AQA GRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY 2017 Compiled by Sue Whittaker GRAMMATICAL PDF
Preview AQA GRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY 2017 Compiled by Sue Whittaker GRAMMATICAL
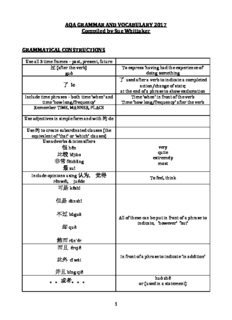
AQA GRAMMAR AND VOCABULARY 2017 Compiled by Sue Whittaker GRAMMATICAL CONSTRUCTIONS Use all 3 time frames – past, present, future 过 (after the verb) To express ‘having had the experience of’ guò doing something 了 used after a verb to indicate a completed 了 le action/change of state; at the end of a phrase to show exclamation Include time phrases – both time ‘when’ and Time ‘when’ in front of the verb time ‘how long/frequency’ Time ‘how long/frequency’ after the verb Remember TIME, MANNER, PLACE Use adjectives in simple form and with 的de Use 的to create subordinated clauses (the equivalent of ‘that’ or ‘which’ clauses) Use adverbs & intensifiers 很 hěn very 比较 bǐjiào quite extremely 非常 fēichǎng most 最 zuì Include opinions using 认为, 觉得 To feel, think rènwéi, juéde 可是 kěshì 但是 dànshì 不过 bùguò All of these can be put in front of a phrase to indicate, ‘however’ ‘but’ 却 què 然而 rán'ér 而且 érqiě In front of a phrase to indicate ‘in addition’ 此外 cǐ wài 并且 bìng qiě huò zhě 。。或者。。。 or (used in a statement) 1 。。还是。。。 hái shi or (used in a question) yīn cǐ 因此 because of this 因为 or 由于。。。所以 yīnwéi / yóu yú………..suǒyǐ Because……therefore……. 所以 can be replaced with 因此 yīn cǐ, (in front of each phrase) 因而 yīn ér,于是 yú shì 虽然。。。但是 suīrán……..dànshì 虽然can be replaced with 尽管jǐn guǎn or Although…..but 固然 gù rán (in front of each phrase, ‘but’ not needed in English but required in Chinese;) 但是 can be replaced with 不过 bùguò, 却 què, 可是 kěshì or 然而 rán'ér 除了。。以外, 也/还 Apart from, also chúle….yǐwài, yě/hài As well as, also (‘also’ goes in front of the verb) 如果/要是。。。就 If………, then…… rúguǒ/yàoshì………jiù (in front of relevant phrases) Not only…..but also…. 不但。。。而且。。 búdàn….…érqiě... Two uses: One subject 不仅。。。而且。 She is not only intelligent but also kind. bù jǐn……… érqiě... 她不但聪明而且亲切。 NB subject IN FRONT OF 不但。 不只。。。而且 Two subjects bù zhǐ………. érqiě... Not only is mum intelligent, little sister is too. (而且 can be replaced with 不但妈妈很聪明而且妹妹也聪明。 并且 bìng qiě, 还 or 也) NB Subject 1 AFTER 不但, subject 2 AFTER 而且 先。。。然后 First (verb 1), after (verb 2) xiān……… rán hòu 先。。再。。 First (verb 1), then (verb 2) xiān.........zài 2 先。。又。。 First (verb 1), then (verb 2) xiān………. yòu 。。的时候, When….. …de shíhou, (in Chinese, non question form ‘when’ goes at the end of the relevant phrase) 有的时候 Sometimes…. yǒu de shíhou (goes at start of relevant phrase) 有的时候。。。有的时候。。 Sometimes…..sometimes….. yǒu de shíhou……… yǒu de shíhou A 比 B (adjective) A compared to B (adjective) A bǐ B (adjective) Eg A is bigger than B A 比 B (adjective) 得多/多了。 A compared to B is much (adjective) A bǐ B (adjective) de duō/ duōle Eg A is much bigger than B A 比 B 更(adjective) A compared to B is even (adjective) A bǐ B gēng (adjective) Eg. A is even bigger than B A 比 B (adjective) 一点儿 A compared to B is a little (adjective) A bǐ B yī diǎn'r Eg A is a little bigger than B A 跟 B 一样 A with B is the same A gěn B yíyàng Ie A is the same as B A 跟 B 一样(adjective) A is the same (adjective) as B A gěn B yíyàng (adjective) Eg A is as big as B A 没有 B (adjective) A méi yǒu B (adjective) A is not as (adjective) as B 又 (adjective)又 (adjective) Descriptive phrase yòu (adjective) yòu (adjective) Both (adjective) and (adjective) 一边。。。一边。。。 In front of verbs to mean ‘to do one thing at yìbiān……….yíbiān… the same time as another’ To express interest in something.. 对。。。(不)感兴趣 duì….(bù) gǎn xìngqù Literally: To/in……(don’t) have interest 3 对。。。(没)有兴趣 duì….(méi) yǒuxìngqù 越。。。越。。 Used before verbs/adjectives to indicate ‘the yuè……..yuè more something happens, the more something else happens’ 越来越 More and more, increasingly yuèláiyuè (used in front of a verb/adjective) Verb 得 adverb/description of verb Constructs a phrase describing how an de action is done, creates adverbial phrase. 