplLasm.andesrS3-P ABsuppreisseos STAsT3 ctargeit geene nexpresscion.eWe . Addition of rS3-PA to the medium specifically reduces analyzed the consequences of STAT3 inhibition by rS3-PA in P-STAT3 levels in cancer cells. We analyzed the molecular tumor cell lines and measured the immediate effects on the mechanisms by which rS3-PA interferes with the function of expression of known STAT3-dependent target genes. Exposure STAT3. In serum deprivedHepG2cells, STAT3isnot activated of Tu-9648 glioma cells and 4T1 mammary tumor cells to rS3- and addition of IL-6 for 15 min caused the accumulation of PAresultedinadose-dependentdownregulationofcyclinD1and P-STAT3inthenucleus(Fig.3A).However,exposureofthecells survivin mRNA within 32 h (Fig.3D). A moderate down- Do not distribute. to rS3-PA for up to 6 h caused a time dependent decrease in regulation was found for Bcl . Exposure of 4T1 and Tu-9648 xL P-STAT3levels.InIL-6inducedcells,rS3-PAtreatmentreduced cells to rS3-PA for 48 h also resulted in decreased levels of the P-STAT3 to 32% in the cytoplasm and 44% in the nucleus Survivin, Bcl and c-Myc proteins (Fig.3E). Time-dependent xL (Fig.3A). Total STAT3 levels were reduced to 45% when treatmentofe.g.,MZ-54cellswithrS3-PAcausedthecontinuous compared with control cells. P-STAT3 levels were also reduced decreaseinSurvivinprotein(Fig.3F).Treatmentofthecellswith by rS3-PA in Tu-9648 glioma cells (not shown). These cells the control vector protein Flag-hTrxDcys did not influence the exhibit a high level of persistently activated STAT3.16 Our expression of STAT3 target genes (Fig.3G). results show that the presence of rS3-PA interferes with the rS3-PA inhibits the migration and the angiogenic induction phosphorylation of STAT3. potential of cultured tumor cells. We analyzed the effects of To confirm the specificity of rS3-PA action, we analyzed the rS3-PA treatment on additional STAT3 regulated target genes effects of rS3-PA on K562 leukemia cells, expressing high levels which play crucial roles in cell motility.23,24 MZ-54 cells were of P-STAT5. We found that rS3-PA treatment did not affect grown for 2 d in the presence of 1 mM rS3-PA. Then, the cell P-STAT5 and STAT5 levels in these cells (not shown). In layer was scratched with a pipette tip and photographed (time addition, the effect of rS3-PA on STAT1 was investigated by point 0) and again 16 h later. We found that control treated inducing MDA-MB-468 cells treated with INFc. The results MZ-54 cells had largely filled the gap, whereas rS3-PA treated showed that P-STAT1 levels, which increase upon INFc cells had lost their motility (Fig.4A–C). Similar observations Table1.Effectsofdifferentinhibitorsoninternalizationofproteinsviaendocytosis-likemechanisms Uptakeparameter Direct Receptor-mediated Macro- Inhibitor Finalconc. Effecton penetration endocytosis pinocytosis rS3-PAuptake* Temperature - + + 4°C No Energy - + - Sodiumazide 0.1% No Interactionwiththecellmembrane + - + Solubleheparansulfates 50mg/ml Yes Caveolin-mediateduptake - - - Nystatin 25mg/ml No Clathrin-mediateduptake - + - BrefeldinA 10mM No Actinpolymerization - - + CytochalasinD 5mM No Endosomalrelease - + + Chloroquine(enhancer) 50,100mM No *Determinedbyproteingelblotting. www.landesbioscience.com JAK-STAT 47 Figure2.CellularuptakeofrS3-PA.(A)Cellsweretransducedfor4hwith1mMrS3-PAinthepresence(+)orabsence(-)of50mg/mlheparansulfate(HS). IntracellularrS3-PAwasvisualizedbyproteingelblottingofcelllysateswithaHis-tagspecificantibody.(B)DetectionofintracellularrS3-PAbyconfocal laserscanningmicroscopy.SK-BR-3cellsweretransducedwith2mMrS3-PAfor30min.Thepeptideaptamerwasvisualizedwithananti-Flagantibody (green)(panel1),theendoplasmicreticulum(ER)isstainedwithconcanavalinA(red)(panel2).UptakeofFlag-hTrxDcysisshowninpanel3,visualized withananti-Flagantibody(red),andtheendosomesweredetectedusingananti-EEA1antibody(green)(panel4).Thenucleiwerestainedwith1mM TO-PRO-3(blue).Panels5and10showhighermagnificationsoftransducedMZ-54andSK-BR-3cellstovisualizetheseparatelocationsoftheendosomes (green)andrS3-PA(red). © 2012 Landes Bioscience. were made with Tu-2449 cells and the results were confirmed in mammary epithelial cells (not shown). This excludes a general transwell migration assays (not shown). cytotoxic effect of rS3-PA. Theformationoftubularstructurescanbeinducedincultures The expression of anti-apoptotic STAT3 target genes is of endothelial cells (HUVEC) by exposure to angiogenic suppressed by rS3-PA treatment (Fig.3D–F). We analyzed if factors, present in supernatants collected from tumor cell lines. rS3-PA causes the induction of apoptosis by determining the We found that factorDs presenot in th enconditiooned mted iumdfromisamoutnt orf DNiAbfragmeuntatiotn inetreate.d and non-treated cells. 4T1, SK-BR-3 and Tu-9648 cells all induced tube formation The enrichment in cytoplamic nucleosomes is measured in an of HUVEC cells (not shown). Since VEGF transcription is ELISA based assay using histone antibodies. The data obtained regulated by STAT3,25 we studied the effects of rS3-PA on the showed that treatment of cells with 2 mM rS3-PA for 24–48 h secretionofangiogenicfactorsby4T1cells.Thecellsweregrown caused a clear increase in DNA fragmentation in Tu-9648, Tu- with or without rS3-PA and after 4 d the growth medium was 2449 and SK-BR-3 cells (5–6-fold) and a moderate increase in collected. This conditioned medium was mixed with EBM (1:1) MDA-MB-468cells(3-fold).NIH-3T3cellswerenotaffectedby without serum and added to HUVEC cells seeded on matrigel. this treatment (Fig.5C). We conclude, that rS3-PA inhibits Tube formation was analyzed after 16 h by measuring tube proliferationandalsoinducesapoptosisincancercells,butnotin length and the number of multicentric junctions (Fig.4D–F). normal cells. Conditioned medium from rS3-PA treated 4T1 cells had a SystemicapplicationofrS3-PAinhibitsSTAT3phosphoryla- strongly reduced capacity to induce tube formation (Fig.4D–F). tion and reduces the growth of transplanted tumor cells. To We conclude that rS3-PA inhibits the secretion of angiogenic investigate the tumor suppressive effects of rS3-PA in animals, factors by these cancer cells. 3 (cid:1) 106 Tu-9648 cells were transplanted into NMRI-Nu/Nu Effects of rS3-PA on the proliferation and induction of miceandtumorgrowthwasmonitoredfor15d.Theexperiment apoptosis of cultured tumor cells. Previous studies have shown was performed with seven animals per group in the first that downregulation of STAT3 expression by siRNA can impede experimentandeightanimalspergroupinthesecondexperiment. the proliferation of tumor cells.13,26-28 We expect that the Mice were treated once a day with PBS, Temozolomide, Flag- treatment of tumor cells with 1 mM rS3-PA should result in hTrxDcys (7.5 mg/kg) or rS3-PA (7.5 mg/kg). Temozolomide similarphenotypes.ThecellulargrowthofcellsexposedtorS3-PA (Temodal, Essex Pharma) is a DNA alkylating agent used in the was analyzed microscopically (Fig.5A) and by XTT assays therapy of glioblastoma patients. The compounds were adminis- (Fig.5B). Compared with control cells, MZ-54, Tu-9648, Tu- tered intravenously each day for 15 d. The tumor volumes 2449, MDA-MB-468 and 4T1 cells are highly sensitive to the reached about 2000 mm3 in the PBS treated control animals inhibition by rS3-PA. SK-BR-3 cells were only modestly affected (Fig.6A and B). In two independent experiments we observed a by1mMofrS3-PA,butgrowthinhibitionwasmorepronounced reproducible therapeutic effect of rS3-PA causing a reduction in at higher concentrations of 2–4 mM (not shown). The prolifera- the average tumor volume of about 35% and slightly exceeding tion of non-tumorigenic NIH-3T3 fibroblasts and MCF-10A the therapeutic effect of temozolomide (Fig.6B). cells remained unaffected. In addition, no adverse effects were Proteins were extracted from the tumors and the levels of observed after treatment of primary endothelial and primary STAT3andP-STAT3weredetermined.Similartocontroltreated 48 JAK-STAT Volume1Issue1 © 2012 Landes Bioscience. Do not distribute. Figure3.rS3-PAsuppressesSTAT3phosphorylation,enhancesP-STAT3degradationandinhibitsSTAT3targetgeneexpression.(A)HepG2cellswere transducedwithrS3-PAfor0to6h.IL-6(10ng/ml)wasaddedtothecellsfor15min(lanes13to24)beforethecellswereharvested.Cytoplasmicand nuclearfractionswerepreparedandanalyzedinproteingelblotsusingspecificantibodiesasindicated.Non-inducedcells(lanes1to12)servedas controls.(B)ProteingelblotanalysisofHepG2cellstreatedwithrS3-PAfor0,2or4handinducedwithIL-6for15minattheendoftheseperiods.To detectproteasomaldegradationofP-STAT3,50mMMG-132wasaddedtothecellsinlanes5and6.NuclearextractswerepreparedandP-STAT3,the uptakeofrS3-PAandthenuclearmarkerLaminB1werevisualizedontheblot.Numbersbelowtheblotsrepresentrelativebandintensities.(C)Same experimentasshownin(B)showingproteasomaldegradationofP-STAT3inTu-9648cellsafterrS3-PAtreatment.(D)Tu-9648cellsweretreatedfor24h withincreasingconcentrations(0.5–4mM)ofrS3-PA.After24hmediumwasreplacedwithfreshrS3-PAandafter8htotalRNAwasprepared. Semi-quantitativeRT-PCR(20cycles)productswereloadedontoa2%agarosegel.M:100bpsizemarker(lane1).(E)Tu-9648cellsand4T1cellswere treatedin24hintervalswithincreasingamountsofrS3-PA.After48hfreshrS3-PAwasaddedagainfor4handcellularproteinlysateswerepreparedfor proteingelblotanalysis.AHis-tagantibodywasusedtoshowtheuptakeofrS3-PAintothecells.DetectionofActinwasusedasaloadingcontrol. (F)MZ-54cellsweretreatedwith2mMrS3-PAfor48handonthethirddayfortheindicatedtimepointslysatesforproteingelblotswereprepared. Anti-Actinwasusedasacontrol.(G)Tu-9648cellsweretreatedwith2mMofthecontrolproteinFlag-hTrxDcys(hTrx)for48handonthethirddayfor theindicatedtimepoints.ExpressionofSTAT3,P-STAT3andofthetargetgenesSurvivinandBcl wasanalyzed,aswellastheuptakeofthe XL Flag-hTrxDcyswithaHisantibody. animals, no changes in P-STAT3 levels was observed if tumors 11and12).ThisindicatesthatthesuppressiveeffectofrS3-PAis were prepared 4 h after the last rS3-PA administration (Fig.6A, limited in time and can be observed only relatively shortly after lanes 9 and 10). In contrast, a reduction in P-Stat3 is clearly rS3-PAinjection.Nevertheless,thistransientinhibitionofSTAT3 detectable,iftumorswerepreparedwithin15min(Fig.6A,lanes seemssufficienttocauseanappreciablereductionoftumorgrowth. www.landesbioscience.com JAK-STAT 49 Figure4.Suppressionofcellularmigrationandsecretionofangiogenic factorsbyrS3-PA.(A)TostudymigrationofMZ-54cells,cellswere seededin6-wellplatesandgrownfortwodaysinthepresenceofPBS (control),1mMFlag-hTrxDcys(hTrx)or1mMrS3-PA.Thecellmonolayers werescratchedwithapipettetipandphotographed(0h,notshown). MitomycinC(10mg/ml)wasaddedtopreventfurtherproliferationofthe cells.Shownarescratches16hafterinjuryofthecellmonolayer.(B)By comparingthephotographstakenat0hand16hthecellsthathad movedintothescratchareawerecounted.Thenumberofcellspresent inthescratchafterPBStreatmentwasconsidered100%.(C)By measuringthewidthoftheopenscratchbeforeandaftertreatment,the reductioninscratchwidthwascalculated.Scratchwidthat0hwassetto 100%.(D)4T1cellsweregrowninDMEMwith2%FCSfor3dinthe presenceof1mMrS3-PAorFlag-hTrxDcys(hTrx).Ondayfour,the conditionedDMEMmediumwasmixed1:1withEBM.Toassaythe presenceofangiogenicfactors,HUVECcellsatpassage3wereseededin 12-wellplatescontainingmatrigeland500mLoftheconditionedEBM wasadded.Inpositivecontrolexperiments,EBMwasmixed1:1with DMEM/5%FCSandtubeformationwasconsidered100%.Cellswere grownovernightat37°Candthenextday,sevenrepresentative microscopicfieldsofallwellswerephotographed.Thetotallengthofthe tubesperfield(E)andthenumberofmulticentricjunctions(F,arrowsin D)aredisplayedinbargraphs.Therelativelengthoramountcompared © 2012 Landewsithcon troBltreatediHUoVECcelslswasccalculaitede.Errorbnarsin(Bc,C,Eeand . F)representSD,*p,0.05and**p,0.01. mouse organs upon systemic administration without causing obvious side effects. Do not distribute. Discussion Persistently activated STAT3 plays a central role in cellular transformation.29,30 It induces target genes which promote tumor cell proliferation, survival and invasion, regulates the commun- icationbetweentumorcellsandnormalcellsandthuscontributes totheimmuneevasionoftumors.31-33Thesefunctionalproperties make STAT3 a very promising drug target.11 In particular cases, the therapeutic value of STAT3 inhibition might be restricted by additional genetic lesions in tumor cells. The expression of thep19/p14ARFgene,e.g.,determinesthetumorenhancingand Weinvestigated,ifrS3-PAisalsotakenupinothertissuesand thetumorsuppressingeffectsofSTAT3expressionandactivation exerts an inhibitory effect on activated STAT3. We found that in Ras transformed liver tumor cells.34 Nevertheless, different rS3-PAcanbeonlydetectedinextractsfromkidneyandlivercells classes of compounds are being investigated as STAT3 inhibitors 15minafterthelastinjection(Fig.6C,lanes4and8).Although andanti-cancerdrugs.Smallmolecularweightcompounds,metal we detected very low P-STAT3 levels in kidney cells (Fig.6C, complexes, oligonucleotides, cell permeable peptides and pepti- lanes1to4),thesecellswerenotaffectedbythepeptideaptamer. domimetics have been taken into consideration.16,35-40 However, However, STAT3 was found slightly activated in normal liver crucial parameters, e.g., cellular permeability, potency, target cellsofcontrol animals(Fig.6C,lanes 5and 6)andtreatmentof specificity and systemic stability still have to be optimized to the animals with rS3-PA resulted in a complete suppression of make these molecules clinically applicable. STAT3 activation (Fig.6C, lanes 7 and 8). No peptide aptamer Here, we describe the characterization and functional analysis was detected in liver cells when the tissue extracts were prepared of a specific STAT3 inhibitor, rS3-PA. This peptide aptamer is 4 h after injection (Fig. 6C, lanes 3 and 7). These results again fusedtoaPTD,asmallcationicpeptidesequencewhichinteracts indicate a relatively fast clearance. with the anionic cell surface through electrostatic forces to We examined sections of liver tissue from control mice and mediate intracellular uptake. Mechanistic studies showed that rS3-PA treated mice and did not detect pathological changes the strength of the peptide-lipid interactions induces either an (Fig.6D). Also the body weight and the behavior of the mice endocytotic pathway or a mechanism involving membrane treated for 15 d with rS3-PA was not different from that of disorganization causing a direct translocation.41-44 Our results controlmice(notshown).WeconcludethatpeptideaptamerrS3- indicatethatrS3-PAenterscellsviadirecttranslocation(Fig.2B). PA is able to inhibit STAT3 activation in tumors as well as in This is an important advantage, since rS3-PA is not trapped in 50 JAK-STAT Volume1Issue1 © 2012 Landes Bioscience. Do not distribute. Figure5.TherS3-PAinduceddownregulationofP-STAT3,whichaffectstheproliferationandsurvivalofcancercells,butnotofnormalcells.(A)Different tumorsandnormalcells(NIH-3T3andMCF-10A)wereculturedinthepresenceof1mMFlag-hTrxDcys(hTrx),rS3-PAoranequalvolumeofPBS.The mediumwasexchangeddailyandthecellswerephotographedafter96hoftreatment.(B)Cancercellsandnormalcellsweretransducedfor72hwith1 mMhTrxorrS3-PA.TheviabilityofPBS-treatedcontrolcellswasconsidered100%at72hforeachcellline.(C)CellsweretreatedwithrS3-PA,hTrxorPBS, for24hor48h.CellswerelysedandtheenrichmentofnucleosomesinthecytoplasmwasdeterminedinanELISA-basedassay(CellDeathDetection ELISA,Roche).Thenucleosomeenrichmentfactorwascalculatedaccordingtotheformula:Treatedcells(A –A )/PBScontrolcells(A – 405nm 490nm 405nm A ).Theabsorbance(A )ofcontroltreatedcells(PBS)wassetto1.Errorbarsin(BandC)representSD.NS,notsignificant,*p,0.05,**p,0.01. 490nm 405 the endosomes or lysosomes and is able to directly exert its a way that it is not accessible for the kinase. rS3-PA also function in the cytoplasm. It has been suggested that the cargo downregulates STAT3 function through effects on its stability. contributes to the choice between direct translocation and an The exposure of HepG2 cells to rS3-PA causes a decrease in endocytotic process and the nature of the hTrx scaffold protein P-STAT3 when compared with untreated cells. This decrease could play a role in the direct penetration ability of rS3-PA.45 can be compensated by the simultaneous exposure of the cells The sequence of the bait construct used for the selection of to the proteasome inhibitor MG-132 (Fig.3B and C) and the rS3-PA peptide aptamer was initially designed to obtain a suggeststhatrS3-PA-STAT3complexesarebeingrecognizedand molecule able to prevent the formation of functional STAT3 destined for degradation. dimers. The peptide aptamer binds and masks the STAT3 The downregulation of P-STAT3 by rS3-PA has immediate dimerization domain. However, additional effects of rS3-PA on consequences for transcriptional programs regulated via the STAT3 can be observed. Upon entry into cells, rS3-PA clearly STAT3 signaling pathway, which in turn result in phenotypic interfered with the IL-6 induced phosphorylation of STAT3 alterations.46-48 Exposure of the highly motile MZ-54 and Tu- (Fig.3A). It is possible that the rS3-PA-STAT3 complex cannot 2449 human glioma cells to rS3-PA for 48 h almost entirely be recruited to the IL-6 receptor; alternatively the bulky rS3-PA inhibitedtheirmotility(Fig.4A).STAT3hasbeenfoundtobind molecule could mask the tyrosine phosphorylation site in such to β-PIX, a Rac1 activator, and it has been proposed that this www.landesbioscience.com JAK-STAT 51 © 2012 Landes Bioscience. Do not distribute. Figure6.TherS3-PAinduceddownregulationofP-STAT3inhibitstumorcellgrowthinvivo.(A)Tu-9648cells(3(cid:1)106/50ml)weresubcutaneously injectedintotheflanksofnudemice.Inexperiment1,eachtreatmentgroupconsistedofsevenmice(n=7),inexperiment2ofeightmice(n=8). Themicewerei.v.injecteddailywith150mlhTrx(7.5mg/kg),with150mlrS3-PA(7.5mg/kg)orwith150mlofPBS.Representativetumorsandthelevels ofP-STAT3andSTAT3inthetumorsareshown.Tumorsshowninlanes1,2,5,6,9and10,wereobtained4h,tumorsinlanes3,4,7,8,11and12were obtained15minafterthelasttreatment.(B)Diagramshowinggrowthoftumorsmonitoredfor15d.Anadditionalgroupofanimalsweretreatedwith 150mloftemozolomide(60mg/kg).ErrorbarsrepresentSEMwith*p,0.05.(C)Kidneyandliverextractswereprepared15min(PBSmouse#1,hTrx, #2andrS3PA-#6),or4h(rS3-PAmouse#1)afterthelastinjection.LevelsofP-STAT3,STAT3andTubulinexpression,aswellasthepresenceof administeredrS3-PAinthetissueextractsareshown.(D)HEstainedliversectionsofPBSandrS3-PAtreatedmice. is a mechanism by which cytoplasmic STAT3 regulates Rac1 molecules.16,40,50 However, there are only very few examples in activity and modulates the organization of the actin cytoskeleton which the direct inhibition of a transcription factor complex by and directional migration.24 This process could possibly be an externally supplied interacting peptide have been studied in affected by the complex formation with rS3-PA. vivo. A recent report describes the delimitation of a binding In addition to a loss of migration potential, we observed a domain from the Notch1 interaction partner Maml1. The intra- downregulation of various STAT3 target genes (Fig.3). rS3-PA cellular delivery of this Maml1 peptide, constrained in a stable reduced the proliferation of all STAT3-dependent cancer cell helical conformation, inhibits the Notch transcription factor lines and enhanced apoptosis processes (Fig.5) implying that complexinT-cellacutelymphoblasticleukemiacellsandrepresses this aptamer triggers the expected biological consequences. These Notch-mediatedgeneexpression.Thetreatmentofmicewiththis effects were not observed in normal cells, which do not express peptide retarded leukemic tumor cell growth.17 The molecule P-STAT3 and are not dependent on P-STAT3 signaling events, dependsona“peptidestaplingsystem”thatstabilizestwoturnsin indicating that rS3-PA is not generally cytotoxic. This is in an a-helical peptide regionand provides anewclassofinhibitory contrast to several other STAT3 inhibitors which have been compounds. The small stapled peptide can be produced in cell investigated, e.g., thenatural compound cucurbitacin, which also permeable forms, have a high binding affinities for their target have severe effects on normal cells.49 Our analysis confirmed structures and exhibit favorable stabilities and bioactivities.51 that rS3-PA acts specifically and affects only the phosphorylation We report that i.v. administration of rS3-PA slows the growth of STAT3, but not that of the closely related family members oftransplantedtumor cellsinmiceupto35%,avalue exceeding STAT1 and STAT5. the therapeutic effect of temozolomide in this system. Despite Interacting peptide domains and peptide aptamers have been the therapeutic effects observed, our experiments suggest that established as effective inhibitors of intracellular signaling rS3-PA is limited in its systemic stability and that the effects 52 JAK-STAT Volume1Issue1