什么都有 Whatever it is, we have it/they have it shénme dōu yǒu Add wǎn/hǎo le to a verb to indicate Verb + 完/好了 something is completed properly Verb + wǎn/hǎo le Literally ‘from a place come’ 从 place 来 ie to come from a place cóng .lái eg 他从中国来。 有点儿 somewhat; rather; a little yǒu diǎn'r eg I am a little tired 我有点儿累 ‘not at all’ used in front of an adjective/verb 一点儿都不/没 eg 一点儿都没有 – literally ‘even a little bit, yī diǎn'r dōu bù/méi there isn’t’ ie we don’t have any at all. Eg 一点儿都不喜欢 - literally ‘a little bit, don’t like’ ie I don’t like it at all p167 Expresses ‘extremely’. Put it after 得不得了 the adjective/adverb débùdéliao 是…的 emphasises the past action, time, place, etc shì….…de 我是八点来的。 I arrived at 8 o’clock 一…就 as soon as….then yī ….jiù (each part in front of the verb) 他一放学就回家 多 to show an approximate number dūo (多 replaces the last number) 我的学校有一千两百多个学生 4 从来 + 都 +negative Used in front of the negative verb to cónglái +doū + negative indicate ‘never’. 我从来都没学汉语。 dì yī 第一 firstly dì èr 第二 secondly dì sān 第三 thirdly 5 CORE VOCABULARY LIST GENERAL VOCABULARY MEASURE WORDS 几个 jǐ ge Several 个 ge the most common measure word 口 kǒu m/w for numer of people in a family m/w for long things (eg a road), fish and selected other 条 tiáo uses 只 zhī measure word for animal 本 běn measure word for books 张 zhāng measure word for table, picture, map etc (flat things) 件 jiàn measure word for clothes 碗 wǎn a bowl of bēi 杯 a cup of 瓶 píng A bottle of 双 shuāng pair of things VERBS 是 shì to be 有 yǒu to have 做 zuò to do, to be/become (occupation) 吃 chī to eat 喝 hē to drink 叫 jiào to call,to be named 学习 xuéxí to learn,to study 6 说 shuō to say,speak, talk 想 xiǎng to want, would like, to think 要 yào to want, be going to, must 喜欢 xǐhuan to like 爱 ài to love 会 huì to know how to, can 觉得 juéde to think, to feel 问 wèn to ask 知道 zhīdao to know 懂 dǒng to understand 听 tīng to listen/hear 写 xiě to write 画 huà to paint 看 kàn to see, read, watch, look at 见/见面 jiàn/jiànmiàn to meet 住 zhù to live 请 qǐng to ask 让 ráng to allow 进 jìn to enter 出 chū to go out 坐 zuò to sit 唱 chàng to sing 跳 tiào to jump 玩 wán to play 睡觉 shuìjiào to go to bed, to sleep 开(灯/电 kāi (dēng/diànshì/ to switch on, turn on, open 视/门) mén) 7 关 (灯/电 guān (dēng/diànshì/ to close, to switch off 视/门) mén) 告诉 gàosu to tell 来 lái to come 去 qù to go 回 huí to return 到 dào to arrive, to get to 对……有 duì....yǒuxìngqù to be interested in 兴趣 to know, recognise 认识 rènshi (of a person) 应该 yìnggāi should 希望 xīwàng to hope 祝 zhù to wish 试 shì to try 帮助 bāngzhù to help 买 mǎi to buy 卖 mài to sell 打 dǎ to play (ball game) make (phonecall), to beat 踢 tī to play (football), kick 穿 chuān to wear, to put on (clothes) 戴 dài To wear, to put on (accessories) 用 yòng to use 换 huàn to change 开始 kāishǐ to begin 开车 kāi chē to drive 停 tíng to stop 等 děng to wait for 8 放 fàng to put, to set free 给 gěi to give 送 sòng to give (present), to say goodbye to someone 发(电子 fā (diànzi to send( an email) yóujiàn) 邮件) 寄 (信) jì (xīn) to send (a letter) 记得 jìde to remember 忘 wàng to forget 笑 xiào to laugh, smile 洗 xǐ to wash 生气 shēngqì to get angry 安静 ānjìng to be quiet 好象 hǎoxiàng to seem 找 zhǎo to find, to look for 花 huā to spend (time/money) flower 参观 cānguān to visit (place) dǒng 懂 to understand 明白 míng bai to understand 参加 cān jiā to take part in ADJECTIVES 好 hǎo good 坏 huài bad 最 zuì most 大 dà big 小 xiǎo small 难 nán hard, difficult 9 容易 róngyì easy 努力 nǔlì hardworking 冷 lěng cold 热 rè hot 对 duì correct, right 错 cuò wrong 好玩 hǎowán interesting, amusing 好吃 hǎochī delicious 快 kuài fast, quick 慢 màn slow 忙 máng busy 累 lèi tired 饿 è hungry 渴 kě thirsty 新 xīn new 老 / 旧 lǎo/jiù old 漂亮 piào liang pretty nán kàn 难看 ugly yǒu yì si 有意思 interesting méi yì si 没意思 boring gān jìng 干净 clean 脏 zàng dirty guì 贵 expensive piàn yí 便宜 cheap qiàng 强 strong ruò 弱 weak 远 yuǎn far 10
Description: